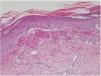
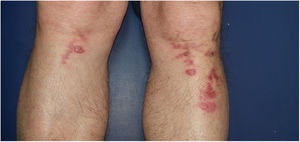
Erythema ab igne is recognized by a reticulated pattern of erythema and hyperpigmentation in an area exposed to heat. Initially the lesions are transient, easily blanching macules in a circumscribed area that reflects the size of the heat source. Later, hyperpigmentation becomes fixed; atrophy, hyperkeratosis, and telangiectasia may develop. Although the pathophysiology of these lesions is poorly understood, their appearance suggests an effect of infrared radiation on the venous plexus of the dermis (Fig. 1).
When the application of heat to alleviate pain is responsible for the lesions, it is important to rule out underlying conditions of which pain might be the first symptom.1,2 Examples are metastasis to the lumbar or sacral spine and musculoskeletal or visceral disease.
Fewer cases of erythema ab igne in recent years have been caused by space heaters, fireplaces, or similar sources of heat by combustion. However, cases are now appearing related to new electrical and electronic devices that emit heat directly or indirectly,3 including laptops,4 blankets, heaters, and heated seats.5 The type of patient who presents with these skin lesions has also changed. Whereas erythema ab igne was originally seen most often in older individuals, it is now relatively common in young or middle-aged persons. Occupations that expose the skin to high temperatures also cause these lesions. When blisters form over erythema ab igne, diabetes mellitus is often present.6
The diagnosis is eminently clinical, requiring careful examination of the skin and a complete medical history in search of the heat source causing the lesions. If both the history and examination are thorough, erythema ab igne is easily recognized. However, patients do not always know the cause, or the lesions may be in atypical locations. In such cases, certain histologic findings in skin biopsies can help orient the diagnosis.7
Differential diagnosis should include livedo reticularis and livedo racemosa, with all their possible causes; dermatomyositis, poikiloderma; livedoid vasculitis; and very rarely, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.8
The literature offers case reports related to different causes or heat sources, but no large patient series bringing together the various causes of erythema ab igne have been published. Patient series are even less likely to describe histologic features. We present a series of 5 cases and analyze common characteristics.
Case DescriptionsWe list the characteristics of 5 patients with clinical and histologic findings consistent with a diagnosis of erythema ab igne (Table 1).
Characteristics of the 5 Patients in the Series.
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 67 | 30 | 49 | 62 | 39 |
| Sex | Man | Woman | Woman | Man | Woman |
| Relevant history | None | None, except oral contraceptives since the age of 23 y | Smoker; hypothyroidism; and alcoholic fatty liver disease, with abnormal liver enzymes since 2018 | Type 1 DM (20 y) | None, except COVID-19, 2 mo earlier |
| Time since presentation | 2 mo | Several months | Years | 4 d | 5 d |
| Acknowledged cause | No | Yes (heater) | Unknown (history taking not possible) | No | No |
| Site | Front and inside of the distal third of legs and ankles | Lower part of the right thigh and lower leg, external side of the left thigh and lower leg | Both ankles and pretibial skin | Upper third of the lower portion of the legs (Fig. 1) | Backs of both legs |
| Additional tests | None required | No abnormal findings in general blood parameters, including coagulation factor; ANA− and ENA− | Serology, imaging, echocardiogram, and blood tests all normal for parameters that would explain the symptoms | None required | Unremarkable serology and blood work-up, including markers for autoimmunity and thrombophilia |
Abbreviations: ANA, antinuclear antibody; DM, diabetes mellitus; ENA, extractable nuclear antigen.
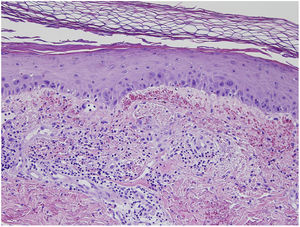
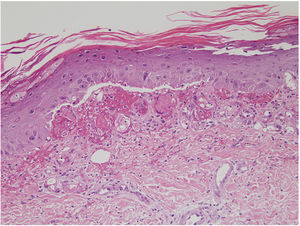
Mild nuclear cellular atypia (discrete enlargement), with edema and an abundance of extravasated erythrocytes were found in the epidermis (Figs. 2 and 3). Hemosiderin was also found in the papillary dermis or occasionally in the stratum corneum. Hyperkeratosis, epidermal atrophy, and apoptotic bodies were other occasional findings, and solar elastosis was present in older patients. We never observed vasculitis in this series, although endothelial swelling was sometimes found.
In the absence of a complete medical history, or if the patient does not acknowledge exposure to heat, it is very difficult to come to a diagnosis of erythema ab igne. A diagnosis will require additional tests to rule out other diagnoses or skin biopsy findings like those mentioned above. Most of the patients in this series did not acknowledge the cause of the lesions during the first visit.
Treatment invariably involves eliminating the cause by avoiding exposing the skin to direct heat at the level the patient had been accustomed to. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, an after effect in most cases, is difficult to treat but may improve with time. The atypia of erythema ab igne, which can resemble the atypia of actinic keratosis, may respond to topical application of retinoids, 5-fluorouracil, or different modalities of laser therapy. Squamous cell carcinoma, marginal B-cell lymphoma, or Merkel cell carcinoma in the affected area has been reported to develop over the long term.4,6 None of the patients in this series presented complications during the time we followed them.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.