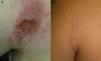
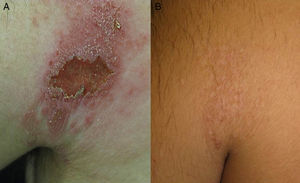
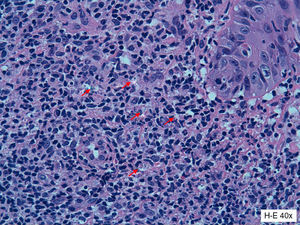
We report the case of a 33-year-old man referred to our department with a skin ulcer that had appeared 1 year earlier on the left posterior axillary fold. His medical history was remarkable for chronic hepatitis B infection being treated with adefovir and for psoriatic arthritis, under treatment with leflunomide 20mg/d, prednisone 5mg/d, and infliximab 5mg/kg every 8 weeks for the past 2 years. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated plaque measuring 9×6cm and several erythematous-scaling papules measuring 1 to 2cm on and around the plaque (Fig. 1A). There was no evidence of enlarged lymph nodes, liver, or spleen on palpation. Histologic examination showed a mixed inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes, histiocytes, and some macrophages with intracellular and extracellular Leishmania amastigotes (Fig. 2). Two additional biopsies were performed to complete the study. Giemsa staining of one of the biopsy specimens showed scarce amastigotes and culture of the other specimen was positive for Leishmania species. The subtype could not be identified. Mycobacterial culture was negative and the fungal culture was positive for Candida albicans. Serology showed a Leishmania antibody titer of 1:80. No parasite material was detected by Giemsa stains or culture of bone marrow aspirate smears. The organs did not appear enlarged on abdominal ultrasound and the blood workup showed mild neutropenia (1.64×109/L) and thrombocytopenia (127×109/L); the results of the liver and kidney function tests were normal.
Following confirmation of the diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis, infliximab therapy was discontinued and treatment was started with intralesional pentavalent antimonial injections and superficial cryotherapy (9 sessions over 2.5 months). Intralesional meglumine antimoniate (MA) injections (4-8mL) were administered every 1 or 2 weeks depending on the patient's tolerance. The total dose administered on completion of treatment was 44mL. The patient was also prescribed itraconazole 100mg/d for a month to treat the C albicans infection identified by culture. The ulcer healed completely after 3 months of treatment. To achieve better control of the patient's arthritis, he was prescribed etanercept 50mg/wk, abatacept 750mg/mo, and golimumab 50mg/mo. He has been taking this medication for 2.5 years and there has been no recurrence of the cutaneous leishmaniasis (Fig. 1B).
Tumor necrosis factor is a proinflammatory cytokine that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders and immune responses to various infections, particularly those caused by intracellular pathogens.1Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites of macrophages and to control infection, it is necessary to active these cells and induce the formation of granulomas. Opportunistic Leishmania infections can occur following the reactivation of a latent, previously undetected, infection or they can develop as a primary infection during immunosuppressive treatment. Of the cases reported in the literature of cutaneous or mucocutaneous leishmaniasis associated with anti-TNF drugs (Table 1),1–9 infliximab was being used at the time of diagnosis in 5 cases. All of the other patients were receiving adalimumab.We did not identify any cases of treatment with etanercept. Furthermore, all the patients described in the above reports either lived in areas where Leishmania species are very common or had travelled to Leishmania-endemic areas. Pentavalent antimonials at a dosage of 20mg/kg/d for 20 days are recommended by the World Health Organization as the first-line treatment of localized cutaneous leishmaniasis (1-10 skin lesions with no evidence of systemic involvement).10 However, many patients do not complete treatment because of the need for daily intramuscular injections, the duration of treatment, and its adverse effects. Several alternatives have been proposed, including liposomal amphotericin B, miltefosine, allopurinol, azoles, paromomycin, dapsone, and azithromycin.
Cases of Cutaneous and Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis Associated With Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Drugs.
| Case No. | Age, y/Sex | Primary Disease | Type of Leishmaniasis | Anti-TNF Drug (Treatment Duration) | Other Immunosuppressants | Treatment | Authors (Year) |
| 1 | 55/F | AS | CL | Infliximab (12 mo) | Methotrexate | Liposomal amphotericin B | Xynos et al.1 (2009) |
| 2 | 51/F | AS | CL | Adalimumab (24 mo) | Methotrexate | Liposomal amphotericin B | Schneider et al.2 (2009) |
| 3 | 56/F | RA | MCL | Adalimumab (2 mo) | Methotrexate, cortiocsteroids, infliximab | Meglumine antimoniate | Baltà-Cruz et al.3 (2009) |
| 4 | 31/M | AS | CL | Infliximab (48 mo) | Not reported | 1. Miltefosine2. Meglumine antimoniate | Mueller et al.4 (2009) |
| 5 | 42/F | RA | MCL | Adalimumab (2 mo) | Corticosteroids, methotrexate | Liposomal amphotericin B | Franklin et al.5 (2009) |
| 6 | 50/M | AS | CL | Infliximab (13 mo) | Corticosteroids | Meglumine antimoniate | Hakimi et al.6 (2010) |
| 7 | 38/M | RA | CL | Infliximab (0.25 mo) | Corticosteroids, methotrexate | Liposomal amphotericin B | Zanger et al.7 (2011) |
| 8 | 36/F | AS | CL | Adalimumab (12 mo) | Methotrexate | Meglumine antimoniate | Gomes et al.8 (2012) |
| 9 | 66/F | RA | CL | Infliximab (25 mo) | Methotrexate, corticosteroids | Meglumine antimoniate | García-Castro et al.9 (2012) |
| 10 | 33/M | PA | CL | Infliximab (48 mo) | Leflunomide, corticosteroids | Meglumine antimoniate + cryotherapy + itraconazole | Current case |
Abbreviations: AS, ankylosing spondylitis; CL, cutaneous leishmaniasis; MCL, mucocutaneous leishmaniasis; PA, psoriatic arthritis; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Asilian et al.11 reported good results for cryotherapy combined with intralesional MA, with higher cure rates observed for the combined regimen (90.9%) than for cryotherapy (57.15%) or MA (55.63%) alone. The use of intralesional MA allows the total dose—and consequently the adverse effects—to be reduced. This treatment option yielded good results in our patient, although it should be noted that even though we used lower doses that would have been required with intramuscular MA, our patient still experienced adverse effects in the form of tachycardia, headache, and chest pain. The effects of treatment with itraconazole must also be taken into account. In conclusion, we highlight the importance of considering the possibility of cutaneous or visceral leishmaniasis in patients treated with anti-TNF drugs in Leishmania-endemic areas. We also recommend considering MA combined with cryotherapy as a more effective and less toxic option than intramuscular MA.
Please cite this article as: Català A, Barnadas MA, Muñoz C, Puig L. Leishmaniasis cutánea en un paciente con artritis psoriásica tratado con infliximab: tratamiento con crioterapia y Glucantime® intralesional. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105:714–716.