Many dermatologists are largely unfamiliar with arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). This is partly due to the low prevalence of these lesions and to the fact that they are generally managed by other specialists, in particular, interventional radiologists and pediatric, maxillofacial, and plastic surgeons. In this article, we review the recommended nomenclature for AVMs and look at their clinical manifestations and diagnosis, as well as the ideal type and time of treatment. AVMs should be managed from a multidisciplinary approach, and the dermatologist's primary goal should be to make a proper diagnosis and thereby avoid unnecessary treatments.
Muchos dermatólogos están muy poco familiarizados con las malformaciones arteriovenosas (MAV). Ello es debido, en parte, a la baja prevalencia de dichas lesiones y al hecho de que generalmente suelen ser tratadas por médicos de otras especialidades, en particular radiólogos intervencionistas de adultos y pediátricos, médicos maxilofaciales y cirujanos plásticos. En este artículo revisamos la nomenclatura recomendada para las MAV y nos centramos en sus manifestaciones clínicas y en su diagnóstico, así como en el tipo ideal y el tiempo de tratamiento. El manejo de las MAV debe hacerse desde una aproximación multidisciplinar, siendo el objetivo principal de los dermatólogos realizar un correcto diagnóstico para evitar, de este modo, tratamientos innecesarios.
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are high-flow vascular anomalies due to a failure of embryogenesis. They involve a direct communication between an artery and a vein with no intervening capillary bed.1
NomenclatureAVMs represent only 10% to 15% of vascular malformations, but we must ask ourselves whether the nomenclature is being used correctly.
Is the Nomenclature Used Correctly?In the past, terms such as salmon patch, strawberry hemangioma, port wine stain, and angioma were often used indistinctly in the nomenclature of vascular malformations and tumors, with no differentiation of the clinical, histopathological, and therapeutic aspects, despite their distinct etiologies and pathogenesis.
It was only in 1982 that Mulliken and Glowacki2 developed a classification by uniting the histological structure and appearance of the predominant endothelium with the biological behavior of the vascular anomalies.
That classification was redefined by Mulliken and Young in 1996 and adopted by the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies (ISSVA). In the new classification, vascular malformations were defined by their predominant component, separating the lesions into malformations and tumors. Malformations were subdivided into low and high flow. This system is today considered to be the reference classification.3
In the 1988 Hamburg classification, vascular malformations were defined according to the predominant vascular lesion (arterial, venous, arteriovenous shunt, or combined/mixed) and were divided into truncular or extratruncular depending on whether or not major axial vessels were involved.
However, in a recent review of articles cited in PubMed in 2009, Hassanein and Mulliken4 drew attention to the fact that the term hemangioma was used erroneously in 71.3% of cases, demonstrating that nomenclature is still a significant problem and that it can lead to confusion when prescribing treatment (such as propranolol, for example), which may not be indicated. Genetic tests and diagnostic investigations based on the molecular biology of the lesion, flow rate, and response to pharmacological treatments will be taken into account in the classification of AVMs in the near future.
EtiologyThe most widely accepted theory of the etiology and pathogenesis of AVMs postulates that these lesions are due to an increase in the number of vessels caused by a defect in vascular development, particularly angiogenesis.5 The most common site of AVMs is the brain and it is here that they have been most extensively studied. Although we do not know if findings from the study of cerebral AVMs can be extrapolated to extracranial AVMs, a number of angiogenic factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor, do appear to be implicated. It has been suggested that this is the cause of the dynamic vascular disturbance present in AVMs, producing an early alteration of angiogenesis, in contrast to what occurs in venous malformations; this is supported by the increase in the serum level of metalloproteinases detected in cases of AVM. The STAT proteins (signal transducers and activators of transcription) are also involved in the pathophysiology of angiogenesis in AVMs. A group of these proteins, specifically the STAT 3 proteins, is most active in the fetal period and may play a significant role in angiogenesis. Thorough knowledge of this process will help us to develop a more specific and appropriate treatment in each situation in the future.
A great deal of research still remains to be done on the genetic importance of these disorders and their triggering factors.
Do Triggering Factors Exist?Yes, triggering factors have been identified. The known factors include hormonal changes (adolescence, pregnancy), infections, trauma, and surgical procedures. Infection is the factor most frequently implicated in the acquired acral AVMs.
Despite these identified factors, many AVMs remain in a quiescent phase throughout their life while others progress rapidly; this has also been seen with malignant tumors, in which some tumors disseminate rapidly while others of similar origin and stage remain stable. These 2 situations can be explained by the Knudson concept,6 in which incomplete penetrance of the affected genes leads to marked variability in clinical expression.
For Buckmilller et al.,7 however, AVMs behave as true slow-growing tumors, based on the demonstrated presence of cell turnover, which does not exist in venous, capillary, or lymphatic malformations.
Have Advances Been Made in Genetics?The majority of AVMs are sporadic, with no genetic defects detected. Genetic alterations have been identified in some forms of familial AVM (Table 1),8 including hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome),9 attributed to a mutation of endoglin (ENG),10and the activin receptor-like kinase-1 gene (ALK-1),11,12 which affects transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) signaling. Mutations have also been detected in ACVRLK1 and SMADH4. In capillary malformation-AVM syndrome there is a mutation in the RASA1 gene13 on chromosome 5q 13–22, whose dysfunction produces an alteration of the Ras signaling pathway (due to an alteration of protein p120 RasGAP).
Familial Arteriovenous Malformations.
| Malformation | Clinical Presentation | Locus | Gene |
| HHT | Epistaxis | 9q 33-34 | ENG |
| Telangiectasias | 12q 11-14 | ACVRL1 | |
| AVM (lung, 30%-50%; liver, 40%; GI, 30%; brain, 5%-20%) | 5q | SMAD4 | |
| 7p14 | |||
| CM-AVM | 30% of AVMs, AVF, Parkes-Weber syndromeMultiple smaller lesions with a whitish halo | 5q 13-22 | RASA1 |
Abbreviations: AVF, arteriovenous fistula; CM-AVM: capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation; GI, gastrointestinal; HHT: hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.
There are many forms of syndromic AVM (Table 2), as is the case for patients with mutations of the PTEN gene (Cowden, Proteus, and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndromes), who also develop arteriovenous anomalies.14–16 Other syndromes associated with AVMs include Cobb syndrome (vertebral and spinal cord AVMs with metameric cutaneous capillary involvement), Parkes-Weber syndrome (generalized hypertrophy of a limb associated with an AVM and a capillary malformation [CM]), Bonnet-Dechaume-White syndrome (metameric cerebral AVM that extends from the craniofacial region to the orbit), and Stewart-Bluefarb syndrome17 (young patients with unilateral lower-limb lesions with an underlying AVM).
