Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) provides growth factors that stimulate fibroblast activation and induce the synthesis of collagen and other components of the extracellular matrix. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of PRP in the treatment of photodamage of the skin of the hands.
Material and methodsExperimental study enrolling persons with photoaged skin on the dorsum of the hands (Glogau photoaging scale, type III, or Fitzpatrick wrinkle classification, type II) were included between August 2012 and January 2013. A histological comparison was made of skin biopsies taken before and after the application of PRP to the skin of the dorsum of the hands.
ResultsThe mean (SD) age of the 18 women enrolled was 47.9 (4.3) years. Histological analysis showed an increase in the number of fibroblasts (P<.001), number of vessels (P<.001), and collagen density (P=.27). These changes produced significant improvements in the Fitzpatrick wrinkle and elastosis scale (P<.001) and in the Glogau photoaging scale (P=.01).
ConclusionsPRP induced a reduction in the manifestations of skin aging, including an improvement in wrinkles and elastosis.
El plasma rico en plaquetas (PRP) aporta factores de crecimiento que inducen la síntesis de colágeno y otros componentes de la matriz extracelular, y estimula la activación de fibroblastos. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar el efecto del PRP en el tratamiento del fotodaño en manos.
Material y métodosEstudio de tipo experimental. Se incluyeron individuos con envejecimiento en el dorso de las manos, de tipo 3 en la escala de fotodaño de Glogau o de clase II de la clasificación de arrugas y elastosis de Fitzpatrick, entre agosto de 2012 y enero de 2013. Se aplicó PRP en la piel del dorso de las manos y se tomaron biopsias cutáneas antes y después del tratamiento para la comparación histológica.
ResultadosSe trataron 18 mujeres con una edad media de 47,9 ± 4,3 años. El análisis histológico demostró un incremento en el número de fibroblastos (p=0,000), número de vasos (p=0,000) y cantidad de colágeno (p=0,27), representado como un cambio en la escala de clasificación de arrugas y elastosis de Fitzpatrick (p<0,001) y en la escala de fotodaño de Glogau (p=0,01)
ConclusionesEl PRP indujo una reducción en los signos y síntomas del envejecimiento cutáneo, con mejoría en las arrugas y elastosis.
Skin aging is the result of accumulated damage that leads to the gradual biological and functional decline of cells over time (intrinsic aging) or the influence of environmental factors such as smoking, exposure to chemicals or UV radiation (extrinsic aging).1
Constant exposure to UV radiation diminishes the structural function and integrity of the extracellular matrix through collagen degeneration and abnormal elastin structure, leading to the loss of both skin tone and elasticity, causing the signs of aging.2
Platelet activation in response to tissue damage and vascular exposure develops to promote hemostasis and secrete biologically active proteins3–6 that undertake functions related to chemotaxis, tissue proliferation and differentiation, angiogenesis, and regeneration of the extracellular matrix. A dose–response relationship between platelet concentration and the proliferation of mesenchymal cells, fibroblasts, and type 1 collagen has been observed in vitro.7–10
Growth factors in platelet-rich plasma (PRP) can stimulate fibroblast activation to regenerate damaged soft and hard tissues.2,3 These regenerative effects are attributed to the presence of biological factors such as platelet-derived growth factor, ß-transforming growth factor, epidermal growth factor, insulin-like growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor, all of which are released locally after PRP is applied.11 Increased dermal and epidermal thickness as well as enhanced numbers and organization of fibroblasts in photodamaged skin indicate that these factors act on cell proliferation and reduce actinic elastosis12,13 even up to 3 months after application.6
Although PRP is used in a variety of conditions, only a few experimental studies have looked at the effects of PRP stimulation to treat skin aging.6,14–17
Material and MethodsThis experimental study was carried out between August 1, 2012, and January 31, 2013. After approval by the local medical research review board and ethics committee (file number R-2013-1301-142), we enrolled patients aged between 40 and 60 years who had mild skin photoaging according to the Glogau scale.18 The exclusion criteria were the use of topical treatments in the 6 months before the study, pregnancy, skin infection, a history of platelet dysfunction, use of corticosteroids, smoking, cancer, hemoglobin level less than 10g/dL, or a platelet count less than 105×109/L.
