Rhinophyma, a rare and progressive disfiguring condition, is thought to be the final stage of rosacea. Several surgical treatments are available, including dermabrasion, cryosurgery, scalpel excision, electrosurgery, and carbon dioxide laser. The last 2 techniques are the most effective for the management of rhinophyma. We describe a series of cases of moderate or severe rhinophyma treated with high-frequency electrosurgery in the dermatology department of Hospital Simón Bolivar and in private clinics in Bogota, Colombia, between 2012 and 2016. The cosmetic result, as assessed by both the clinicians and the patients, was satisfactory in all cases. Three patients presented hypertrophic scars that were treated with steroid injections and silicone gel sheeting. Two patients presented persistent erythema. However, there were no serious infections and none of the patients required further surgery. Electrosurgery is one of the simplest and most cost-effective techniques currently available for the treatment of rhinophyma by dermatologists.
El rinofima se considera el estado final de la rosácea, siendo una condición desfigurante progresiva y poco común. Existen diferentes alternativas quirúrgicas como la dermoabrasión, la criocirugía, la escisión con escalpelo, la electrocirugía y el láser CO2. Estas 2 últimas técnicas son las más efectivas en el manejo del rinofima. Se describe una serie de casos de pacientes con rinofima moderado-grave que recibieron manejo con electrocirugía de alta frecuencia en el Servicio de Dermatología del Hospital Simón Bolívar y práctica privada entre 2012 y 2016. Todos los pacientes mostraron respuesta estética satisfactoria basada en el criterio médico y la percepción del paciente. Tres pacientes presentaron cicatrices hipertróficas manejadas con infiltraciones y bandas de silicona. Dos pacientes presentaron eritema persistente. Ningún caso requirió un segundo tiempo quirúrgico, ni infección grave. La electrocirugía es una de las técnicas vigentes más coste-efectivas y de fácil realización por el dermatólogo para el tratamiento del rinofima.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that affects blood vessels and pilosebaceous units.1 Of the various clinical presentations of rosacea, the least common is rhinophyma, accounting for 3.7% of rosacea cases and occurring almost exclusively in men between the fifth and seventh decades of life.1,2 The highest prevalence of rhinophyma is found in western Scotland.2 Rhinophyma is characterized by sebaceous hyperplasia, fibrous tissue proliferation, vascular bed alteration, and induration of the skin.3 Although the term rhinophyma refers to involvement of the nasal tip, the condition can spread to other parts of the face, including the chin (gnathophyma), ears (otophyma), forehead (metophyma), and eyelids (blepharophyma).3 Several surgical treatments are available, including dermabrasion, cryosurgery, scalpel excision, electrosurgery, and carbon dioxide laser.4,5 The last 2 techniques are most effective for the management of rhinophyma.6–9 In this article, we describe a series of cases of moderate or severe rhinophyma treated with high-frequency electrosurgery.
Patients and MethodsAll patients with moderate or severe rhinophyma treated with high-frequency electrosurgery in the dermatology department of Hospital Simón Bolívar or in the authors’ private clinics in Bogota, Colombia, between 2012 and 2016 were enrolled in the study. Rhinophyma severity was assessed using the criteria proposed by El-Azhary et al.10: mild (telangiectasias and hyperplasia of the dermis), moderate (nasal hypertrophy and formation of lobular areas), or severe (nasal hypertrophy and prominent lobules).2 All patients underwent high-frequency (30-40W) electrosurgery in cutting-coagulation mode at 2.5-3MHz (Ellman Surgitron FFPF EMC, Ellman International, Inc., United States). Before the procedure, all patients received local anesthesia with 1% lidocaine with 1:200000 epinephrine and underwent electrocoagulation treatment of any varicose veins or prominent telangiectasias. Layer-by-layer decortication was performed with a triangle-tip electrosurgical knife to the depth of the reticular dermis. The aesthetic units of the nose were respected and the deepest third of the sebaceous glands was preserved. Dermabrasion with water sandpaper (220- and 360-grit) was carried out until uniform punctate bleeding was achieved. Hemostasis was achieved with electrocoagulation and 40% ferric chloride solution was applied until hematic crusts formed. Patients attended a follow-up visit 15 days after the procedure. Six of the 7 patients used silicone gel sheeting (Dermasof, Laboratorio Incit, Colombia) and all patients received anti-inflammatory drugs for pain management for 24 to 48hours after the procedure. Follow-up visits were scheduled at 2, 4, and 12 weeks after the procedure.