Syndromes Associated With Arteriovenous Malformations.
| Bonnet-Dechaume-White syndrome: Retinal or choroidal AVM |
| Wyburn-Mason syndrome: neurological symptoms and mental alterations |
| Brégeat syndrome: AVM of the conjunctiva, cheeks, nose, and mouth |
| Cobb's syndrome: AVM of the spinal cord and of the same metamere |
| Parkes-Weber syndrome: AVM of a limb |
| Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome |
| Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia |
| Cowden syndrome |
| Neurofibromatosis |
| Epithelioid hemangioma |
| Stewart-Bluefarb syndrome |
| Diffuse dermal angiomatosis |
| Lhermitte-Duclos syndrome |
| Acroangiodermatitis of Mali |
| Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia |
| Reactive angioendotheliomatosis |
| Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum without Fabry disease |
| Capillary malformations: changes in the RASA1 gene |
| Multiple cutaneous follicular hamartoma |
| Multiple glomus tumors |
| Facial hemangiomas |
| Aplasia cutis congenita |
| Sebaceous nevus syndrome |
| Posterior fossa malformations–hemangiomas–arterial anomalies–cardiac defects–eye abnormalities–sternal cleft and supraumbilical raphe (PHACE) syndrome |
The clinical presentation of AVMs can be varied (Table 3).18 In their early stages they are difficult to differentiate from other conditions such as port wine stain.
Clinical Presentation.
| Red/pink macule |
| Bluish/violaceous mass |
| Several small lesions, often with a whitish halo (in CM-AVM) |
| Dilated veins (sometimes with a thrill) or skin vibration |
| Pulsatile lesions |
| Nodular lesion arising on a macule |
| Diffuse hypertrophy with increase in the size of the affected limb (Parkes-Weber syndrome) |
| Skin changes of Kaposi pseudosarcoma (Stewart-Bluefarb syndrome) |
| Lytic bone lesions |
| Heart failure with multiple AVFs |
We should not therefore be surprised by the number of errors in the past, when noninvoluting congenital hemangiomas were erroneously diagnosed as AVMs.
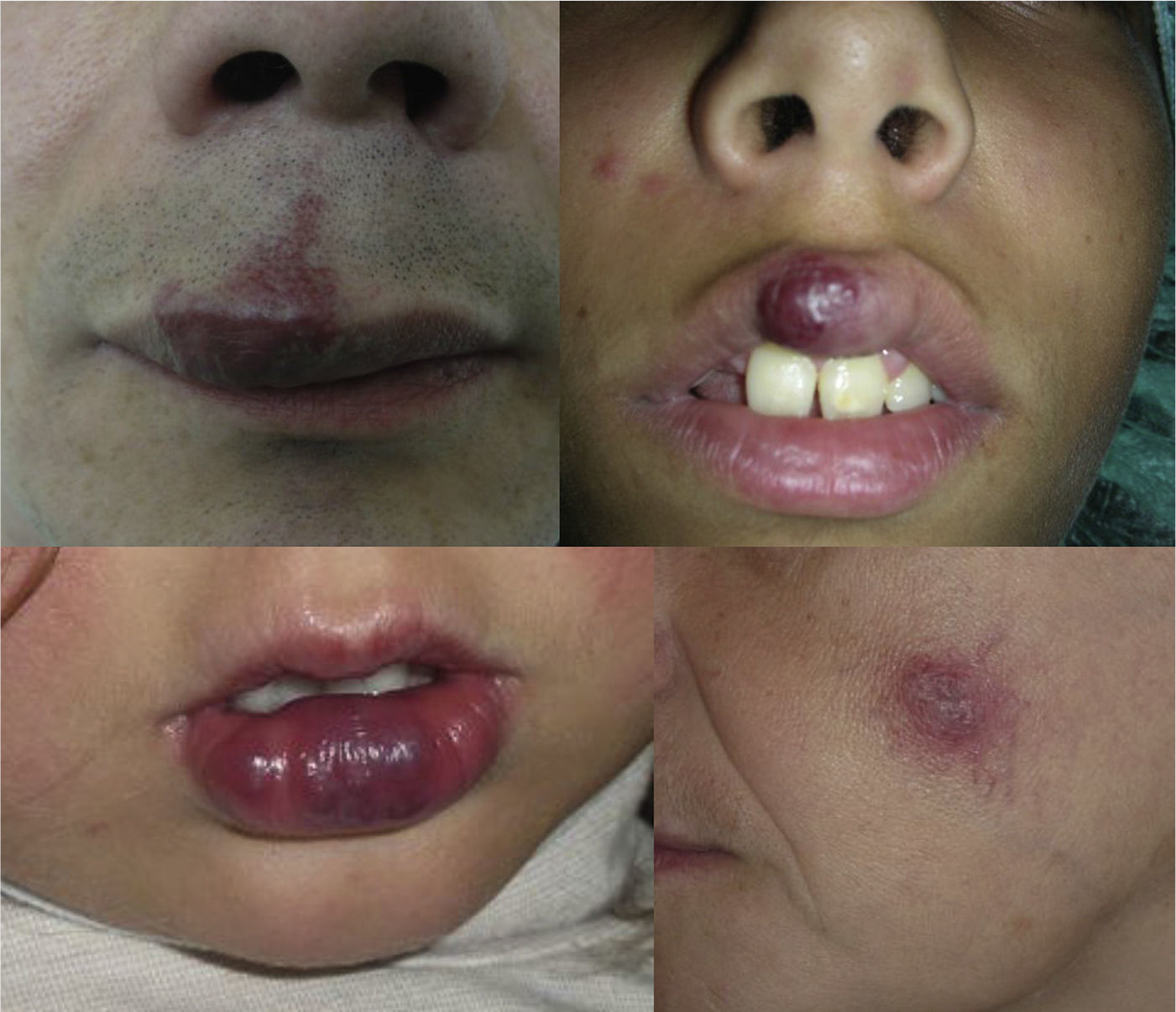
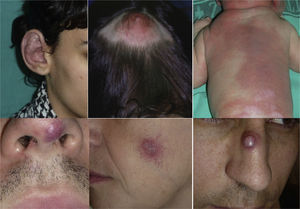
AVMs are lesions present at birth and visible at that moment in 60% of cases; 20% to 30% become evident during adolescence and 10% to 20% in adult life. They are most commonly situated on the head and neck (Fig. 1).
