Morphea “en coup de sabre” (MCS) is a type of linear morphea that can involve the frontal and parietal region of the scalp, and the face. It mainly affects the skin and subcutaneous tissue, resulting in cicatricial alopecia.1,2 Morphea sites have been reported to coincide with those of other, pre-existing, inflammatory dermatoses, including herpes zoster. A thorough review of the English-language literature, however, found no report of MCS appearing at the site of healed herpes zoster ophthalmicus to date. We report what is probably the first case of MCS at the site of healed herpes zoster ophthalmicus.
A 40-year-old woman visited our department with changes in the color and texture of the skin on the forehead that had begun 2 months earlier. The lesions began insidiously and advanced to the frontal scalp, giving rise to cicatricial alopecia. The patient had no history of prior trauma, abnormal vision, headaches, or convulsions. Five months earlier, the patient had visited our department with painful lesions containing fluid around the left eye and on the forehead. The lesions were diagnosed as herpes zoster; the diagnosis was confirmed by means of the Tzanck test and the lesions were treated with 500mg of famciclovir 3 times a day for 7 days. Remission of the lesions occurred over a period of 2-4 weeks, leaving residual hyperpigmentation and scarring. In the previous 2 months, the patient observed thickening and hardening of the scalp near the forehead but no involvement of the area around the left eye.
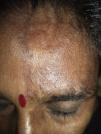
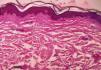
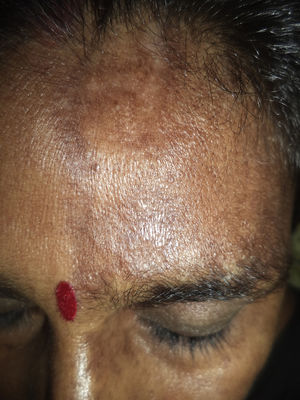
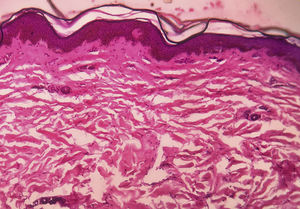
Medical examination revealed hyperpigmentation and induration of the skin on the left side of the forehead, extending from the nasal root to the frontal scalp in a paramedian location, which led to linear cicatricial alopecia of the frontal scalp (Fig. 1). Other mucocutaneous, ophthalmologic, and systemic examinations revealed no findings of interest. Serology for Borrelia burgdorferi was negative. Radiography of the skull, including MRI, revealed no abnormalities. The biopsy revealed flattening of the dermis with atrophy of the epidermal crests, and thick hyaline collagen strands accompanied by disperse inflammatory cells and a reduced number of adnexa in the dermis (Fig. 2). In light of the clinical findings and subsequent examinations MCS secondary to ophthalmic herpes zoster was diagnosed.
Concomitant environmental factors such as mechanical trauma, reactions to insect bites, vaccines, radiation, drugs, infections, and even psychogenic stress have been reported in a small proportion of patient with morphea. Few case reports exist in which morphea has developed at the sites of prior herpes zoster.3–7 Grabell et al8 reported 2 cases of morphea at the site of healed herpes zoster in a study population of 329 patients, which included both adults and children. Those authors, however, did not characterize the cases, as they did not indicate the type of morphea, the time elapsed between the 2 processes, or the sites. Table 1 shows the comparison of those cases with our patient (Table 1). A thorough review of the English-language literature revealed no cases of MCS at the same site as healed ophthalmic herpes zoster, which makes our case unique.
Comparison of Cases of Morphea at the Site of Healed Herpes Zoster.
| Case No. | Case Report | Age/Sex | Type of Morphea | Dermatome Involved | Time Elapsed Between Diseases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Qu T et al.3 | 24/M | Bullous morphea | T9-12 | 2 y |
| 2 | Noh TW et al.4 | 57/M | Plaque morphea | T2-4 | 4 mo |
| 3 | Forschner A et al.5 | 40/F | Plaque morphea with characteristics of lichen sclerosus | C4-7 | 1 mo |
| 4 | Lopez N et al.6 | 45/M | Zosteriform morphea | T2-4 | 2 y |
| 5 | Ruiz Villaverde R et al.7 | 19/F | Zosteriform morphea | T9-10a | 2 y |
| 6 | Grabell D et al.8 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 7 | Grabell D et al.8 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 8 | This case | 40/F | Morphea en coup de sabre | V1 | 3 mo |
F indicates female; NA, information not provided by the authors in their article; M, male.
Herpes zoster scars are the most frequent site for another disease known as Wolf isotopic response.9 The causes of this phenomenon are still unknown. Local immune dysfunction and vascular changes, which would favor the consequent inflammation, have been proposed as predisposing factors.9 Abnormal levels of neuropeptides in the nerves as a result of herpes infection may trigger an alteration of the immune system and facilitate the development of inflammatory dermatoses such as morphea.4,9 The sclerosis observed in morphea is attributed to the prolonged activation of the fibroblasts under the influence of Th2 cytokines such as interleukin-4 and transforming growth factor-ß, caused by varicella-zoster viruses.6 Isolation of viral DNA in lesions of the second disease suggest that the herpes virus may itself be directly responsible for the clinical process.4,10
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Arif T. Morfea en coup de sabre sobre el área cutánea de un herpes zóster oftálmico cicatrizado. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2019;110:617–619.