ResultsSeven men between 40 and 69 years of age were treated with electrosurgery (Table 1). All patients had a skin phototype between ii and iv and had been diagnosed with moderate or severe rhinophyma. Six of the patients (85%) had received prior treatment for rosacea; of these, 4 (57%) were treated for phymatous rosacea with isotretinoin and 2 (28%) were treated with carbon dioxide laser with no clinical response. One patient had received no prior treatment (Table 1).
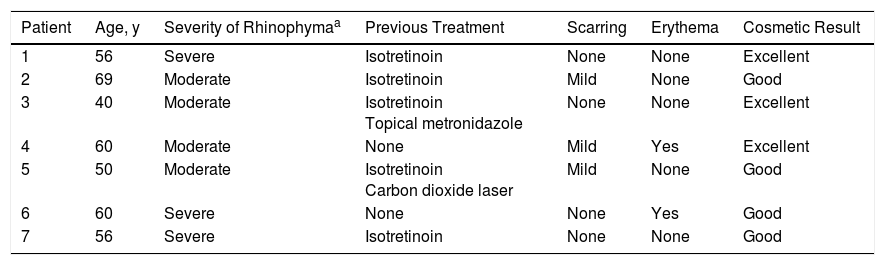
Characteristics and Clinical Responses of Patients Treated With Electrosurgery.
| Patient | Age, y | Severity of Rhinophymaa | Previous Treatment | Scarring | Erythema | Cosmetic Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56 | Severe | Isotretinoin | None | None | Excellent |
| 2 | 69 | Moderate | Isotretinoin | Mild | None | Good |
| 3 | 40 | Moderate | Isotretinoin Topical metronidazole | None | None | Excellent |
| 4 | 60 | Moderate | None | Mild | Yes | Excellent |
| 5 | 50 | Moderate | Isotretinoin Carbon dioxide laser | Mild | None | Good |
| 6 | 60 | Severe | None | None | Yes | Good |
| 7 | 56 | Severe | Isotretinoin | None | None | Good |
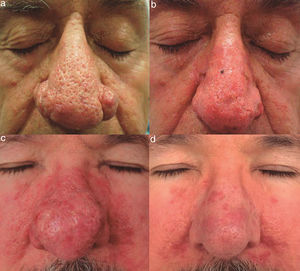
The cosmetic result, as assessed by both the clinicians and the patients, was satisfactory in all cases. The postsurgical follow-up period ranged from 12 weeks to 2 years (Fig. 1). Three patients presented scars, which were treated with infiltrations and silicone gel sheeting, and 2 patients presented persistent erythema (Fig. 2). None of the patients required further surgery or had severe complications such as infection or keloids. No posttreatment pigmentation changes were observed in patients with skin phototype iii or iv (Fig. 1). Dilated pores were observed in 3 patients (Figs. 1A and 1B).
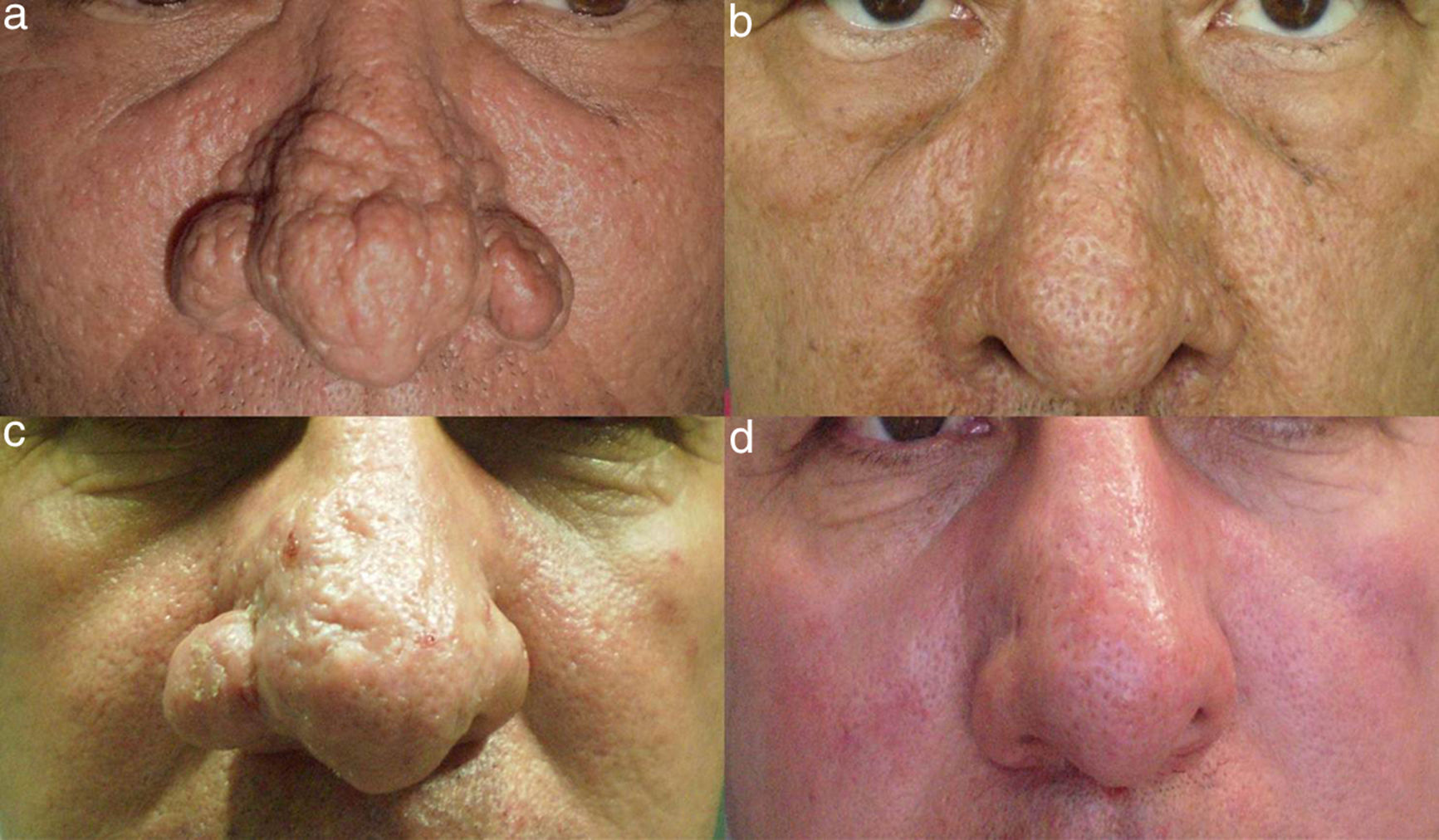