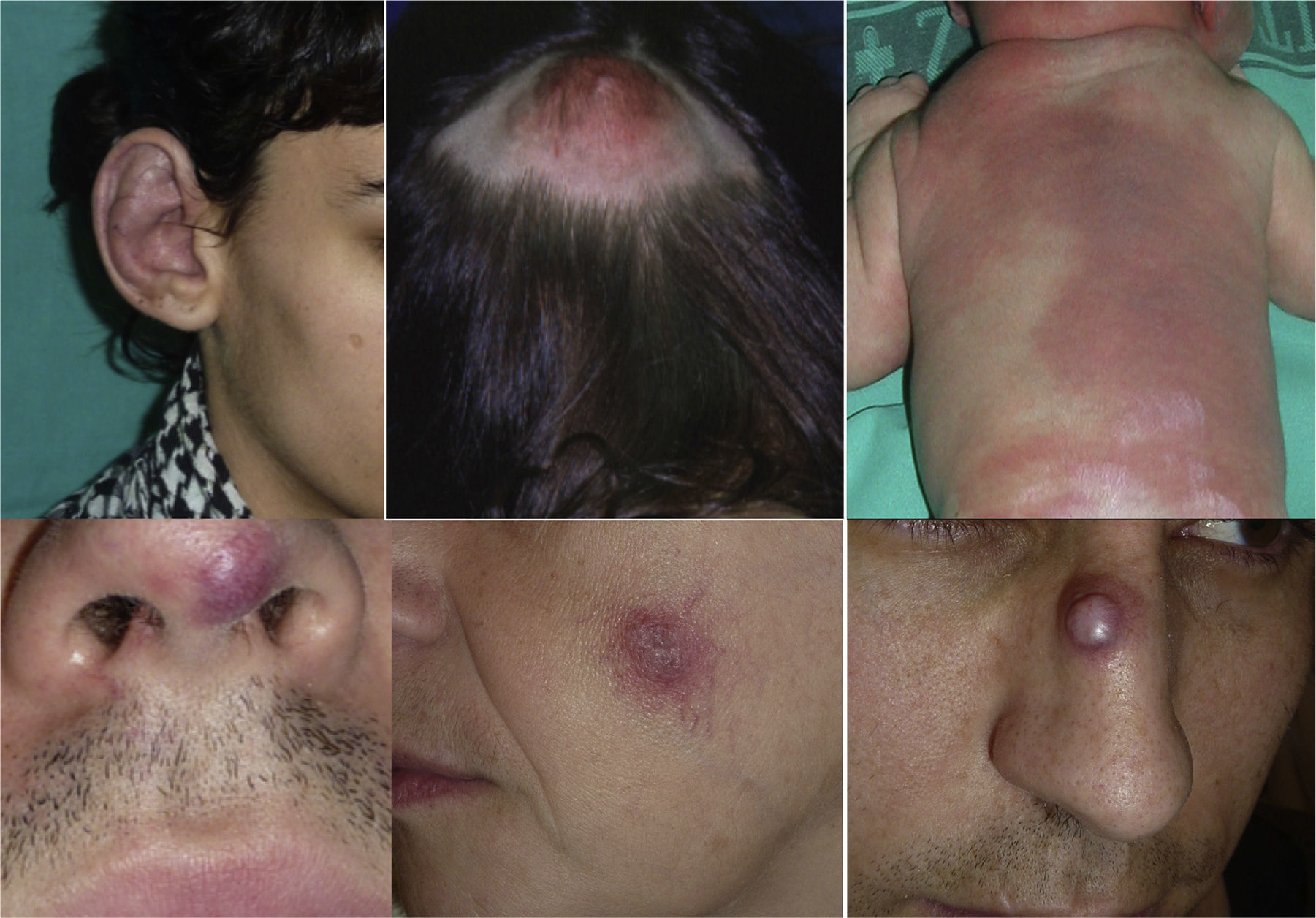
AVMs will not disappear as hemangiomas do, but instead they grow slowly or start to grow after a trigger (Fig. 2).
When associated with other malformations, AVMs can affect the underlying tissue or cause bone hypertrophy.19
They are usually considered to be pulsatile lesions.
Are All Lesions Pulsatile?No, not all AVMs are pulsatile. A thrill is highly characteristic but is not present in all cases, such as very early lesions, lesions with only a minimal shunt and those in which the arterial and venous hypertrophy secondary to the communication between the two systems is greater on the venous side.
Do Lesions Behave Differently According to Whether They Are Diagnosed Before 20 Years of Age or After 40 Years of Age?It is not known why some AVMs remain asymptomatic until adult life while others produce symptoms during early adolescence.20
Children who present an exacerbation of an AVM at an early age will have a poorer prognosis, with a greater number of surgical procedures, greater morbidity, and more sequelae compared with adult patients in whom changes develop during their fifth decade of life.
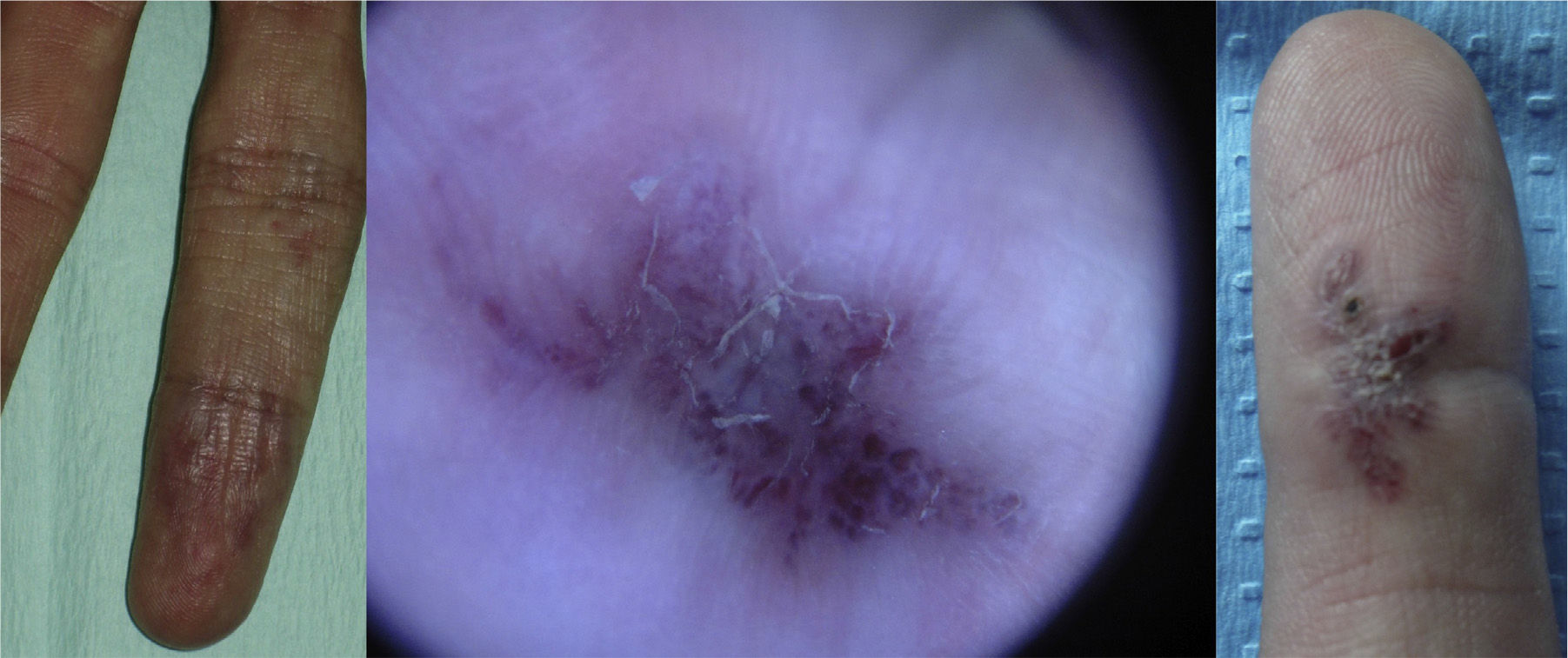
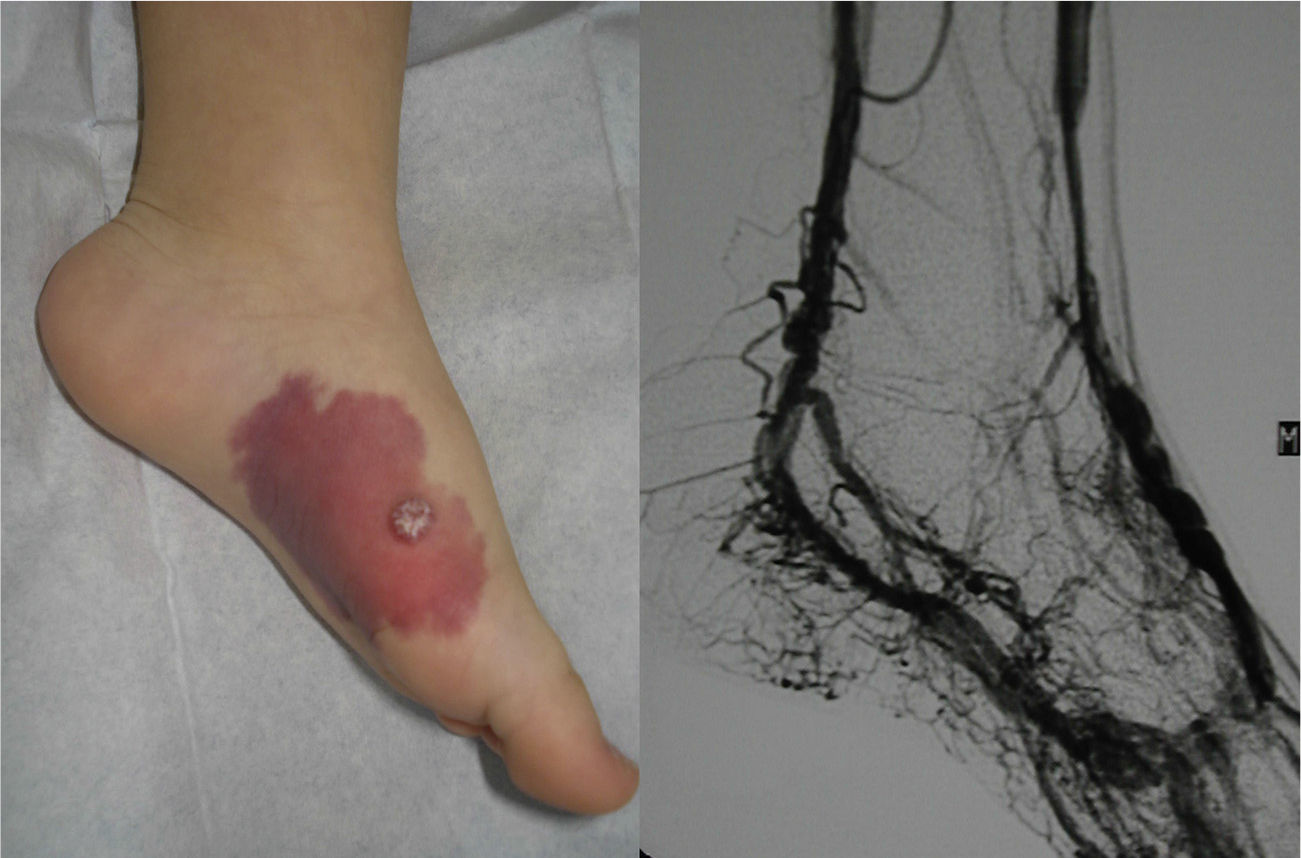
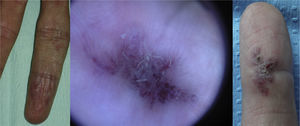
Lesions diagnosed after 40 years of age may sometimes be acquired, particularly after trauma, as may occur in acral regions (Fig. 3).21 These appear to be reactive lesions and they are not influenced by the hormonal changes that affect lesions diagnosed early in life.
