Chronic lymphatic leukemia (CLL) is the most common type of leukemia in adults in Europe and North America. It is characterized by enlarged lymph nodes, visceromegaly, and clonal B-cell lymphocytosis in the peripheral blood. Skin involvement can be seen in up to 25% of patients, mainly in the form of nonspecific manifestations such as neoplasias, viral infections, vasculitis, or Sweet syndrome.1 However, leukemia cutis (LC) or infiltration of the skin by leukemic cells is a rare clinical manifestation in CLL and almost always occurs in advanced stages of the disease.1,2 We report a rare case of LC mimicking granulomatous rosacea at the onset of CLL.
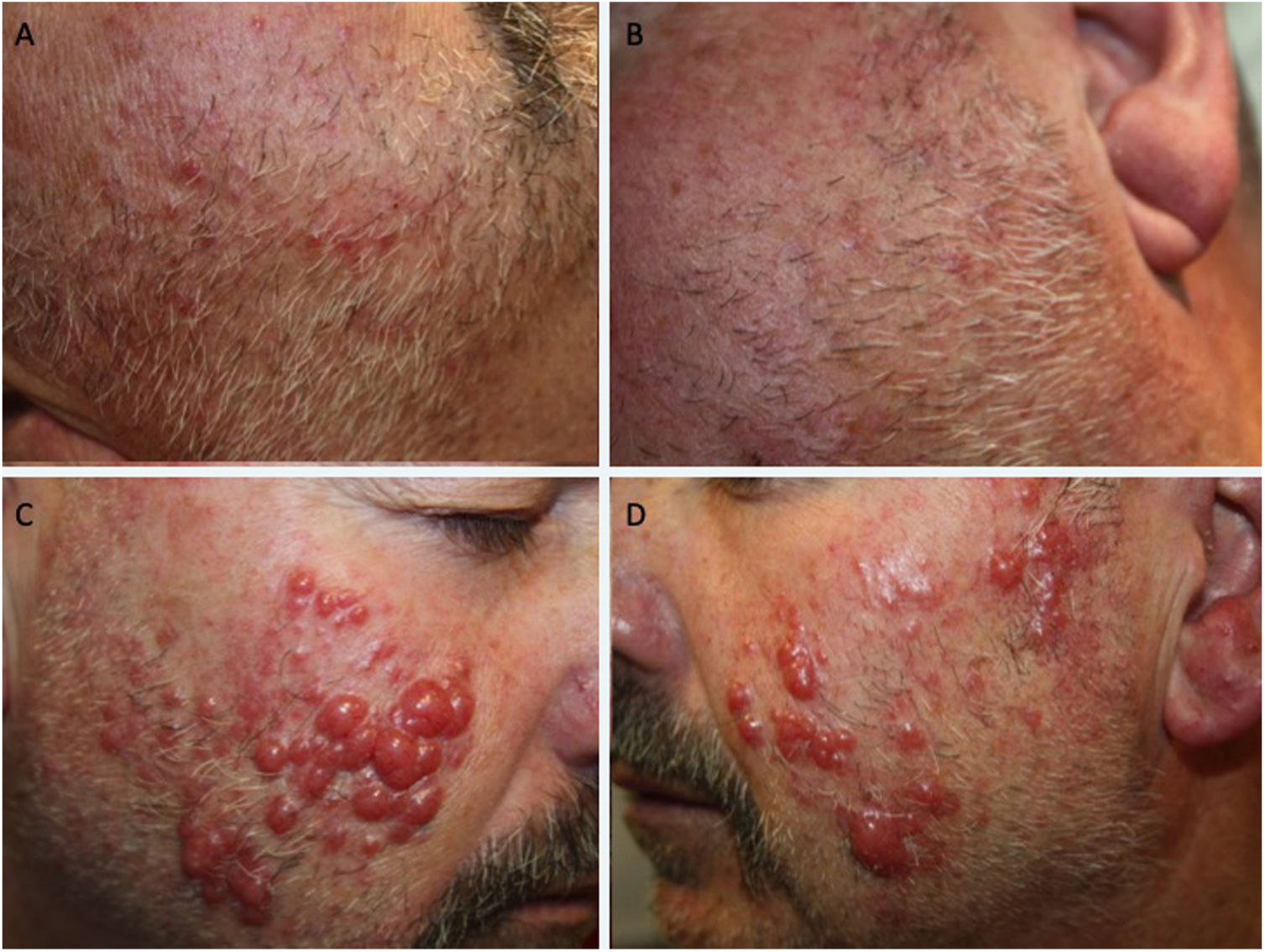
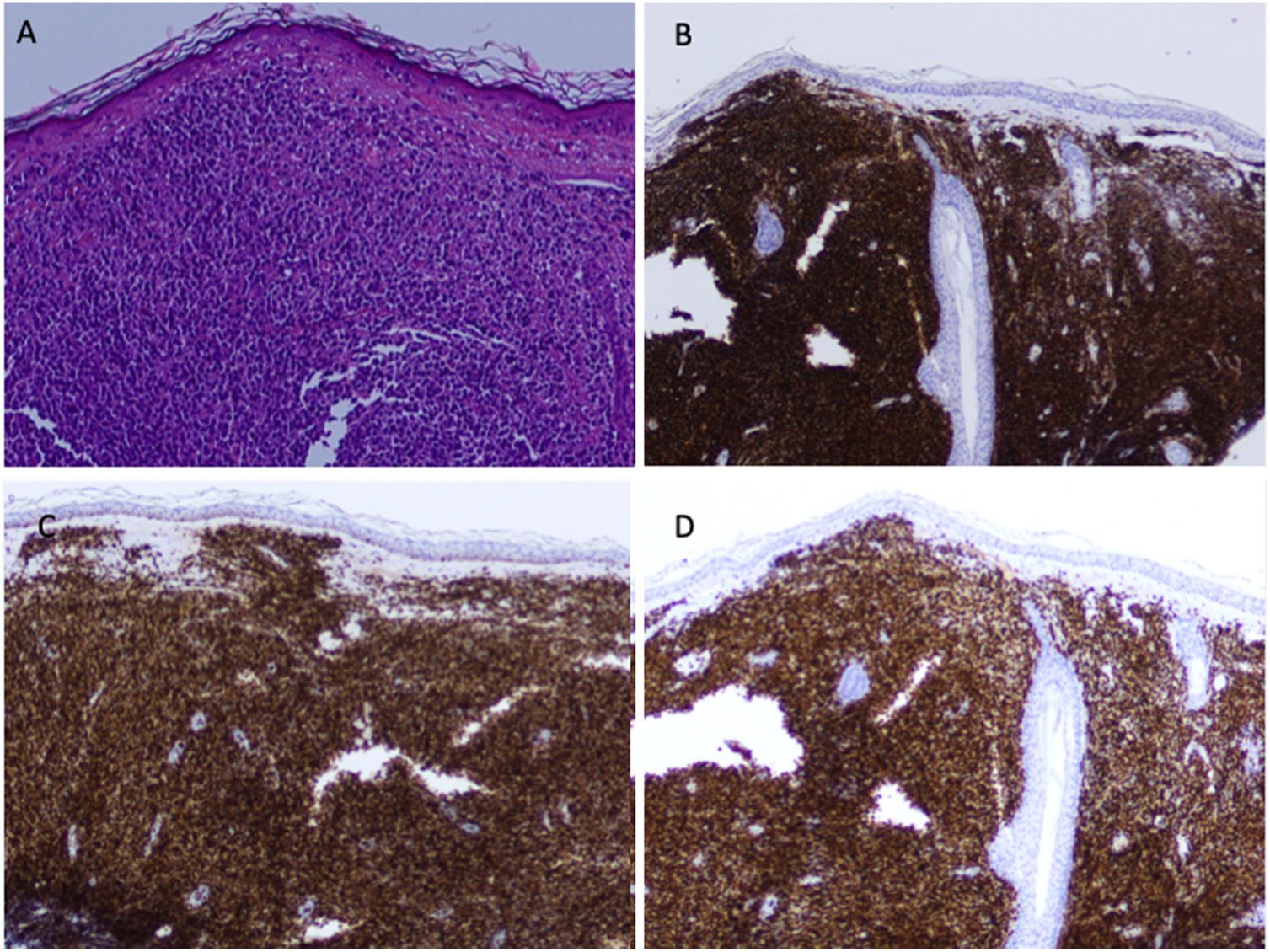
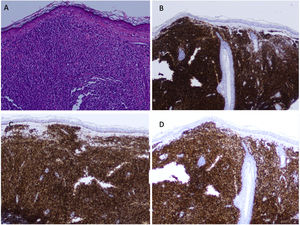
A healthy 60-year-old man with a history of erythematotelangiectatic rosacea visited our department with asymptomatic lesions that had appeared a year earlier on both cheeks. Physical examination revealed erythematous papules on congested skin (Fig. 1A and B). In light of the clinical suspicion of papulopustular rosacea, treatment with oral doxycycline and topical ivermectin was instated. The course was unfavorable and the patient developed multiple firm, erythematous nodules on the cheeks and outer ears (Fig. 1C and D). Lymph-node examination revealed a mobile, painless, enlarged