Three PRP application sessions were given 30 days apart.
Outcomes were assessed on the Glogau scale and the Fitzpatrick wrinkle scale19 and through histologic examination of posttreatment skin biopsies. Patients were asked not to change their routine skin care habits during the study.
Method for Obtaining PRPWe extracted autologous venous blood into sterile vacuum collection tubes containing a solution of 3.2% sodium citrate. The tubes were then placed in a digital centrifuge (MS2000). The first cycle was set at 1500rpm for 10minutes to separate blood components (erythrocytes, buffy layer, and plasma). The plasma was then separated into 2 upper layers of platelet-poor plasma and a lower layer of PRP. Using sterile technique, we collected the 2upper fractions from each patient sample into 2 sterile vacuum tubes using 10-mL syringes and 25-gauge, 16-mm hypodermic needles. The same procedure was then used to transfer each of the lower fractions to a third sterile vacuum tube for each sample. The 3 tubes containing the 3 plasma layers from each sample were then centrifuged at 2000rpm for 10minutes.20
Anesthetic TechniqueThe dorsal surface of the hand was disinfected and an antiseptic solution was applied. Using sterile technique we performed radial and ulnar nerve blocks with subcutaneous injections of lidocaine in 2% solution. A total of 3cc was injected proximal to the styloid apophysis of the radius (anatomical snuff box), and 2cc was injected at the ulnar styloid apophysis between the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon and the ulnar artery.