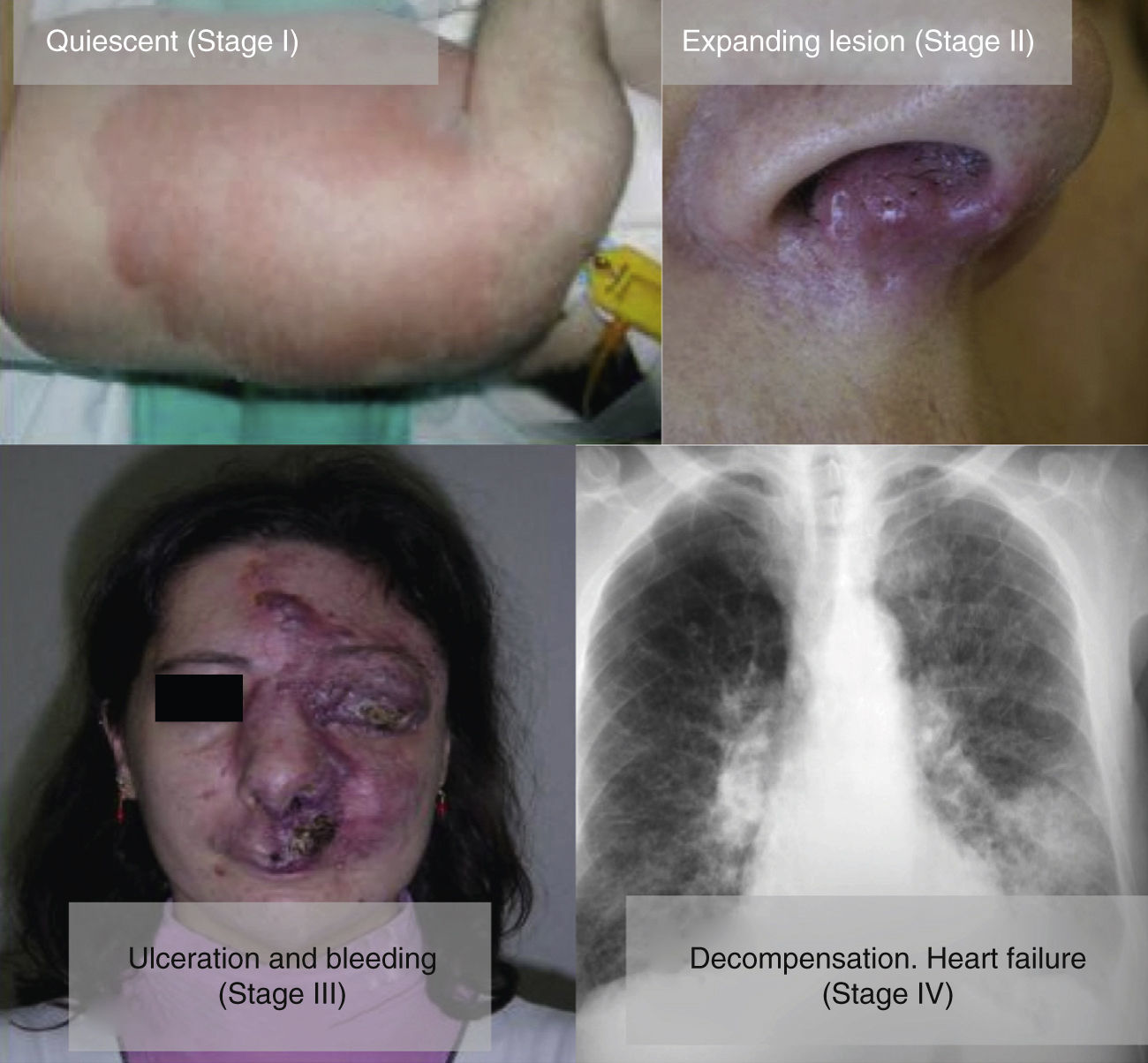
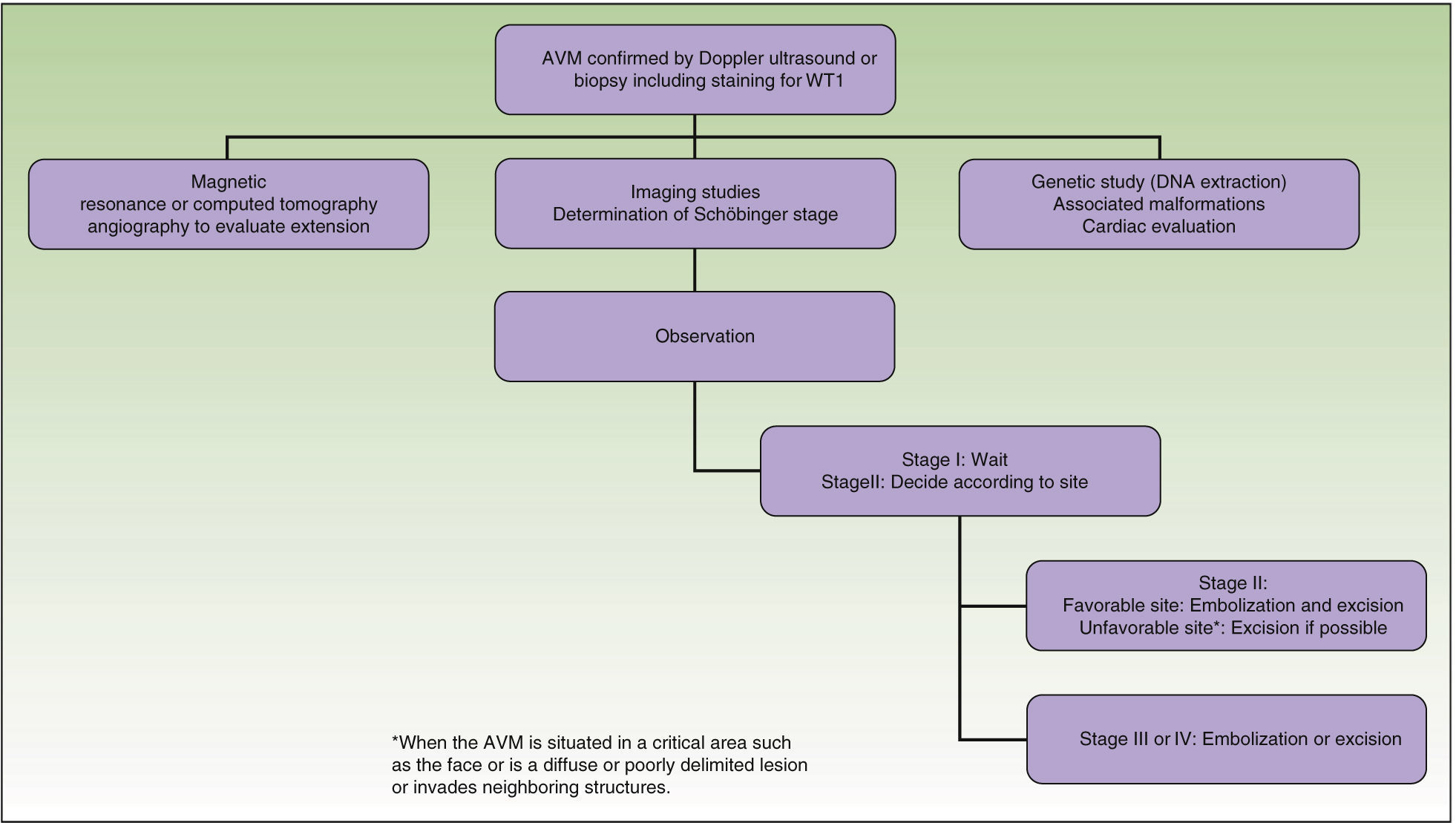
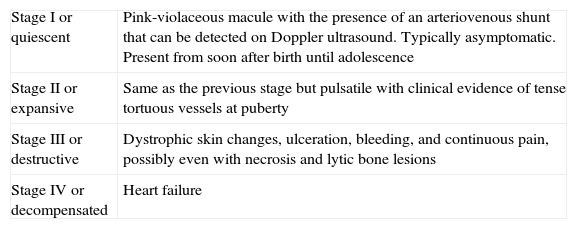
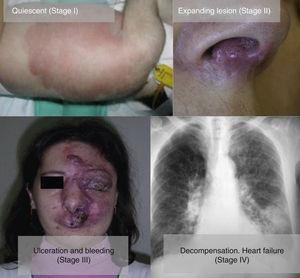
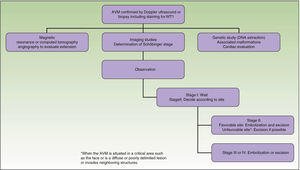
From a practical point of view, the clinical stage of these malformations is defined according to the Schöbinger classification (Fig. 4 and Table 4).
Schöbinger Stages.
| Stage I or quiescent | Pink-violaceous macule with the presence of an arteriovenous shunt that can be detected on Doppler ultrasound. Typically asymptomatic. Present from soon after birth until adolescence |
| Stage II or expansive | Same as the previous stage but pulsatile with clinical evidence of tense tortuous vessels at puberty |
| Stage III or destructive | Dystrophic skin changes, ulceration, bleeding, and continuous pain, possibly even with necrosis and lytic bone lesions |
| Stage IV or decompensated | Heart failure |
In patients under 20 years of age, the lesions are vascular anomalies (the majority wrongly diagnosed as hemangiomas) that start to grow and bleed, particularly at puberty or with hormonal changes.
Patients over 40 years of age have been unaware of any previous lesion and they give a history of recent onset. Patients typically report the appearance of lesions after trauma.
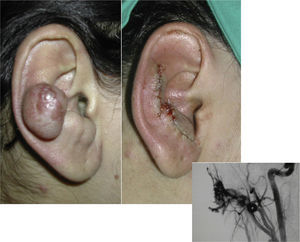
When the pinna of the ear is affected, an AVM can also usually be found on the scalp and on the neck.