right submandibular lymph node. The patient did not present B symptoms. A skin biopsy revealed a diffuse dermal lymphocytic infiltrate with no epidermotropism and with a subepidermal Grenz zone. It consisted of small lymphocytes with round hyperchromatic nuclei and scarce cytoplasm (Fig. 2A). Demodex folliculorum was not identified. The immunohistochemical analysis revealed a predominantly B phenotype (positive for CD5, CD20 CD23, CD43, BCL-2, LEF-1, and PAX5) (Fig. 2B–D). Morphological and immunohistochemical findings were compatible with a skin infiltration due to CLL. Blood tests showed a normal blood count and hypogammaglobulinemia with no monoclonal bands (IgG, 6.21g/L: IgM, 0.13g/L). Serology was negative for HBV, HCV, HIV, EBV, CMV, and Toxoplasma species. A full-body CT scan revealed multiple enlarged lymph nodes in different locations, with no enlarged liver or spleen. The myelogram identified an infiltration of 83% small, mature lymphocytes, indicative of CLL. Flow cytometry analysis of bone marrow showed 50% B cells with an immunophenotype identical to that found in the skin. The 17p13 deletion was not identified in bone marrow.
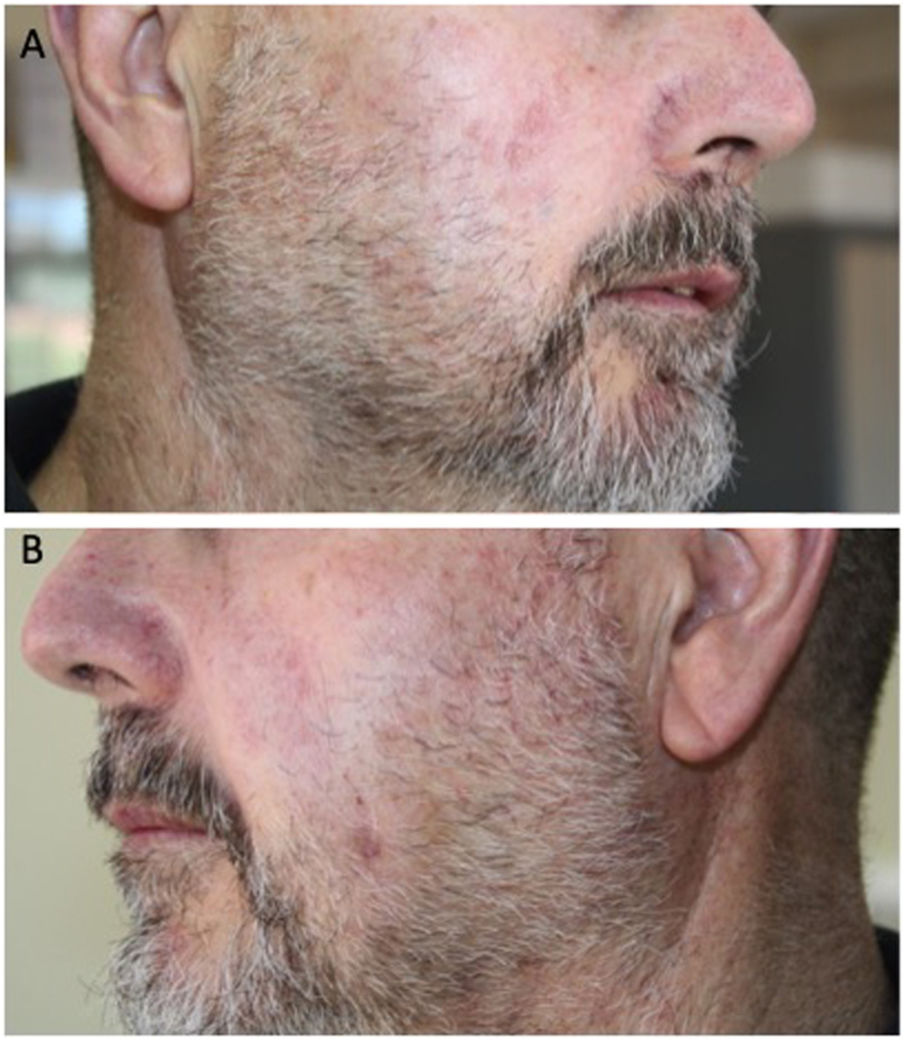
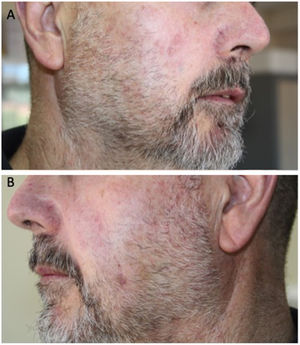
