Erythema multiforme (EM) is an acute skin disorder characterized by cutaneous lesions and variable mucosal involvement. We present a case of EM that occurred following the application of topical imiquimod to treat a basal cell carcinoma (BCC) in a woman with Gorlin syndrome.
Case DescriptionA 56-year-old woman with Gorlin syndrome who was seen regularly at our dermatology unit for the evaluation and treatment of BCCs developed a pruritic skin rash on her upper arm (including her palms) and ankles after applying topical imiquimod 5% cream to a BCC on the tip of her nose. In total, she had applied the cream 18 times within a once-daily Monday to Friday regimen. The patient had been taking ezetimibe 10mg, simvastatin 20mg, and clonazepam 0.5mg daily for several years.
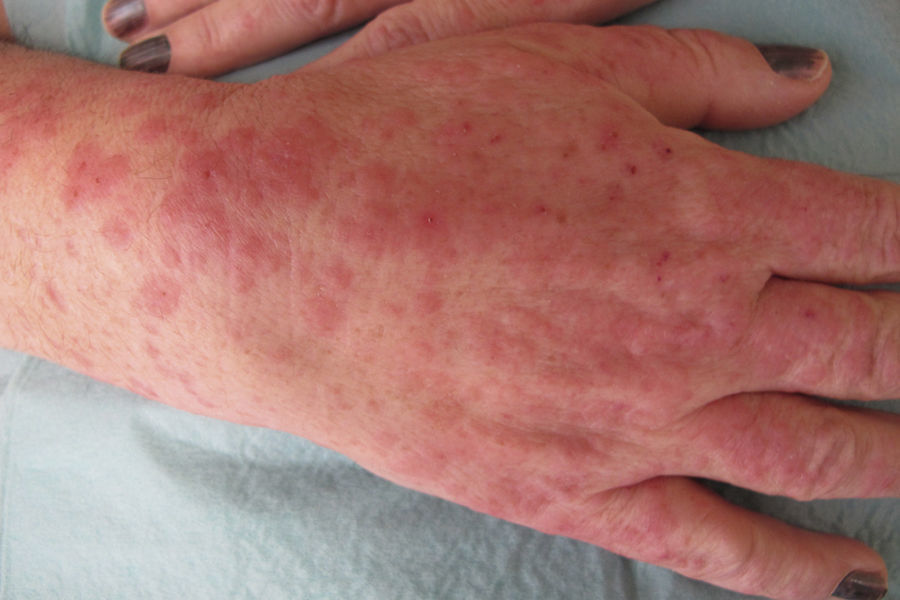
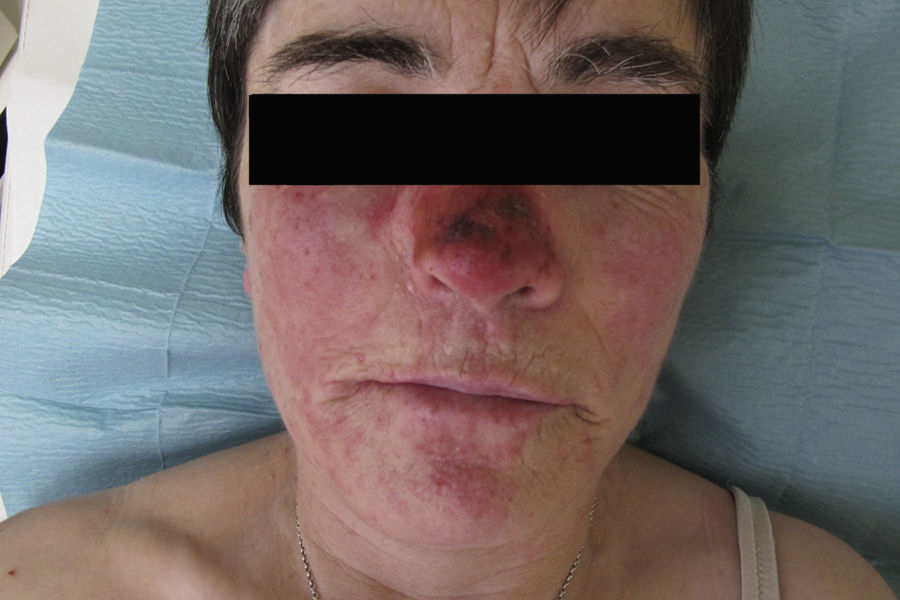
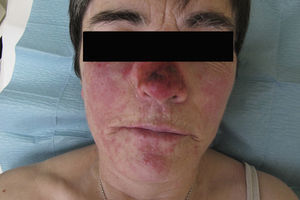
Physical examination revealed erythematous-edematous papules and plaques on the dorsum of the hands, forearms, arms, and ankles (Fig. 1) and a local inflammatory reaction in the area of the nasal dorsum where she had been applying the imiquimod cream (Fig. 2). Some of the plaques had the appearance of a target lesion but no mucosal involvement was observed.
