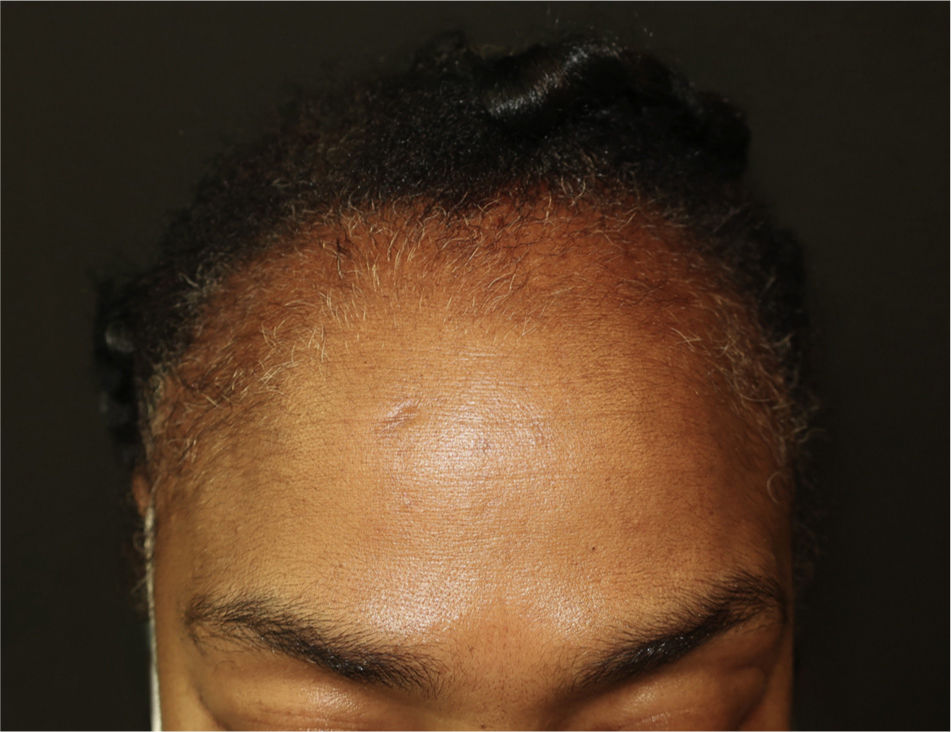
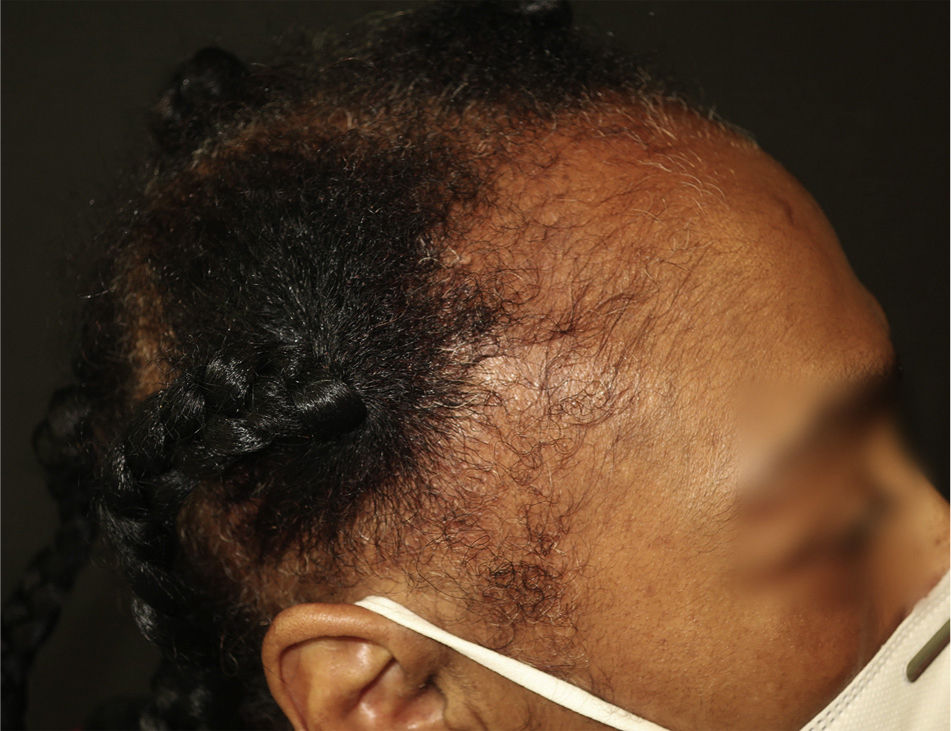
A 51-year-old Colombian woman visited our department with predominantly frontal and bitemporal capillary hypodensity that had begun 10 years earlier (Figs. 1 and 2).