A, Patient 1, a 56-year-old man with severe rhinophyma. B, Excellent results 2 years after the procedure. Note the persistence of dilated pores and the absence of pigmentary alterations in this patient with skin phototype iv. C, Patient 5, a 50-year-old man previously treated with isotretinoin and carbon dioxide laser. D, Significant improvement in hyperplasia on the right ala nasi and nasal tip 20 weeks after electrosurgical treatment.
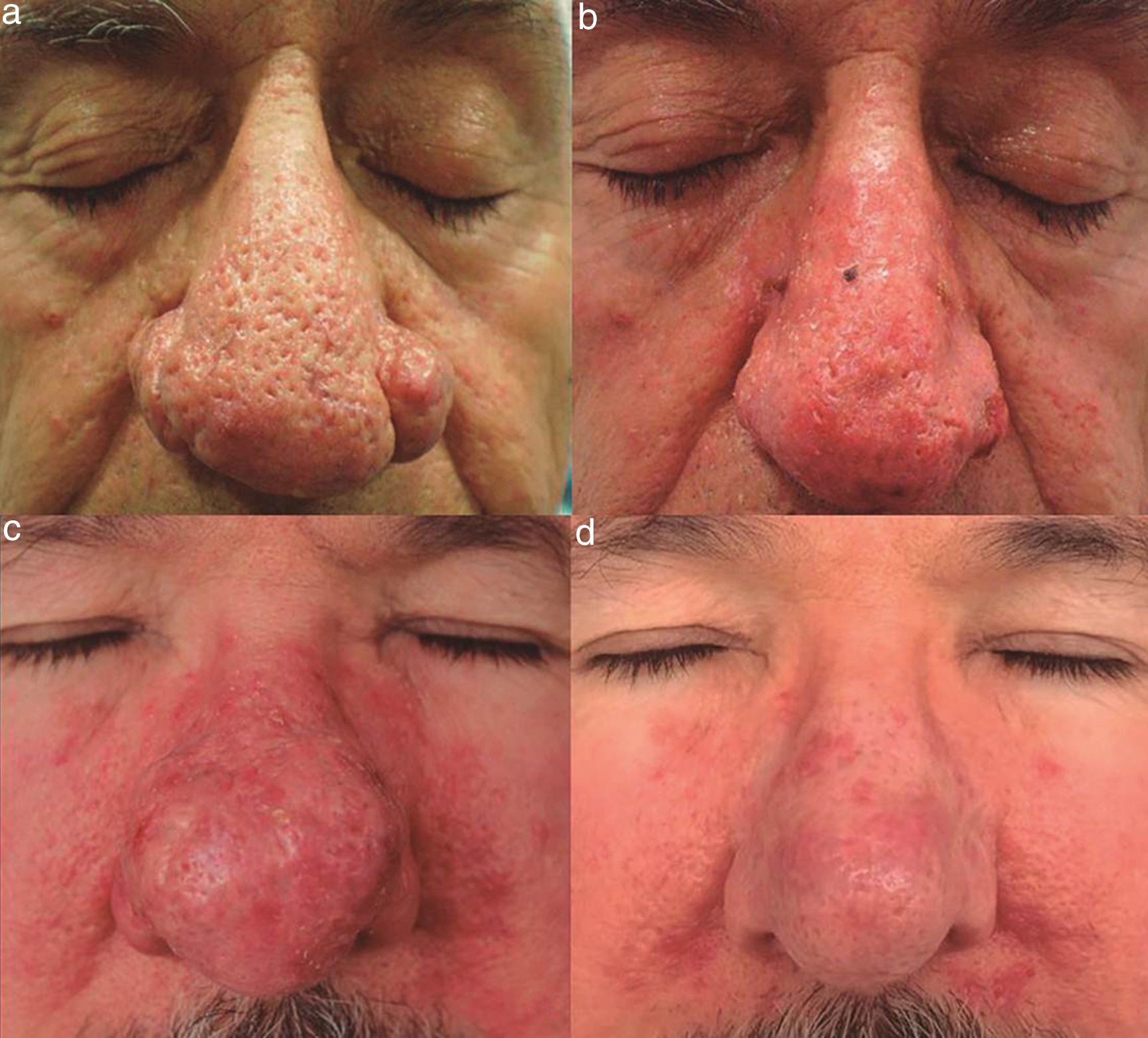
A, Patient 6, a 60-year-old man with severe rhinophyma. B, Good clinical response 2 weeks after electrosurgical treatment. Note the mild postsurgical erythema. C, Patient 7, a 56-year-old man with severe rhinophyma previously treated with isotretinoin. D, Surgical response with good scarring 12 weeks after the procedure.
Given the low incidence of rhinophyma and the lack of randomized studies assessing the various techniques available, the ideal management of this condition has not been standardized.7 Due to its speed, efficiency, and low cost, high-frequency electrosurgery allows satisfactory management of rhinophyma.5 Favorable cosmetic results can be achieved by remodeling and removing nasal tissue with a triangle-tip electrosurgical knife. Heat-induced damage of the surrounding tissue is minimal, as is the risk of necrosis of cartilage and scarring.8 In this case series, 3 patients presented visible scarring; nevertheless, the patients’ perception of the cosmetic result was very satisfactory. The key to successful surgery is to achieve sufficient depth of decortication while respecting the aesthetic units of the nose—in particular the alae nasi and the tip—because the there is risk of scarring due to the proximity of the cartilage to the dermis. The objective of the surgery is to preserve the deepest part of the pilosebaceous unit, thereby guaranteeing adequate epithelization, which gives the nasal skin a normal porous appearance and prevents atrophic scarring.7–9 Carbon dioxide laser vaporization has been widely used in mild to severe rhinophymas, with satisfactory cosmetic results.6,11 However, carbon dioxide laser treatment