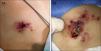
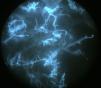
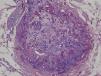
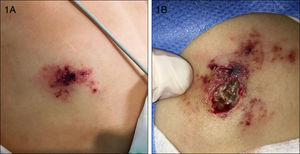
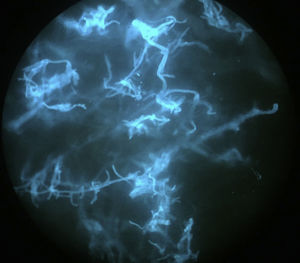
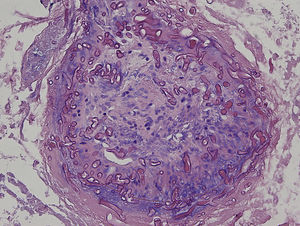
An 8-year-old girl with a personal history of severe epileptiform encephalopathy was admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit for epileptic status with decreased consciousness, for which treatment with anticonvulsants and systemic corticosteroids was instituted. Two weeks after admission she underwent assessment at the dermatology department for lesions on the abdomen that had appeared a few hours earlier. Erythematous and purpuric papules and pseudovesicles were clustered irregularly on an erythematous base with a necrotic center (Fig. 1A). An underlying firm, infiltrated plaque covered an area greater than that of the visible lesions. Ultrasound showed a poorly defined mass of increased echogenicity in the subcutaneous tissue that was compatible with inflammatory alterations. Given the acute course and the presence of an underlying mass, a deep biopsy was performed, revealing the presence of foul-smelling fatty tissue with a putrefied appearance (Fig. 1B), suggestive of a necrotic infection. A sample was taken for microbiological analysis and calcofluor-white staining and fungal culture were ordered. Direct observation revealed the presence of numerous broad, branched, aseptate hyphae compatible with mucormycosis (Fig. 2). After extensive early surgical resection liposomal amphotericin B treatment was instituted and corticosteroid treatment gradually withdrawn. Histology revealed intense dermal necrosis and blood vessel obstruction by numerous fungal structures (Fig. 3). Diagnosis was confirmed based on the results of the fungal culture, from which Rhizopus arrhizus was isolated following ethanol-formic acid extraction and MALDI-TOF (matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization – time-of-flight) mass spectrometry.1 After lesion spread was ruled out the patient was diagnosed with primary cutaneous mucormycosis due to R. arrhizus. The early initiation of treatment resulted in a favorable response and progressive improvement of the patient's clinical picture. No new lesions appeared nor were other organs affected.
Mucormycosis is an opportunistic fungal infection with a rapid, fulminant course caused by fungi of the order Mucorales. The most frequently isolated fungi are those of the genera Rhizopus, Mucor, and Rhizomucor.2 There is some debate as to whether this group of infections should be described as zygomycosis or mucormycosis, but use of the latter term is supported by the results of molecular studies.3
Distinct clinical forms of mucormycosis are described. The most common is rhinocerebral mucormycosis, followed by pulmonary, gastrointestinal, cutaneous, and disseminated forms. The cutaneous form (10%–19% of cases) is the result of direct inoculation of the spores into the dermis or direct contact of the skin with contaminated material.4 It can also be caused by traumatic injuries (70%), surgical interventions (15%), burns (3%), and, in the case of nosocomial infections, contact with contaminated material such as sheets,5 intravenous lines, adhesives,6 or wooden tongue depressors.7
Mucormycosis predominantly affects immunocompromised patients. The majority of reported cases have involved patients with blood or metabolic disorders. Our patient was receiving high-dose intravenous corticosteroids for the treatment of an underlying neurological condition.
The typical clinical picture consists of an erythematous, edematous plaque with central ulceration that progresses rapidly and may affect subcutaneous tissue, muscle, and bone.8 Atypical clinical presentations include that of our patient, in whom the aforementioned clinical picture was accompanied by eczematous lesions.6,9
It is important to establish diagnosis early. This requires a high level of clinical suspicion, especially in cases with atypical presentations, and the use of early diagnosis techniques such as direct examination of samples treated with KOH or calcofluor-white. A presumptive diagnosis can be established and early treatment initiated based on identification of the characteristic hyphae of Mucorales. The hyphae are wide (5–15μm in diameter), septate, and branched at a 45° angle. Microbiological culture, on which definitive diagnosis is based, can take several days.10
In both children and adults, extensive surgical debridement and the administration of systemic antifungals (liposomal amphotericin B, 5–10mg/kg/d) is the treatment of choice. Once stabilized, patients can be treated with oral posaconazole or isavuconazole, either alone or in combination with systemic antifungals.11,12 The duration of treatment has not been clearly established, but usually spans several weeks, until clinical resolution is achieved and the signs and symptoms of infection have disappeared.
The mortality rate associated with primary cutaneous mucormycosis ranges from 4% to 10%, and only 3% of cases progress to disseminated infection, mainly in patients with risk factors (in whom the mortality rate increases to 83%–94%).4
The case described here illustrates the importance of the recognition and early diagnosis of cutaneous mucormycosis in order to quickly institute appropriate treatment, which is an important determinant of the clinical course of this infectious disease.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Albízuri-Prado MF, Sánchez-Orta A, Rodríguez-Bandera A, Feito-Rodríguez M. Mucormicosis cutánea primaria por Rhizopus arrhizus en una niña de 8 años. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2018;109:562–564.