Biopsy MethodWe biopsied the most severely photodamaged area with a disposable 2.5-mm punch (Uni-Punch) at 2 moments: immediately before the first treatment application and 28 days after the last application.
PRP ApplicationThe upper plasma fractions were activated by adding a 10:1 (10%) solution of calcium gluconate to the tube and shaking. The resulting mixture was extracted to a 100-IU syringe with a 25-gauge, 16-mm hypodermic needle. A No. 11 blade was used to make stab incisions on the dorsal surfaces of the second, third, and fourth interdigital spaces; 17-mm blunt-tipped catheters for lipids were inserted for radial and crossed-pattern injection of the plasma.21,22 Next, the lower fraction was activated in the same way, and injections of approximately 1.5mL were made into the dermis from the dorsal surface of the hand with a 25-gauge, 16-mm needle. The injections were spaced 1.5to 2mm apart.
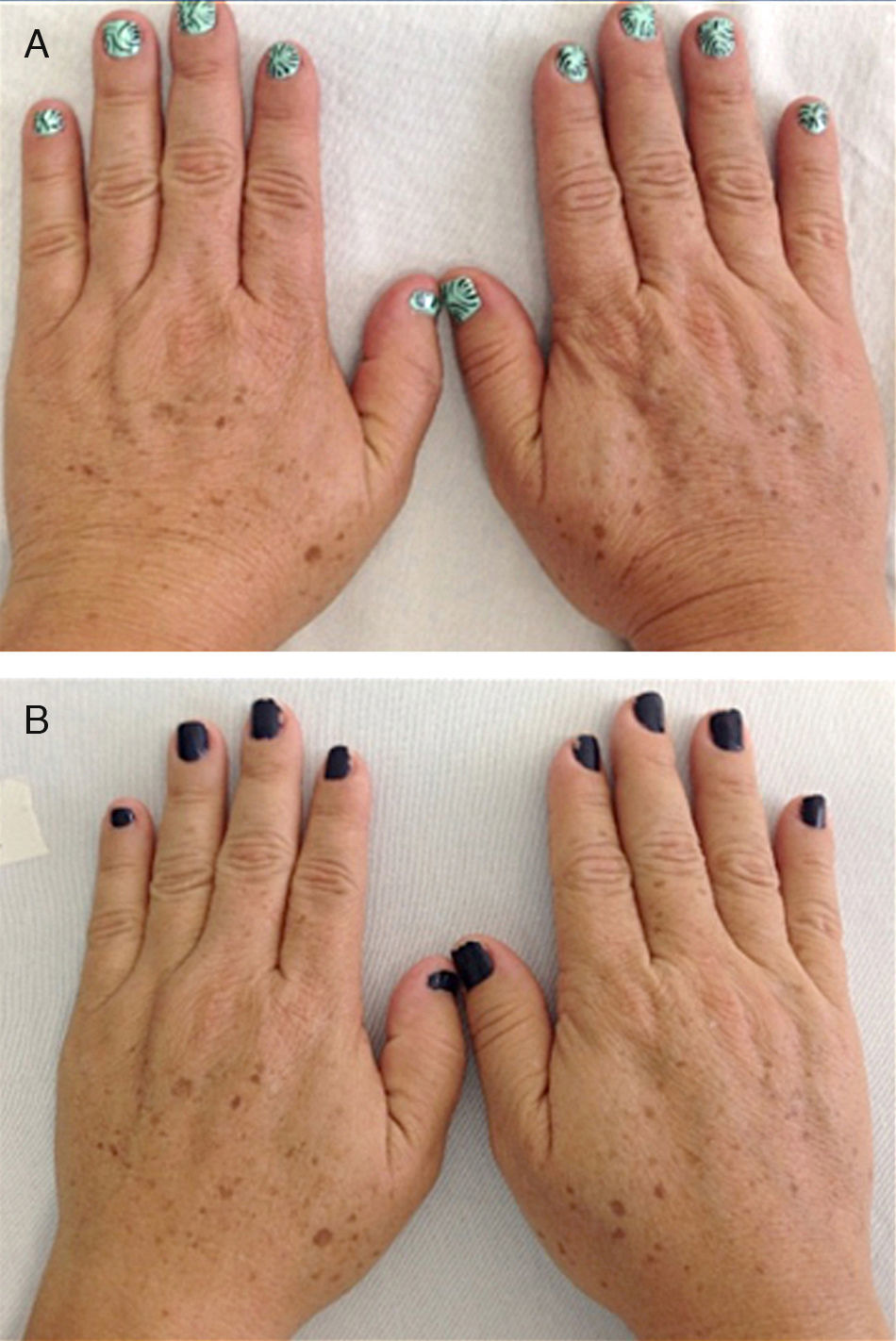
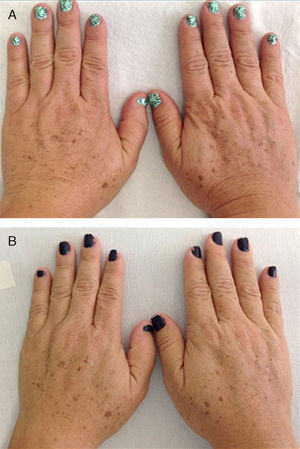
Clinical EvaluationParticipants were evaluated and classified on the Glogau photoaging scale18 before starting treatment and a month after the last application. The classifications were as follows: type I, early photoaging, no wrinkles; type II, early photoaging, appearance of wrinkles when skin moves; type III, advanced photoaging, wrinkles at rest; type IV, severe photoaging, wrinkles throughout. The patients were also evaluated on the Fitzpatrick wrinkle scale19 as class I, fine wrinkles and mild elastosis; class II, fine to moderately deep wrinkles and moderate elastosis; and class III, severe elastosis with fine to deep wrinkles.