Following the diagnosis Rai stage I and Binet stage B CLL, the patient underwent 6 cycles of chemotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab, achieving complete remission (Fig. 3A and B). The patient has not experienced a recurrence. After 2 years of follow-up, the patient has not presented cutaneous or bone-marrow recurrences.
LC can be observed in between 4% and 20% of patients with CLL.3 Although it tends to occur in advanced stages, LC may be the first manifestation of CLL in up to 16.7% of cases.4 Clinical presentation varies widely and includes papules, plaques, nodules, and erythematous-violaceous tumors located essentially on the head and neck, or generalized.1
Onset of CLL mimicking rosacea is a rare form of presentation, with only 4 cases reported to date, 3 of which were in women.5–7 Patients with CLL have also been reported who developed a rosacea-like facial cutaneous infiltration years after diagnosis.8 This atypical cutaneous manifestation of CLL is mostly observed in women in the 6th decade of life, which makes the differential diagnosis with rosacea more plausible. This leads to a delay in diagnosis, which may range from months to years, given that patients are treated with topical or systemic antibiotics in the event of clinical suspicion of rosacea.6
The etiology and pathogenesis of this form of presentation of CLL are unknown. The appearance of LC in the same location as prior rosacea lesions may represent Wolf's isotopic response, as occurs in patients with a prior infection by the herpes zoster virus or herpes simplex virus.4,9 It has also been suggested that chronic stimulation by D. folliculorum may lead to the development of lymphoma, as occurs with Helicobacter pylori and gastric MALT lymphoma.10 The presence of D. folliculorum in the histology study, however, has not been shown in all cases of rosacea-like CLL.6–8
Specific involvement of the skin by leukemic cells in patients with CLL has not been associated with a worse outcome, provided that there is no systemic progression or signs of transformation to large cell lymphoma (Richter syndrome).1,4
Treatment in these cases includes nucleoside analogs such as fludarabine and cladribine, alkylating agents such as chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide, or local radiation therapy. The combination of rituximab and systemic corticosteroids has also been shown to be effective, especially in patients with poor tolerance of chemotherapy agents.6,7,11
Thus, the onset of CLL mimicking rosacea is an extremely rare form of clinical presentation. We must, therefore, include atypical rosacea-like lesions or those that respond poorly to the usual treatments in the forms of clinical presentation of CLL to avoid delayed diagnosis.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.