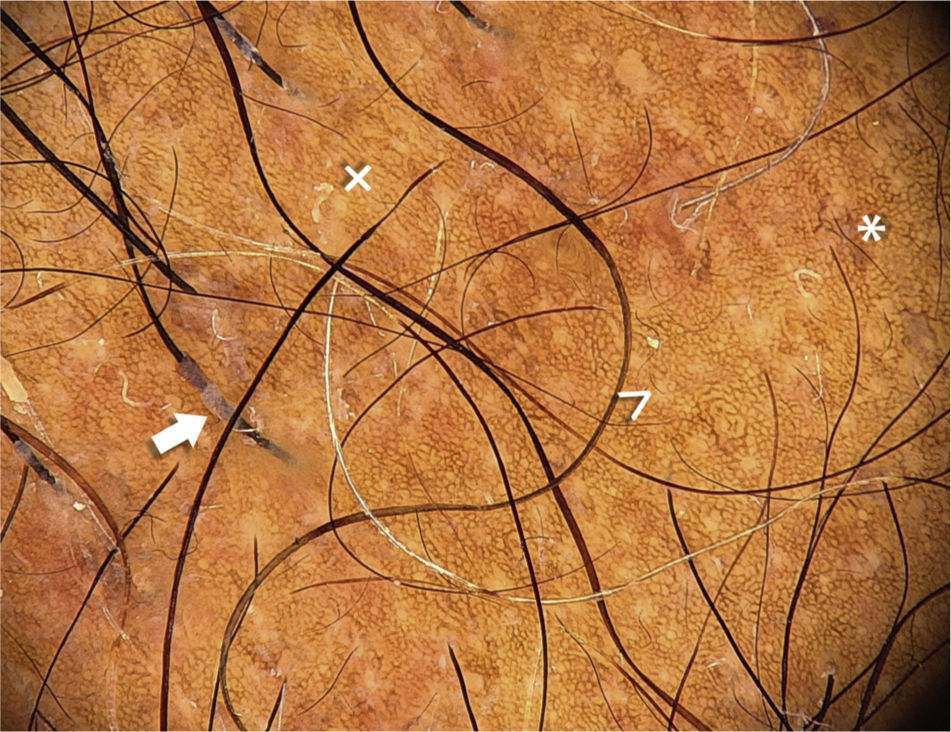
Trichoscopy revealed miniaturization of the follicles, a fine pigmented reticulum, and hair casts (Fig. 3).
What is your Diagnosis?
Traction alopecia
Traction alopecia (TA) is caused by the direct mechanical damage done by hairstyles involving considerable traction1. It is more frequent in women and has been reported in up to a third of African-American women, although it can affect all phenotypes2. It is associated with the use of pony tails, plaits, extensions, chemical hair-shaft relaxers, turbans, and headbands3,4. The condition is a reversible alopecia in the initial stages but progresses to permanent alopecia if the triggering factors are not corrected2. Physical examination reveals the band sign that corresponds to an area immediately anterior to the area of alopecia, with shorter terminal hairs. The eyebrows, eyelashes, nails, and body hair are not involved.
In the initial stages of TA, trichoscopy reveals miniaturization of the follicles and hair casts (HCs). Papules and/or pustules may also be observed, together with perifollicular erythema, black spots and the recently described flame or torch sign, which is more frequent in more pigmented phototypes, corresponding to white areas at the base of the terminal hairs.5 In advanced stages, signs of cicatricial alopecia are observed2,5.
The HCs tend to be found on the periphery of the alopecia plaque. They are present in more than 80% of cases of TA and correspond to grayish-white mobile cylindrical structures, located in the region proximal to the hair shaft, coinciding with the areas of maximum tension. Their presence indicates permanent traction, and they may, therefore, help to monitor cessation of this factor by the patient. HCs are not a specific sign. They can also be observed in seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis of the scalp, and it is important to distinguish them from nits in order to avoid unnecessary treatments6.
The differential diagnosis of TA includes other entities that may mimic or even coexist the condition, such as fibrosing frontal alopecia, androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, and trichotillomania, which do not present HCs1,2. Biopsy should only be performed if the diagnosis is in doubt5.
Treatment is based on avoiding traction. Topical or intralesional corticosteroids, antibiotics, and minoxidil may be used in the initial stages. In advanced stages, camouflaging techniques and hair transplant may be considered1–6.
Please cite this article as: Giacaman A, del Pozo Hernando LJ, Martín-Santiago A. Vainas peripilares: claves tricoscópicas. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113:176–177.