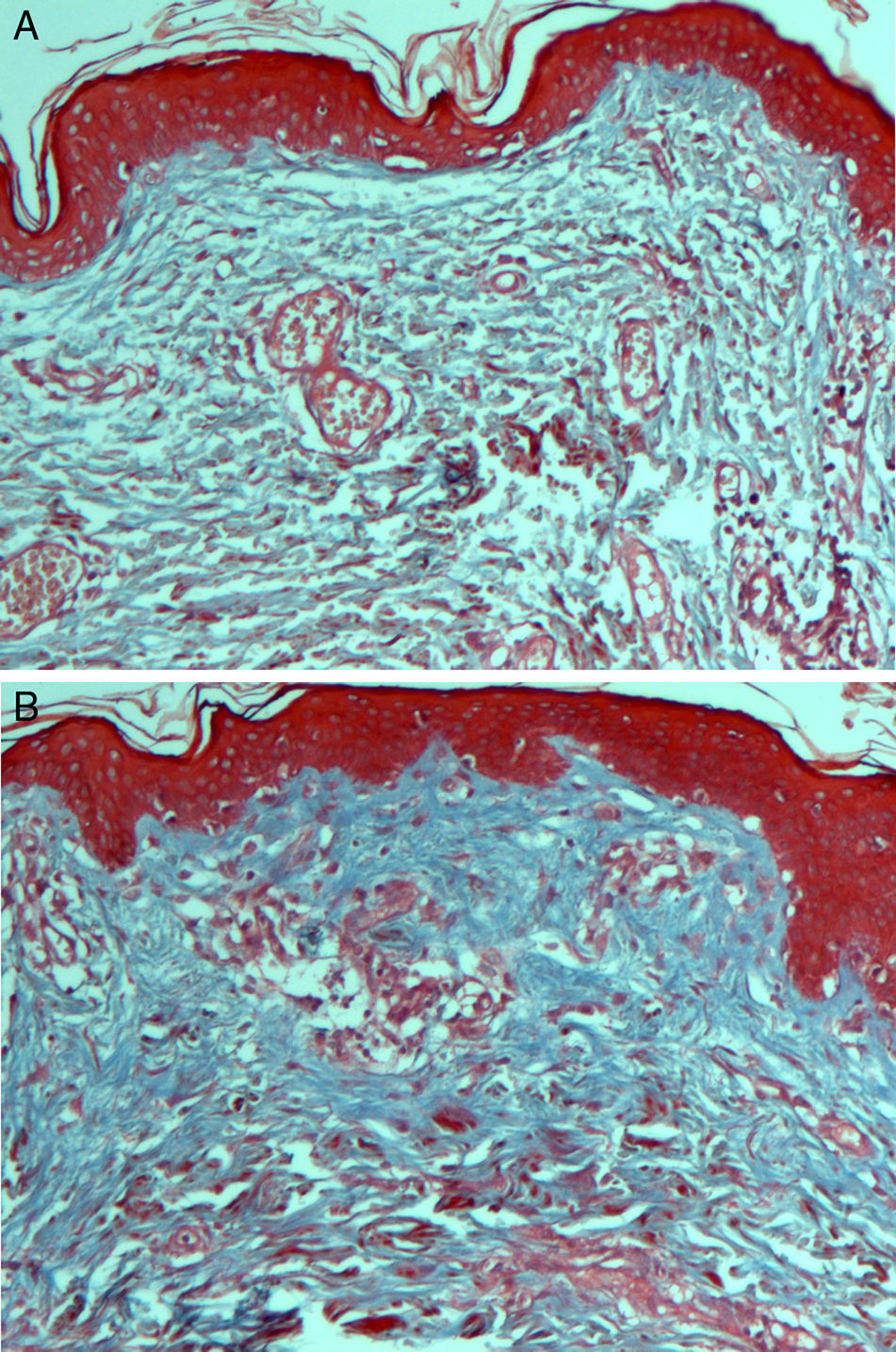
HistologyBiopsied tissue samples were fixed with 10% formalin, sectioned (6μm), and stained with hematoxylin-eosin for fibroblasts and nuclei; Masson's trichrome for type I collagen fibers, and periodic acid-Schiff stain for basement membranes of blood vessels.
