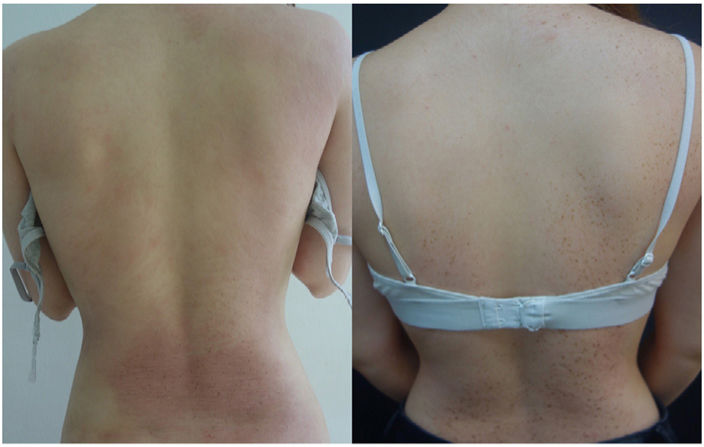
A 24-year-old woman with severe childhood-onset atopic dermatitis had received multiple treatments with incomplete responses in most cases. The last treatment received was tralokinumab, which almost completely resolved her eczematous plaques and lichenification, leaving numerous pigmented lesions behind consistent with lentigines limited to the areas of the previous eczematous plaques (figure 1).
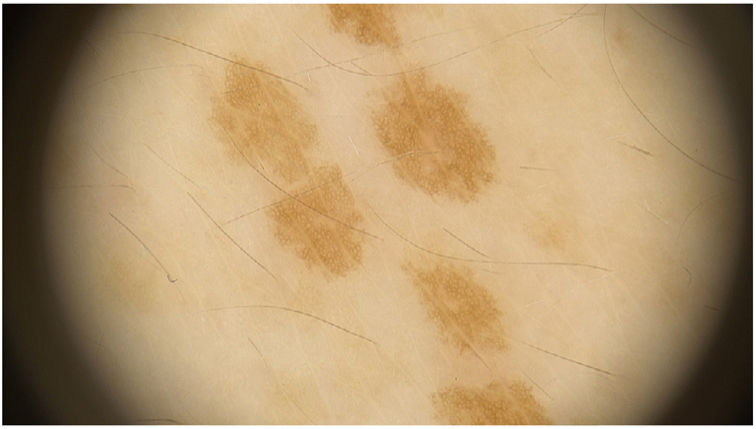
Dermoscopy showed a reticular pattern of thin and delicate lines with fingerprint-like structures, characteristic of lentigines in the absence of typical features such as dots, globules, and other structures typical of melanocytic nevi (figure 2). No histopathological examination was performed for the absence of atypia or malignancy signs. Finally, a conclusive diagnosis of lentigines was established based on clinical and dermoscopic findings.
This phenomenon—well-documented in patients with psoriasis—is much less common in patients with atopic dermatitis and has been scarcely described in the scientific medical literature.
It is considered a benign phenomenon due to the chronic damage caused by the underlying disease to the affected skin, leading to increased cell turnover and subsequent proliferation of melanocytes. It has been primarily associated with the use of topical calcineurin inhibitors, and with the prolonged use of topical corticosteroids or biologic drugs. In our patient, as in most published cases, this lentiginosis probably had a multifactorial origin, with chronic damage and the use of these treatments contributing to its development.
FundingNone declared.