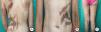The epidermal nevus syndromes are a group of conditions in which any type of epidermal nevus is associated with extracutaneous changes. The most common associated alterations are skeletal, neurologic, and ophthalmic.1
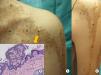
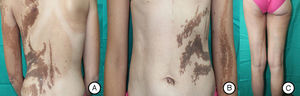
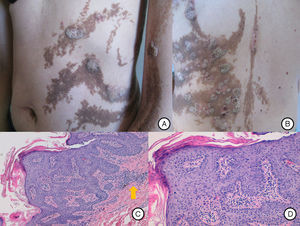
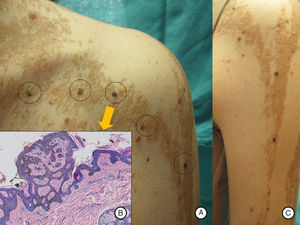
Our patient was a 37-year-old woman with a systematized epidermal nevus, present since birth and affecting the left side of the body. The nevus was formed of brownish papillomatous plaques with a characteristic distribution along the Blaschko lines (Fig. 1). She also presented a plaque of alopecia in the temporal region, hyperkeratotic lesions on the left hand, and ipsilateral plantar keratoderma. These findings were associated with multiple musculoskeletal alterations, including marked scoliosis, dysmetria of the hips with atrophy of the left lower limb, painful joint disease affecting the interphalangeal joints of the right hand, and vascular alterations consisting of bilateral chronic lymphedema of the lower limbs secondary to insufficiency of the internal saphenous vein. Neurologically, the patient presented paralysis of the left third cranial nerve, with no evidence of other cerebral abnormalities. In addition, for the previous 7 years she had presented outbreaks of inflammatory lesions in the area of the epidermal nevus, with no apparent cause. These lesions were formed of round or oval plaques with a psoriasiform appearance and a patchy distribution; they improved with topical corticosteroids. Biopsy of 1 of these lesions revealed verrucous epidermal nevus architecture with acanthosis and papillomatous, associated with a lymphocytic infiltrate in the superficial dermis and alternating areas of parakeratosis with mild spongiosis and areas of orthokeratosis (Fig. 2). For the previous several years, our patient had also presented pigmented macules that developed progressively on the underlying epidermal nevus, in a clearly linear distribution on the trunk and on the left limbs. Biopsy of 1 of the pigmented lesions showed epidermal nevus architecture together with junctional melanocyte hyperplasia, indicating the presence of a junctional lentiginous nevus with no atypia (Fig. 3).
A and B, Systematized epidermal nevus affecting the left side of the body, presenting as brownish papillomatous plaques distributed along the Blaschko lines. C, Hip asymmetry with atrophy of the left gluteus and bilateral chronic lymphedema secondary to insufficiency of the internal saphenous vein.
A, Inflammatory lesions over the epidermal nevus on the trunk and left upper limb. The lesions presented as round and oval plaques with a psoriasiform appearance. B, Patchy distribution of the inflammatory lesions on the patient's back, not affecting some areas of the epidermal nevus. C, Biopsy of 1 of the lesions showed epidermal nevus architecture with acanthosis and papillomatosis, associated with a lymphocytic infiltrate in the superficial dermis (arrow). Hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification×10. D, Area of parakeratosis with mild spongiosis. Hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification×20.
A and B, Pigmented macular lesions on the epidermal nevus in a linear distribution on the trunk and left upper limb. C, Biopsy of a pigmented macule on the trunk showed epidermal nevus architecture associated with junctional melanocyte hyperplasia, indicating the presence of a junctional lentiginous melanocytic nevus with no atypia. Hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification×10).
In 2010, Happle2 described 9 well-defined epidermal nevus syndromes; our case presents greatest similarity with phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica. This disease is defined as the combination of an epidermal nevus with sebaceous differentiation with a nevus Spilus, associated with extracutaneous changes. However, atypical variants of phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica have been described, in which the epidermal nevus is verrucous and does not show sebaceous differentiation3,4; our patient presented this variant. It must be understood that this is not a definitive classification, and further entities based on clinical and molecular criteria will be described in coming years.5
Regarding the inflammatory plaques on the epidermal nevus, we considered a differential diagnosis including inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN). ILVEN is a variant of epidermal nevus that typically appears in young children,6 presenting as pruritic inflammatory plaques that can be similar to linear psoriasis.7 The distribution of the lesions in our case differed from that observed in ILVEN, as the round or oval inflammatory plaques appeared in patches, leaving areas of epidermal nevus unaffected, and the outbreaks always arose in the same areas of the epidermal nevus. This particular distribution has not previously been described and suggests that there may be some molecular alteration in the keratinocytes of the inflamed areas of the epidermal nevus that would trigger a localized immune response, a hypothesis supported by the finding on histopathology of a lymphocytic infiltrate in the superficial dermis.
We hypothesize that the late appearance of the melanocytic nevus on the epidermal nevus in our patient was due to a mutation in the melanocytes that had remained silent until adult life, when expression occurred in mosaic form, following the path of the epidermal nevus. The linear distribution of the lesions and the extracutaneous alterations involving a number of cell lines suggests an early postzygotic mutation. Recently, postzygotic gene mutations have been described in the RAS-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) pathway, interpreting the epidermal nevus syndromes as RASopathies expressed as cutaneous mosaicism.8,9
In our patient, the genetic analysis performed on a sample of epidermal nevus revealed a BRAF-Glu586Lys mutation (exon 15). The genetic analysis was completed on a sample of healthy skin and of melanocytic nevus, finding no alterations, a circumstance that further supports the hypothesis that the mutation described in the epidermal nevus is not a casual finding. Although this alteration has not been described in the context of epidermal nevus,9 the pathogenicity of the BRAF-Glu586Lys mutation has been demonstrated in in vitro experimental models.10 The substitution of glutamate for lysine at position 586 of the amino acid chain produces a structural change that increases the activity of the BRAF protein.10 It should be remembered that the RAS-MAPK pathway participates in cell differentiation, growth, and death. It is involved in up to 20% to 30% of somatic cancers, and the majority of mutations provoke pathway upregulation,11 as in our case.
In conclusion, we have described an atypical case of phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica that presented as outbreaks of inflammatory lesions on the epidermal nevus, with a distinctive distribution, associated with the progressive appearance of melanocytic nevi distributed along the Blaschko lines. The genetic analysis revealed a mutation in the BRAF gene not previously described in the literature in relation to epidermal nevus, making this a RASopathy expressed in mosaicism.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Ayala D, Ramón MD, Martín JM, Jordá E. Facomatosis pigmentoqueratótica atípica como expresión de rasopatía en mosaicismo con mutación en gen BRAF Glu586Lys. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016;107:345–347.