Digital images were taken and analyzed with Image software. Histologic assessment of blood vessels, collagen, and fibroblasts was performed on 10 fields, original magnification ×40; the tissue examined was from a location 2mm below the basement membrane of the epithelium (toward the deep dermis) in areas not adjacent to adnexa. Atypia, or fibroblastic reactivity in the nucleus, and elastosis were recorded as present or absent.
Statistical AnalysisResults for qualitative variables were described with absolute frequencies and percentages; they were compared with the Fisher exact test or the χ2 test. Quantitative results were reported with mean (SD) and medians as appropriate; they were compared with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. P values less than .05 were considered statistically significant.
ResultsWe included 20 women, 2 of whom interrupted treatment (1 because of isolated phlebitis of the arm and 1 because of uncontrolled dyslipidemia). The remaining 18 patients finished the study. The mean age was 47.9 (4.3) years.
The Fitzpatrick wrinkle scale evaluations improved significantly after the PRP treatments (P<.001). The mean pre- and posttreatment scores were 4.94 (0.80) and 2.78 (0.42), respectively, representing a change in category from class II to class I.
Eleven patients were initially classified as type III and 7 as type II according to the Glogau photaging scale. After treatment, 7 of the 11 patients (63.64%) were reclassified as type II (P=.01); the classification for the remaining patients did not change (Fig. 1).
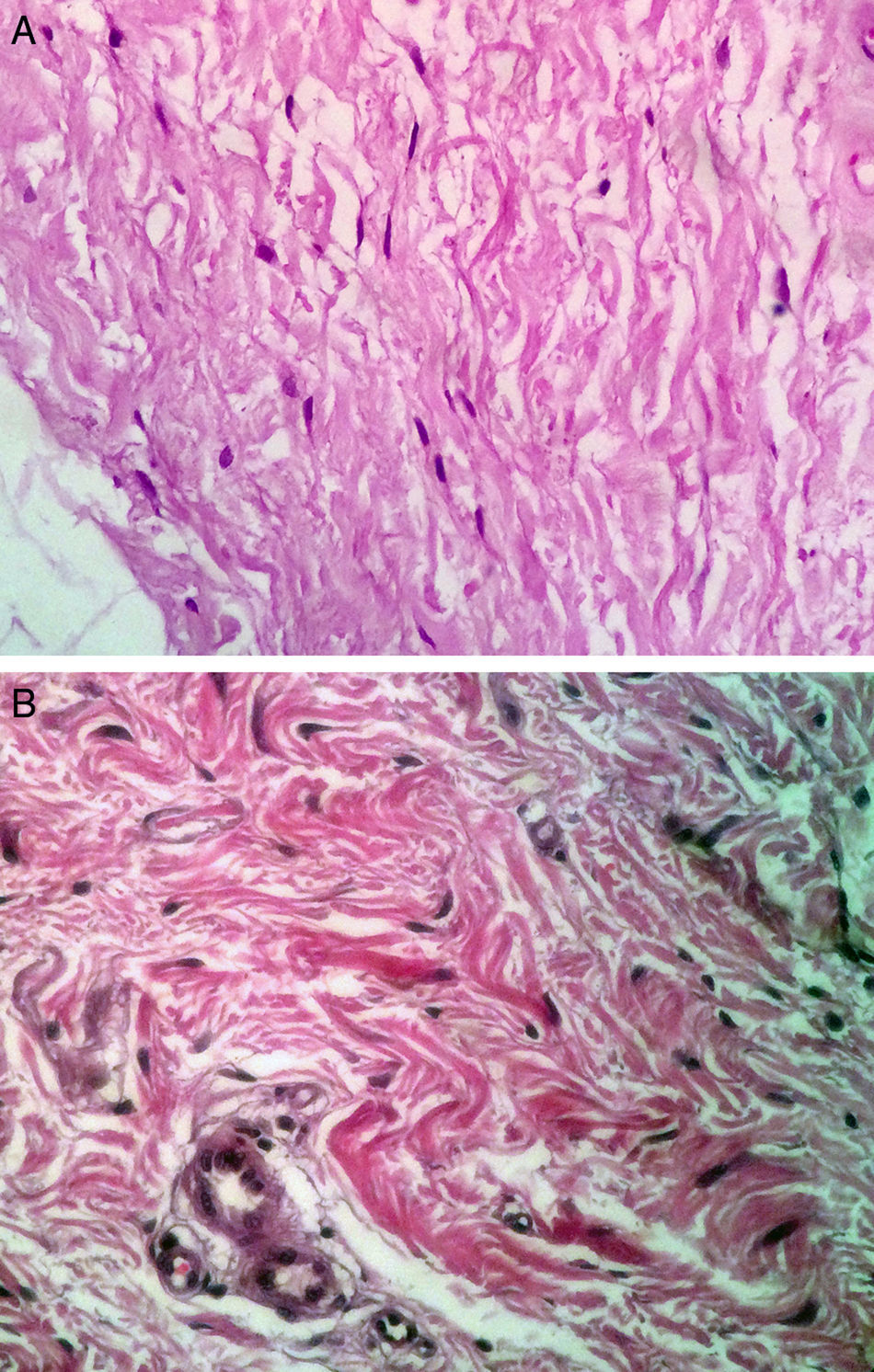