requires training on the part of the clinician applying the technique and greater expertise in the appropriate parameters for the specific equipment used; moreover, it is an expensive surgical alternative.11 In other case series, simple techniques such as decortication by scalpel and electrosurgery yielded no differences in postinflammatory pigmentary alterations in comparison to carbon dioxide laser treatment.11 Surgical techniques involving decortication of hypertrophic tissue that preserve the deepest part of the sebaceous glands in order to guarantee adequate reepithelization—such as scalpel excision and electrosurgery—are easy to use and achieve good cosmetic results.12 This study—one of the few case series involving a nonwhite Latino population—achieved excellent cosmetic results and good patient satisfaction.
Electrosurgery is one of the most cost-effective techniques currently available,9 easy for dermatologists to perform, and more effective in the treatment of moderate to severe rhinophyma. Innovative techniques such as carbon dioxide laser treatment should be reserved for mild to moderate cases of rhinophyma and performed by trained specialists with experience in the use of these devices. Moreover, patients should be consulted in assessing the cost of these techniques.
Ethical DisclosuresProtection of persons and animalsThe authors declare that the procedures followed complied with the ethical standards of the corresponding human experimentation committee and the World Medical Association and with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Data confidentialityThe authors declare that they followed their hospital's regulations regarding the publication of patient information.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no private patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: González LF, Herrera H, Motta A. Tratamiento con electrocirugía del rinofima moderado-grave Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2018;109:e23–e26.