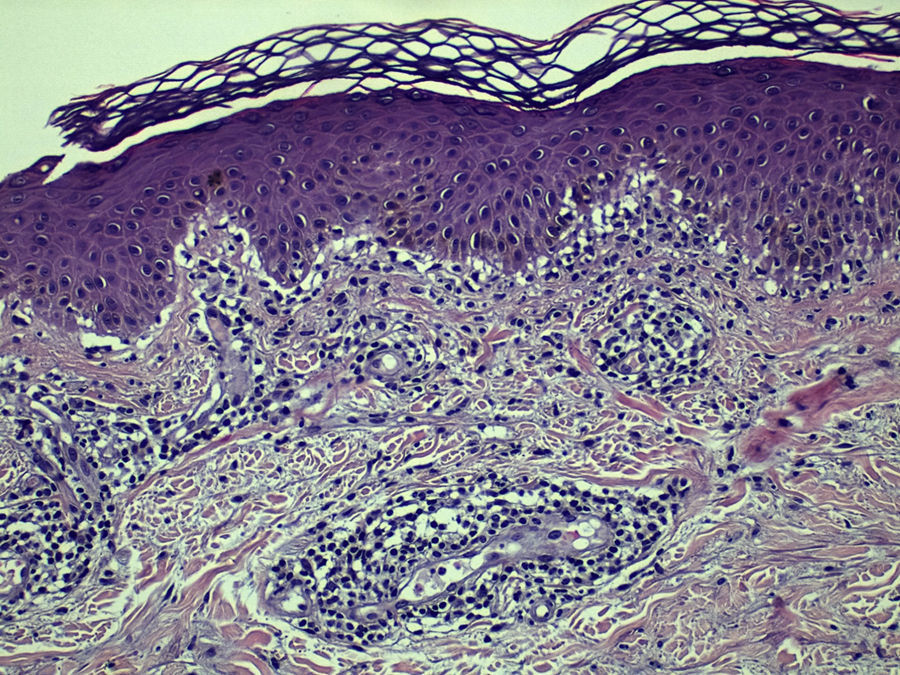
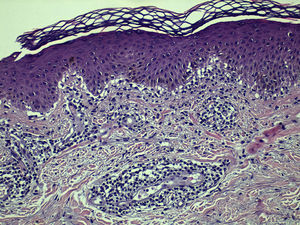
Histopathologic examination of a lesion from the left elbow showed a lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate with a predominantly perivascular distribution in the dermis, epidermal exocytosis, several areas of epithelial necrosis, and signs of incipient intraepidermal blister formation (Fig. 3), confirming the suspected diagnosis of EM. Treatment with imiquimod was interrupted and replaced with topical mometasone furoate, which resulted in complete clearance within 15 days.
Imiquimod 5% cream is a topical immunomodulator approved for the treatment of actinic keratosis, BCC, and genital warts. Its antitumor and antiviral properties are related to its ability to stimulate both innate and acquired immune responses, activating toll-like receptors 7 and 8, stimulating the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (α-TNF, interferon alpha, interleukin 6),1 and triggering inflammation and the destruction of tumor and virus-infected cells.
Most of the adverse effects associated with imiquimod are local, and include erythema, edema, and ulceration. Lesions occurring at a distance from the application site have also been described and include Stevens-Johnson syndrome, EM, and cutaneous lupus.
In our review of the literature, we found many drugs described in association with EM (antibiotics, corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), but there were few reports linking EM to topical treatments.1–3 We detected just 3 cases of EM associated with topical imiquimod, and none of the patients had Gorlin syndrome. Systemic absorption could explain why topical imiquimod causes EM, as the immunomodulatory effects of the drug could trigger a type III and/or IV hypersensitivity reaction, ultimately leading to EM. An intense local inflammatory reaction such as that experienced by our patient would probably favor this systemic absorption, predisposing patients to an EM-type skin eruption. Nonetheless, whether or not patients with Gorlin syndrome have an immune-based predisposition to EM remains to be confirmed.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Peña-López S, Suárez-Magdalena O, Monteagudo B, Cabanillas M. Eritema multiforme secundario a imiquimod tópico al 5% en paciente con síndrome de Gorlin. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2018;109:277–278.