Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), together with Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), forms part of a spectrum of medical emergencies characterized by peeling of the epidermis and risk of hemodynamic instability and sepsis.1 Mortality is approximately 35% and, while survival is greater in children, it has been linked to higher rates of long-term complications.2 In most cases, TEN is secondary to an idiosyncratic drug reaction, most commonly triggered by antiepileptic drugs, antibiotics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. No standardized guidelines exist and traditionally, both systemic corticosteroid therapy and intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) have been used, with questionable results. New therapeutic options, including classic immunosuppressants such as cyclosporin and anti-TNF-α drugs, have recently been tried. Considering the scarcity of current cases in the literature, we believe that the report of a new case of pediatric TEN treated satisfactorily with cyclosporin is of interest.
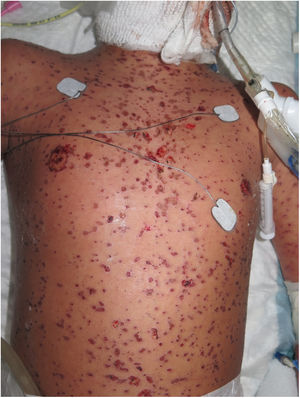
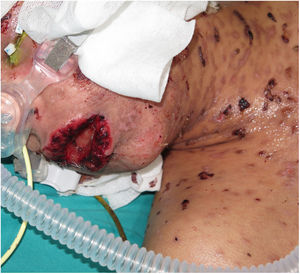
Three weeks after beginning treatment, a 10-year-old boy with a history of multifocal epilepsy undergoing treatment with lamotrigine, developed a fever of 39 °C, blisters on the face, torso, and extremities, and areas of denuded skin with positive Nikolsky sign, which, in total, covered approximately 40% of the total body surface and was associated with major involvement of the ocular, oral, and genital mucosa (Figs. 1 and 2). In light of suspected TEN, the lamotrigine was suspended immediately and treatment with systemic corticosteroids was instated (1-2 mg/kg/d). Skin symptoms continued to progress, however, with the addition of hemodynamic instability requiring vasoactive and respiratory support. In the pediatric intensive care department of our hospital, treatment with intravenous cyclosporin was instated, at a dosage of 4 mg/kg/d. On day 4 of treatment progress of the disease began to stop, with no new active lesions or denuded areas. When partial re-epithelization of all the lesions had taken place, 6 days later (day 10 of treatment), the dose of cyclosporin was gradually reduced with no new signs of activity of the disease.
In the treatment of patients with TEN, priority measures are based on suspension of any suspected drugs and ensuring fluid, electrolyte, nutritional and respiratory support. Due to the lack of randomized studies, insufficient evidence exists on the efficacy of the different treatments in the pediatric population suffering from TEN.3 The literature available to date is scarce and published studies focus on the debate surrounding the use of corticosteroids and IVIg, most of them in the adult population. Several authors argue that survival and speed of re-epithelization are increased in patients treated with corticosteroids or IVIg compared to those who receive supportive treatment alone. These results, however, contrast with other studies, in which increased morbidity has been shown with the use of corticosteroids and IVIg. Several studies have recently been published on SJS/TEN in adults who were treated satisfactorily with cyclosporin (3-5 mg/kg/d, por un minimum of 14 days); the studies show that the results appear to be superior to the use of IVIg in terms of survival, speed of re-epithelization, and reduction of length of stay in hospital.4,5
To date, only 4 pediatric cases of SJS/TEN treated with cyclosporin have been published6,7 (Table 1). All of them show the utility of the drug in stabilizing the disease, re-epithelization of the lesions, and reducing mortality in comparison to supportive treatment. One of the most noteworthy findings, which is constantly reported in the literature, is the speed of the drug at halting progression of the disease, with a response time that ranges from hours to a maximum of 3 days from start of treatment, regardless of the delay between onset of the disease and admission to hospital.1,4,6,8
Clinical Characteristics of Pediatric Patients Treated With Cyclosporins.
| Age | Trigger | CsA Dosage | Other Treatments | Duration of CsA Treatment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| St. John et al (2017) | 17 mo | Phenytoin | 3 mg/kg/d | Systemic corticosteroids prior to CsA (1.5 mg/kg/d) | 7 d |
| St. John et al (2017) | 5 y | M pneumoniae | 3 mg/kg/d | – | 15 d |
| St. John et al (2017) | 8 y | M pneumoniae | 3 mg/kg/d | – | 21 d |
| Aihara et al (2007) | 10 y | Paracetamol | 1 mg/kg/d | Systemic corticosteroids adjuvant to CsA (30 mg/kg × 3 d) | 14 d |
| Quintana et al (2019) | 10 y | Lamotrigine | 4 mg/kg/d | Prior systemic corticosteroids (1-2 mg/kg) | 20 d |
Moreover, based on results in the adult population,9,10 only 1 case of a pediatric patient treated with etanercept (2 doses of 25 mg subcutaneously) has been reported, showing comparable results to cyclosporin in terms of re-epithelization and halting the progression of the disease.11 This drug appears to be of particular utility in cases with kidney failure or a history of malignant disease, situations in which cyclosporin is contraindicated.4,6,11
This case supports the previously published results obtained in 4 other pediatric patients and contributes additional evidence on the use of cyclosporin in single-drug therapy in patients with SJS/TEN. Cyclosporin may be considered a good therapeutic option with a reasonable safety profile in a situation such as this, which may severely threaten the patient’s life.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Quintana-Castanedo L, Nieto-Rodríguez D, Rodríguez-Álvarez D, Feito-Rodríguez M, de Lucas-Laguna R. Necrólisis epidérmica tóxica en un niño tratada de forma satisfactoria con ciclosporina A. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:468–470.