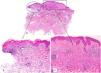
A 61-year-old woman with no remarkable past history presented with slightly raised, annular erythematous macules of approximately 3 months’ duration on the neckline and dorsal surface of the arms.
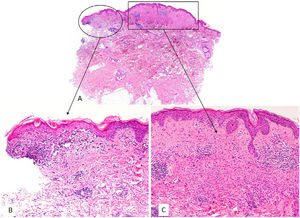
Skin biopsy of 1 of the lesions revealed 2 findings: interface dermatitis and an intradermal melanocytic nevus (Fig. 1A). The interface dermatitis was characterized by vacuolar changes, a perivascular lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate, and interstitial mucin deposition (Fig. 1B). The intradermal nevus was composed of amelanotic epithelioid melanocytes accompanied by a focal lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate. The melanocytes had abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with well-defined borders and mild nuclear pleomorphism (Fig. 1C).
The histologic diagnosis was an intradermal melanocytic nevus co-occurring with subacute lupus erythematosus.
Although melanocytic nevi are known to co-occur with inflammatory disorders such as eczema (Meyerson nevus), psoriasis, and lichen sclerosus, few cases have been described, and this is the first report of co-occurrence with lupus erythematosus.
This finding is important as it may indicate that inflammatory conditions can lead to morphologic changes in a benign proliferation that simulate melanoma. In the present case, observation of epithelioid melanocytes accompanied by an inflammatory infiltrate (probably from the lupus) suggested a nevus with a loss of BAP-1 expression (not confirmed by immunohistochemistry).