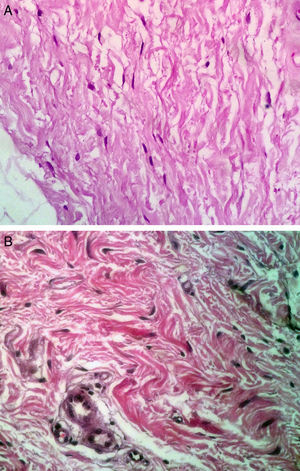
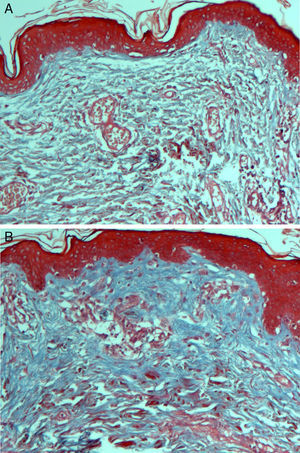
On histologic assessment, we found increases in the number of blood vessels per standardized basement membrane measure and fibroblasts per number of nuclei examined. Papillary dermal collagen had also increased with treatments (Figs. 2 and 3).
We identified no changes in elastosis or basement membrane structure that could be attributed to PRP treatment, however. Nor did we find atypia in fibroblasts, other than vesicular nuclei and a few nucleoli in relation to slight fibroblastic reactivity.
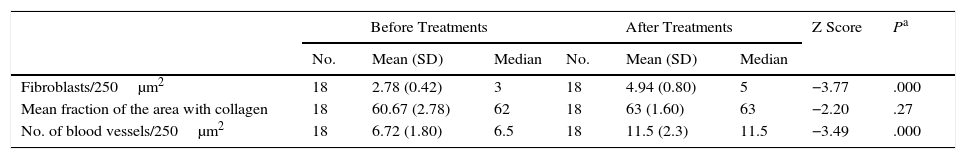
The number of fibroblasts and blood vessels observed and the amount of collagen are shown in Table 1. Fibroblasts and blood vessels both increased.
Histologic Findings Before and After Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatments.
| Before Treatments | After Treatments | Z Score | Pa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Mean (SD) | Median | No. | Mean (SD) | Median | |||
| Fibroblasts/250μm2 | 18 | 2.78 (0.42) | 3 | 18 | 4.94 (0.80) | 5 | −3.77 | .000 |
| Mean fraction of the area with collagen | 18 | 60.67 (2.78) | 62 | 18 | 63 (1.60) | 63 | −2.20 | .27 |
| No. of blood vessels/250μm2 | 18 | 6.72 (1.80) | 6.5 | 18 | 11.5 (2.3) | 11.5 | −3.49 | .000 |
Skin shows the aging process through multiple clinical signs. One of the most important is the development of wrinkles, which gives the skin an undesirable appearance when combined with elastosis, color variations, and keratosis. Underlying these signs are histologic changes.
