Association of sarcoidosis and autoimmune thyroiditis is rare. We report a case of cutaneous sarcoid surrounded by livedo on the lower extremities in a patient with Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
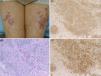
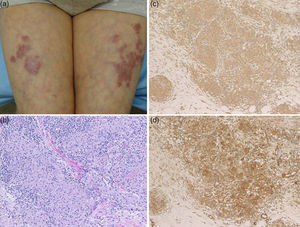
A 72-year-old female visited the Department of Dermatology of Hoshi General Hospital, complaining of asymptomatic reddish eruptions on the lower extremities which appeared six months previously. She had Hashimoto's thyroiditis for several years, but had been followed without medications. Physical examination showed multiple reddish, infiltrative round and irregular-shaped, up to 4-cm sized plaques on the anterior aspects of the bilateral thighs and lower legs (Fig. 1a). The erythematous plaques coalesced on the left thigh, and livedo was observed in the surroundings of the plaques on the thighs. Laboratory examination showed normal levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) (13.6U/L, normal: 7–25). Anti-thyroglobulin antibody showed high titers (86.8IU/ml; normal <28), however, anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody, thyroid stimulating hormone, free T3 and T4 levels were within normal ranges. Chest X-ray did not reveal bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. Computed tomography revealed a few lymph nodes within normal ranges and thyroid nodule. Ophthalmological examination denied uveitis. A tuberculin test revealed positive erythematous reaction sized 2-cm without induration. A skin biopsy taken from reddish plaque showed non-caseating granulomas with epithelioid cells throughout the dermis (Fig. 1b). Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) and Ziehl–Neelsen staining did not detect bacilli. Immunohistochemistry revealed a number of CD68-positive macrophages in the lesional skin. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) positive cells were also detected densely (Fig. 1c and d). Elastica van Gieson stain showed that multiple sarcoidal granulomas were located around the vessels, but without fibrinoid degeneration.
Autoimmune thyroiditis is sometimes seen in association with sarcoidosis,1 and to date, several cases of co-occurrence of sarcoidosis and Hashimoto's thyroiditis have been reported. Isernet et al.2 reported that 10 out of 348 patients with sarcoidosis had autoimmune thyroiditis, and sarcoidosis preceded autoimmune thyroiditis in 9 cases. The diagnosis of autoimmune thyroiditis was made when sarcoidosis was in remission. Papadopoulos et al.3 reported that 13 patients had thyroid autoimmunity (6 with Hashimoto's thyroiditis, 2 with Graves’ disease and 5 with isolated positive thyroid serology) among a series of 78 patients with sarcoidosis. Nakamura et al.4 found 7 cases of Hashimoto's thyroiditis in a series of 62 patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Unfortunately, an open biopsy of thyroid nodule was not carried out to differentiate thyroid sarcoidosis in the present case. At present, sarcoidal lesions were not detected in other organs, i.e. lung or eyes. Moreover, a tuberculin test revealed positive reaction. Therefore, we consider that the patient developed cutaneous sarcoid only; however, we will carefully follow-up this patient whether symptoms of systemic sarcoidosis will appear in the future.
Macrophages play an important role in sarcoidal granuloma formation via several cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β. Several recent studies have reported the effectiveness of TNF-α inhibition for sarcoidosis. Our studies showed a number of CD163-positive macrophages surrounding the degenerated collagen in the dermis. In addition, strong expression of IL-17 and TNF-α was detected in the lesional skin of sarcoidosis. TNF-α activates Th17 cells leading IL-17 production, and recent studies have shown that IL-17 was abundantly detected in sarcoidal lesions, suggesting that Th17 cells induce granuloma formation by suppressing regulatory T-cells.5 Recent findings suggest an important etiologic role of Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) in sarcoidosis. P. acnes induces IL-17 and interferon-γ,6 and is thus implicated to play a pathogenic role in sarcoidosis via Th1/Th17 cytokines.
Finally, livedo was seen around sarcoidal plaques on the bilateral thigh. To date, only a few cases have been presented with livedo in association with sarcoidosis.7–9 A biopsy was taken from the sarcoidal plaque, but not from the surrounding livedo. However, histological examination showed granulomas around the vessels, which may induce livedo.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human subjects and animals in researchThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this investigation.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.