Progression of the lesions is evident as an increase in the communication, giving rise to arterial steal and venous hypertension, with a reduction in tissue perfusion. The manifestations of this tissue ischemia include pain, ulceration, and bleeding.
BleedingBleeding occurs in 3% to 4% per year in patients between 10 and 55 years of age, and can lead to death in 1% of cases.
When a patient has bled, the risk of rebleed in the first year is approximately 20% if no treatment is performed.
However, it is rare for a high-flow AVM/AV fistula present since birth to be a threat to the life of a child due to cardiac overload (with the exception of intracranial lesions).
Should an AVM Be Considered Whenever a Nodule Develops on a Capillary Malformation?If a pyogenic granuloma appears over what is assumed to be a capillary malformation, we should consider the possible presence of an AVM.
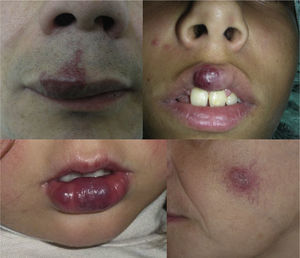
This issue has been discussed in a number of recent articles. One of them involved 31 patients with capillary malformations on which nodules appeared.22 Histological analysis of those lesions revealed that 45.1% were pyogenic granulomas, 32.3% were AVMs (Fig. 5), the 2 types of lesion (pyogenic granuloma and AVM) coexisted in 16%, and cavernous-like vascular ectasia was present in 6.5%. These lesions appeared most commonly in the territory innervated by the second branch of the trigeminal nerve.