Several studies have shown that intradermal PRP injections can stimulate growth factors, favoring the regeneration of skin cells.23,24 We saw a considerable increase in the number of fibroblastic nuclei and augmentation of blood vessel basement membranes after PRP treatments. Although the assessed variables changed significantly, the increase in the amount of collagen present was not as marked as in some other studies.6,17
In one of these studies, histology of skin biopsies after treatments with plasma rich in growth factors showed increased dermal and epidermal thickness and a significant increase in fibroblasts and collagen fibers 3 months after treatment ended.6 It is possible that the timing of the biopsy may affect whether histologic changes can be visualized or not. However, our findings were consistent with a study in which patients reported a change in the severity of wrinkles in spite of the lack of a significant increase in the amount of collagen.25
Fibroblasts are responsible for synthesizing the reticular, collagen, and elastic fibers of the extracellular matrix of tissues; thus, stimulating the production of fibroblasts will enhance the matrix.26,27 We therefore believe that the processes of tissue repair and regeneration will continue to take place in our patients beyond the moment when we took our measurements. Histologic changes would probably have become significantly more evident in later biopsies. The early timing of the biopsy procedures in our study was therefore a limitation.
The proangiogenic factors released by PRP also promote a change in endothelial cell phenotype, favoring proliferation and enabling cells to remodel the extracellular matrix of circulating blood, as well as migrate to the focus of angiogenesis and differentiate to form new blood vessels.8,28 Cell lines responsible for angiogenesis are also involved in the recognition, repair, and chemotaxis required for regeneration. Angiogenesis could therefore be critical for sustaining the clinical effects of PRP treatment. We suggest that angiogenesis should be assessed in future clinical trials.
Some authors have found that topical or subcutaneous application of PRP and growth factors lead to significant changes in the skin.29,30 These treatments restore elasticity and vitality as well as increase thickness and enhance blood flow, suggesting that PRP and growth factors regulate dermal and epidermal remodeling in facial skin. However, the fact that the mere use of a needle to inject any substance might in itself activate fibroblasts in the skin and stimulate collagen synthesis was mentioned in one study.3 Abuaf et al.17 recently showed that the amount of collagen increased with mesotherapy even without the application of PRP. It would be reasonable, therefore, to expect that our study would demonstrate even greater changes, given the technique we used; we did not see a large effect, however.
Because the hands are generally under repeated exposure to sunlight, our findings may be useful for deciding how to treat photodamaged skin in areas that are less exposed. Our review of the literature indicates that this is the first study on the effect of hand skin rejuvenation through PRP treatments. We believe that more such studies should be done to further our understanding of the effects of applying PRP to photodamaged skin.
ConclusionPRP treatments reduced signs of skin aging, favored collagen synthesis, and increased the number of fibroblasts and blood vessels in the superficial layer of the dermis.
Ethical DisclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that the procedures followed adhered to the ethical guidelines of the responsible committee on human experimentation and comply with the Declaration of Helsinki of the World Medical Association.
Data confidentialityThe authors declare that they followed their hospitals’ regulations regarding the publication of patient information and that written informed consent for voluntary participation was obtained for all patients.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the informed consent of the patients and/or subjects referred to in this article. The signed forms are in the possession of the corresponding author.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Cabrera-Ramírez JO, Puebla-Mora AG, González-Ojeda A, García-Martínez D, Cortés-Lares JA, Márquez-Valdés AR, et al. Plasma rico en plaquetas en el tratamiento del fotodaño cutáneo en las manos. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:746–751.