In some studies it has been postulated that the characteristic pathogenesis and clinical course of pyogenic granulomas on capillary malformations are observed because the lesions are actually AVMs.23 These nodules are typically solitary, but there are reports of multiple grouped pyogenic granulomas in which histology and Doppler ultrasound suggest the presence of an underlying AVM.24
DiagnosisThe medical history and physical examination are diagnostic in 90% of cases. Greatest diagnostic difficulty occurs in the first months of life when investigating a congenital macule of pink color.
Is it a CM or an AVM? (Table 5)In neonates, hemangiomas must be included in the differential diagnosis, particularly in very early phases of the lesion.25
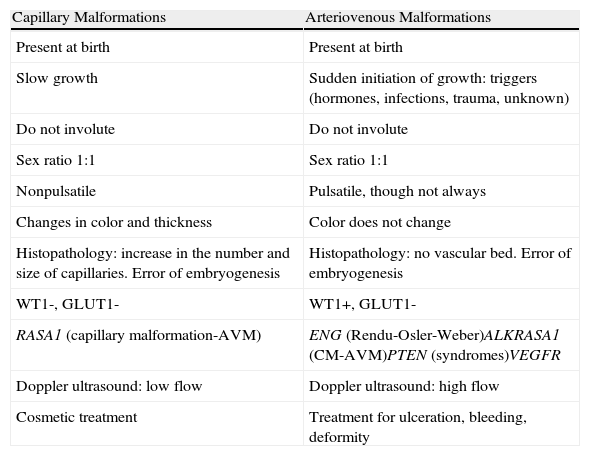
Differences Between Capillary Malformations and Arteriovenous Malformations.
| Capillary Malformations | Arteriovenous Malformations |
| Present at birth | Present at birth |
| Slow growth | Sudden initiation of growth: triggers (hormones, infections, trauma, unknown) |
| Do not involute | Do not involute |
| Sex ratio 1:1 | Sex ratio 1:1 |
| Nonpulsatile | Pulsatile, though not always |
| Changes in color and thickness | Color does not change |
| Histopathology: increase in the number and size of capillaries. Error of embryogenesis | Histopathology: no vascular bed. Error of embryogenesis |
| WT1-, GLUT1- | WT1+, GLUT1- |
| RASA1 (capillary malformation-AVM) | ENG (Rendu-Osler-Weber)ALKRASA1 (CM-AVM)PTEN (syndromes)VEGFR |
| Doppler ultrasound: low flow | Doppler ultrasound: high flow |
| Cosmetic treatment | Treatment for ulceration, bleeding, deformity |
Abbreviations: AVM, arteriovenous malformation; CM, capillary malformation.
The clinical manifestations and even the usual diagnostic tests cannot differentiate between the 2 entities at such an early age; it is the clinical course of the lesions that gives us the definitive diagnosis in the majority of cases. This difficulty should soon be resolved thanks to the latest advances in immunohistochemistry26 with the Wilms Tumor 1 (WT1) marker.27,28 WT1 is positive in vascular neoplasms and in AVMs and negative in venous and capillary malformations. As a confounding factor, 30% of AVMs associated with capillary malformations (CM-AVMs) present a mutation in RASA1,29–31 and positivity for this mutation will not therefore differentiate the lesions.
Diagnostic tests (Fig. 6)Are Diagnostic Tests Necessary?32Firmness on palpation, rapid filling after emptying the lesion by pressure, and a palpable pulse (if present) will make us suspect the diagnosis.
In those cases in which the diagnosis is unclear in the neonatal period, the key to diagnosis is the clinical course of the lesion: hemangiomas increase rapidly in size whereas AVMs do not show such early changes.33
What Diagnostic Tests Should Be Requested and When?The request for diagnostic tests depends on the age of the patient, the area affected, and the Schöbinger stage.34
Doppler ultrasound is used for the initial investigation as it is a noninvasive test that differentiates easily between AVMs and venous and lymphatic malformations.35 In addition to anatomical information, this study provides hemodynamic data by measuring vascular flow. In AVMs, Doppler ultrasound reveals the arterial and venous pulse waves (large feeding artery and equally large and pulsatile draining veins) with abundant turbulent flow at moderate-to-high speed. Doppler ultrasound will better characterize a small vascular lesion, and will provide information that will help us to exclude lymphatic, venous, and mixed lesions.
In cases of small atypical lesions with low flow in newborn patients, it is essential for the radiologist to have experience in Doppler ultrasound studies and the use of transducers of up to 20MHz.
AVMs, like venous malformations, are not visible on x-rays, but they do have effects on adjacent bone structures (lytic lesions, asymmetric hypertrophy or atrophy, etc.).36
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) weighted in T1 and T2 continues to be the main diagnostic test for the study of vascular malformations.37 This investigation is performed after confirming the diagnosis on Doppler ultrasound and its advantages include an absence of ionizing radiation, images in various planes, and hemodynamic information; it can thus also be used as a follow-up study. But MRI is often insufficient to identify the afferent and efferent vessels, nests, and flows. This requires computed tomography (CT) angiography.
CT is a technique that usually requires contrast (with the possible side effects that this entails) and often the patient must be sedated, particularly children. This study also exposes the patient to ionizing radiation.
CT angiography is of great help prior to surgery, as it provides information on the underlying bony structures and on the vascular system. Multisection CT angiography continues to be used when surgery is going to involve a critical area, substituting arteriography, which is only indicated if embolization is to be performed.
Arteriography is thus a therapeutic procedure (it is performed whenever embolization is to be done, but not as a diagnostic test). When CT angiography and MRI angiography do not provide the information necessary for embolization or surgery, arteriography must be performed. However, this does not usually occur if the interventional radiologist is experienced.
Less invasive tests that have been developed recently to follow up vascular malformations include transarterial lung perfusion scintigraphy (TLPS) and whole body blood pool scintigraphy (WBBPS).
TLPS has the sole function of determining the extent of arteriovenous communication in an AVM in a limb, and is used in preference to angiography in such cases. However, this technique is not available in all hospitals.
WBBPS is very useful to follow-up the progression of deep vascular malformations, particularly when TLPS is not available.
Biopsy is rarely necessary as 99% of AVMs can be diagnosed on the basis of clinical manifestations and Doppler ultrasound studies. It is only performed when there is doubt about differentiation from other tumors or lymphomas, with staining for WT1 in the case of CMs. In the early stages, given the similarities between CMs and AVMs, histopathological characteristics have been described to help differentiate the 2 lesions.25 However, biopsy should be avoided as far as possible due to the risk of bleeding and the possibility of triggering growth of an AVM. Histological information therefore comes from the study of surgical specimens.
Finally, new tests, such as artery spin labeling (ASL) magnetic resonance, performed with a 3 tesla device, provides flow data and will probably soon become a standard for the study and differentiation of subtypes.
TreatmentTreatment requires a multidisciplinary approach.38
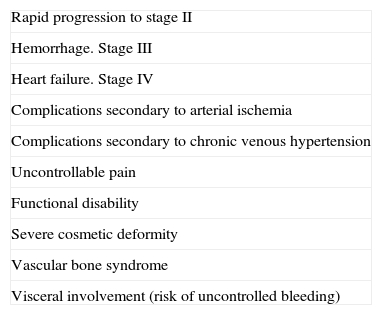
Treatment or no Treatment, and When to TreatThis will depend on the Schöbinger stage, size, and site of the AVM, the age of the patient, and whether or not the lesion shows progression (Tables 5 and 6).39
Indications for the Initial Treatment Regimen.
| Rapid progression to stage II |
| Hemorrhage. Stage III |
| Heart failure. Stage IV |
| Complications secondary to arterial ischemia |
| Complications secondary to chronic venous hypertension |
| Uncontrollable pain |
| Functional disability |
| Severe cosmetic deformity |
| Vascular bone syndrome |
| Visceral involvement (risk of uncontrolled bleeding) |
Protection of the area, avoiding injury.
If the patient is taking oral contraceptives, these should only contain progesterone due to the proangiogenic effect of the estrogens.41 However, although pregnancy will theoretically favor AVM expansion, no changes have been reported in stageI lesions.
The compression of lesions in the legs can improve the pain, but may also worsen an AVM because of the associated hypoxia.
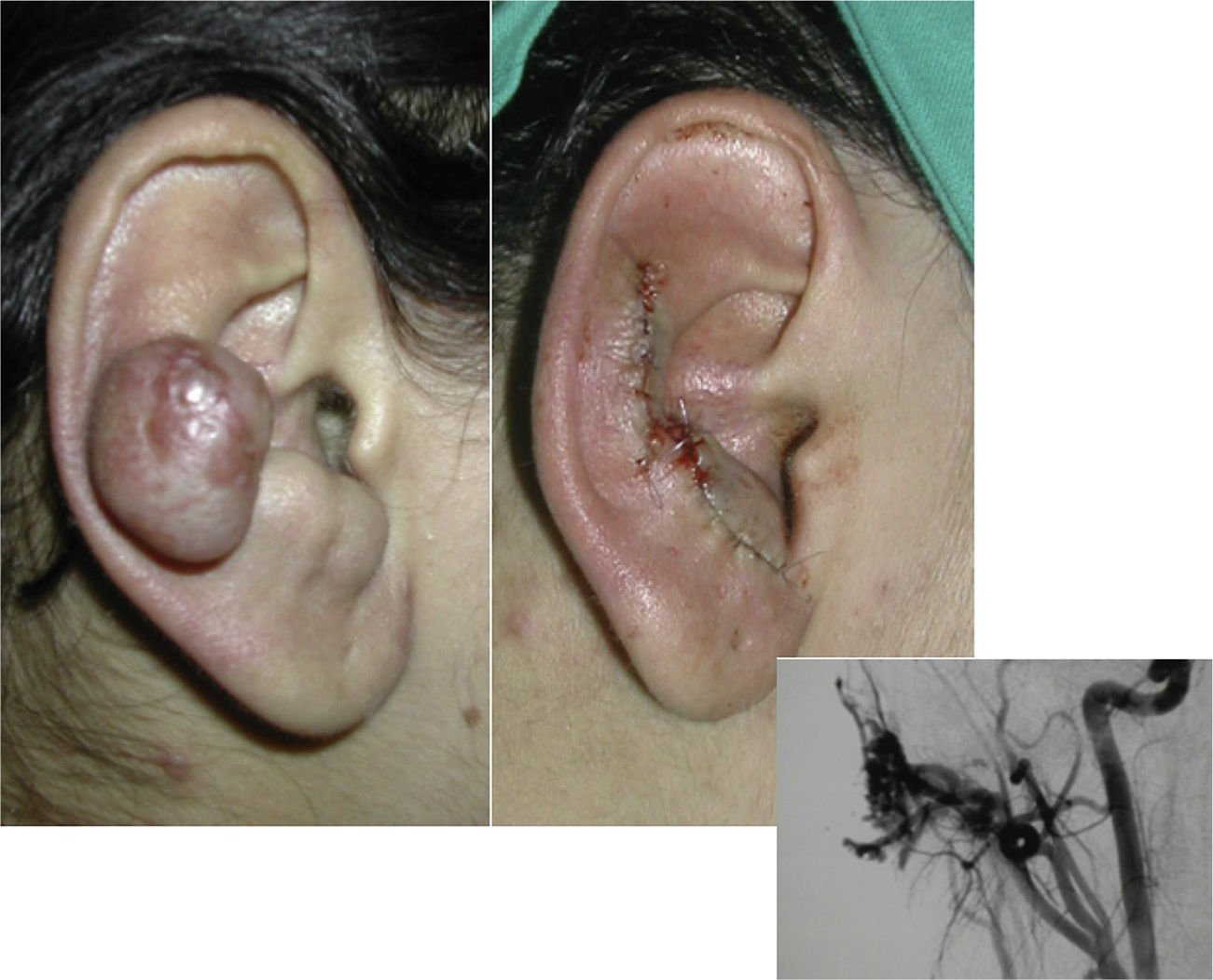
SurgeryThe definitive treatment is surgical, which can be total or subtotal depending on the site and size of the lesion; cure can only be achieved by complete surgical excision (Fig. 7).
Surgeons divide the extracranial sites into 4 areas: head and neck, visceral, upper limbs, and lower limbs. Each area has its specific characteristics that, when considering a surgical approach, will help us evaluate the risks and benefits of a proactive approach.
Subtotal surgical excision, though not curative, can sometimes improve quality of life and delay progression. Subtotal surgical excision must guarantee the removal of at least 70% of the lesion as it could otherwise even be counterproductive.
The most difficult aspect of the management of AVMs is the timing of surgery.
When an AVM is situated in a noncritical area (for example, on an arm, a leg,42 or on the trunk), surgical excision can be performed at any time and is recommended to prevent possible deformities and other problems.43
Surgical excision with free margins is extremely difficult when the AVM is situated in a critical area, such as the face, or in the case of diffuse, poorly delimited lesions or ones that invade neighboring structures. In these cases, the best option, when feasible, is observation; surgical excision would probably be incomplete and there is a risk of recurrence or exacerbation. Should surgery be performed, the primary objectives are symptom relief, the preservation of vital functions, and improvement of deformities. Thanks to the advances in endovascular techniques and the materials now available, surgery can be less aggressive. Furthermore, it should not be forgotten that when an intervention is performed late, it will be more complex and will be less likely to be curative.
Differentiation between normal and pathological vessels can be complicated during surgery and this will make it difficult to determine the limits of the lesion in order to achieve correct surgical resection. In AVMs there is hyperplasia of anomalous vessels around the malformation due to the increased venous return, although the vessels have normal characteristics.
Three of every 4 patients require surgery during childhood or adolescence, and one of every 4 patients during adult life.
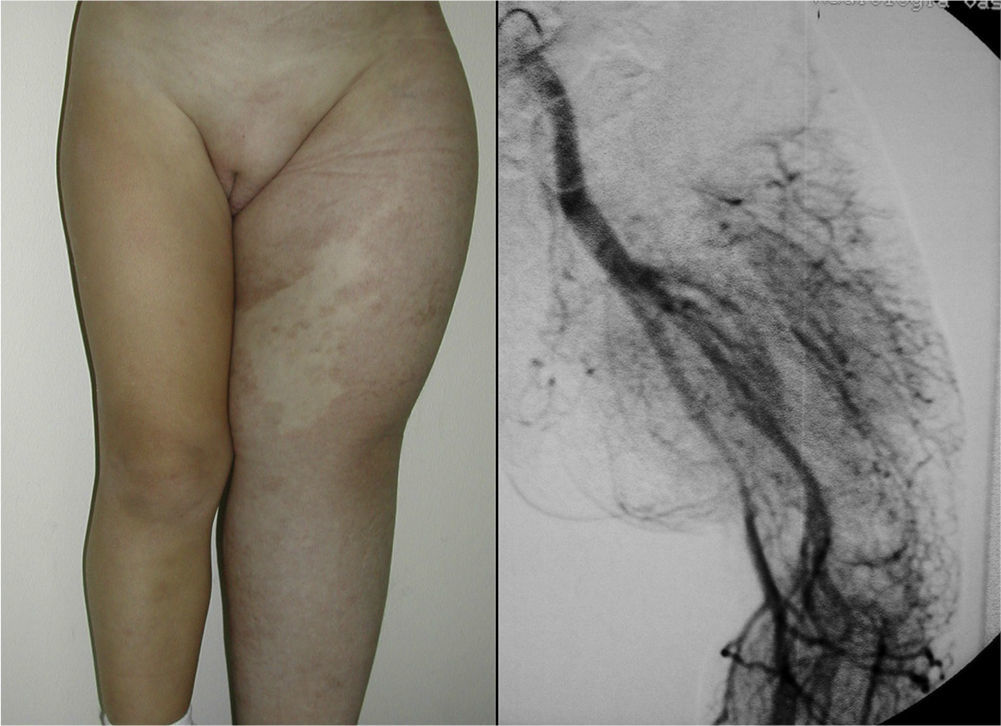
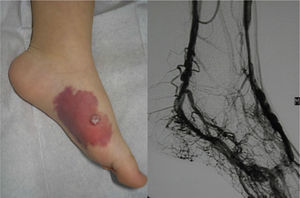
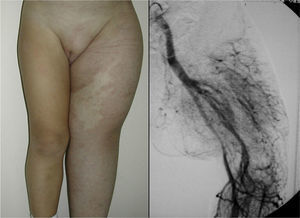
In Parkes-Weber syndrome (Fig. 8), surgery is useful to improve quality of life, for example by correcting dysmetria or treating ischemic ulcers.
Embolization is performed 24 to 72hours prior to surgery in order to reduce blood loss. However, some interventional radiologists perform percutaneous transarterial and transvenous embolization simultaneously, as the only treatment, achieving results similar to surgery, particularly in complex sites such as the head and neck44; however, this usually requires several interventions. In contrast, embolization via a single access route in the hands of an inexperienced radiologist can trigger worsening of the lesion. The embolization materials used will depend on the radiologist's preference and whether the intervention is a presurgical embolization, in which temporary occlusive materials can be used, or definitive embolization, in which long-lasting materials are indicated. At the present time, the Onyx Liquid Embolic System, alcohol, cyanoacrylate, and platinum coils are used.45–48 There is general consensus that embolization must be very distal, within the nest itself if possible, and it is also now considered essential to perform simultaneous percutaneous sclerosis of the drainage veins to reduce flow and potentiate the effect of the arterial embolization agent.
The most common complication is ulceration, particularly in superficial lesions.
As patients spend a night in hospital, swelling of the treated area can be detected and intravenous corticosteroids administered for 24hours, followed by a week of oral corticosteroid therapy.
The large majority of recurrences (98%) occur within the first 5 years after embolization. After this period, there is good long-term control.
Other TreatmentsLaser treatment of lesions in the skin is, in principle, contraindicated, although experience is limited and the neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser49 may possibly be useful in early acral (stage I) AVMs.50 The pulsed dye laser has been used in combination with photodynamic therapy,51 but results in various vascular alterations,52 including capillary malformations,53–55 have been inconsistent. There is no evidence for the success of treatment with pulsed dye laser in AVMs.
At the present time, venous malformations are the lesions that benefit most from laser treatment with the intravascular diode laser.56 In coming years, this treatment is likely to be broadened to include intra-arterial therapy.
Angiogenesis can explain the arteriovenous expansion,5 and elevated levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin 2, as well as other proangiogenic factors, have been detected in AVMs, making antiangiogenic therapy a new therapeutic target.57 Promising results have also been obtained with metalloproteinase inhibitors; the metalloproteinases are proteolytic enzymes that break down the extracellular matrix.58
There are other treatments in experimental phases,38 in addition to the aforementioned antiangiogenic therapies,59 and although clinical investigations are ongoing with several of them (sirolimus,60–62 marimastat, doxycycline,63 and thalidomide64) none is as yet officially included in treatment protocols or formally supported by the ISSVA. Sirolimus is contraindicated in AVMs over which the skin has broken down as it exacerbates the ulceration. In recent publications, recognized experts have stated that pharmacological treatment for AVMs is currently nonexistent.65
PrognosisMany factors can affect the clinical course of AVMs, including age at diagnosis and the management approach used. However, it is still not fully understood why some lesions remain quiescent while others grow, and the prognosis is therefore uncertain.
In the review by Lui et al.,43it was found that children with stage I AVMs had a 43.8% risk of progression before adolescence and an 82.6% risk of progression before adulthood. Gender, site of the lesion, and pregnancy were not found to affect the clinical course. With regard to treatment, poorer results were achieved by embolization without surgery.
Arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) secondary to trauma warrant special mention, as they also have an unpredictable course and their response to treatment differs from that of primary or congenital AVFs.66 Melliere et al.67 reported that the mean time between the trauma causing an AVF and diagnosis was approximately 20 years. High-flow AVFs could be associated with cardiac complications and those with intermediate flow could be associated with proximal arterial dilatation and be discovered later, with or without concomitant cardiac complications.
ConclusionThe AVMs are not well understood and are often incorrectly diagnosed. A multidisciplinary therapeutic approach is necessary, with surgeons and radiologists; the dermatologist must provide an early diagnostic suspicion.
The diagnosis is mainly clinical and is confirmed by Doppler ultrasound when doubt exists. As we have explained, difficulty arises when the lesion presents as a pink macule in the first months of life; at the present time there are no simple diagnostic tests that differentiate between one entity and another, and biopsy becomes necessary.
It is not always easy to choose the most appropriate treatment. Surgery is the treatment of choice for quiescent AVMs in areas amenable to surgical excision without significant loss of healthy tissue. There is doubt about whether or not to operate on AVMs localized on the head and neck before puberty, as this surgery is more destructive. However, if a surgically accessible AVM starts to grow, excision should be considered, with or without prior embolization. New medical treatments, such as inhibitors of the mTOR pathway, are being studied for advanced stages.62
As AVMs of the central nervous system (CNS) are 20 times more common than AVMs of the skin, they have been studied in much greater detail. However, conclusions drawn from AVMs of the CNS cannot be extrapolated to cutaneous AVMs, as we do not know if they behave in the same way. Nor do we know if the association between cutaneous AVMs and certain syndromes carries a poorer prognosis.
After an extensive review of the literature, and with the numerous questions that remain unanswered, we should expect more data to become available on this condition in the near future and for this to be followed by new treatment alternatives.
Ethical DisclosuresProtection of human and animal subjects.The authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this investigation.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they followed their hospital's regulations regarding the publication of patient information and that written informed consent for voluntary participation was obtained for all patients.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no private patient data are disclosed in this article.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: de Miguel R, López-Gutierrez J, Boixeda P. Malformaciones arteriovenosas: un reto diagnóstico y terapéutico. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105:347–358.