Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is an uncommon, malignant, multifocal systemic disease derived from the proliferation of endothelial cells. The disease has predominant cutaneous involvement and follows a benign course, but in severe cases it can affect other organs, especially the gastrointestinal tract and the lungs. In 1994, Chang et al.1 demonstrated that human herpesvirus type 8 (HHV-8) infection is involved in the etiology of KS. Its presence has been detected in over 90% of biological tissues affected, and it is now considered a valuable diagnostic marker of the disease. Classic KS (described in 1872 by Moritz Kaposi) is the most common form of KS, and it usually affects elderly males of Eastern European or Mediterranean origin. Clinically, it manifests as red-bluish papules, plaques, and nodules on the lower extremities that exhibit a slow but steady growth. There are 4 types of KS: classic KS, endemic (African) KS, immunocompromised (iatrogenic) KS (related to aggressive immunosuppressive treatment), and AIDS-related (epidemic) KS. A new variant related to homosexuality was recently described in men who have sex with men: non-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated KS.2
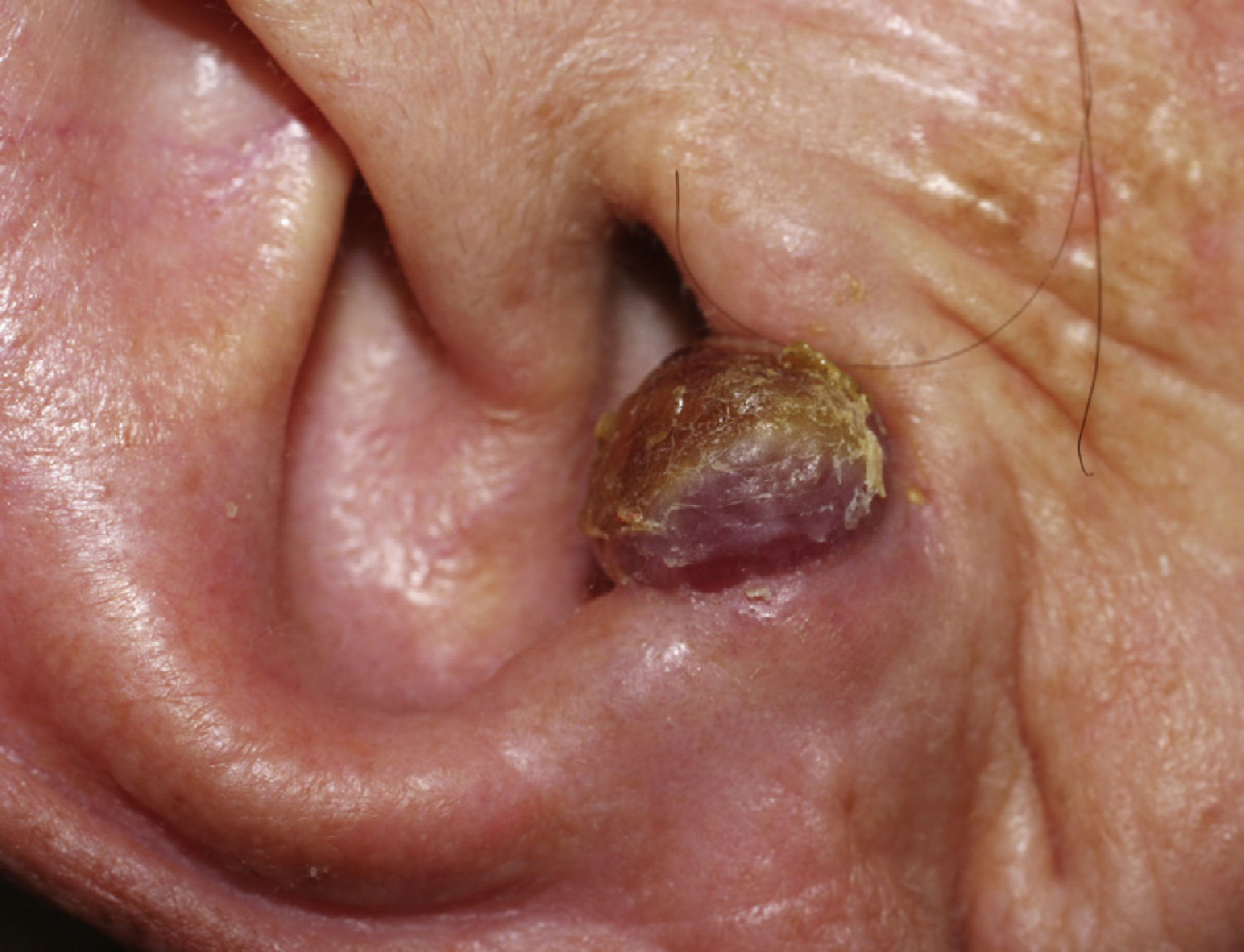
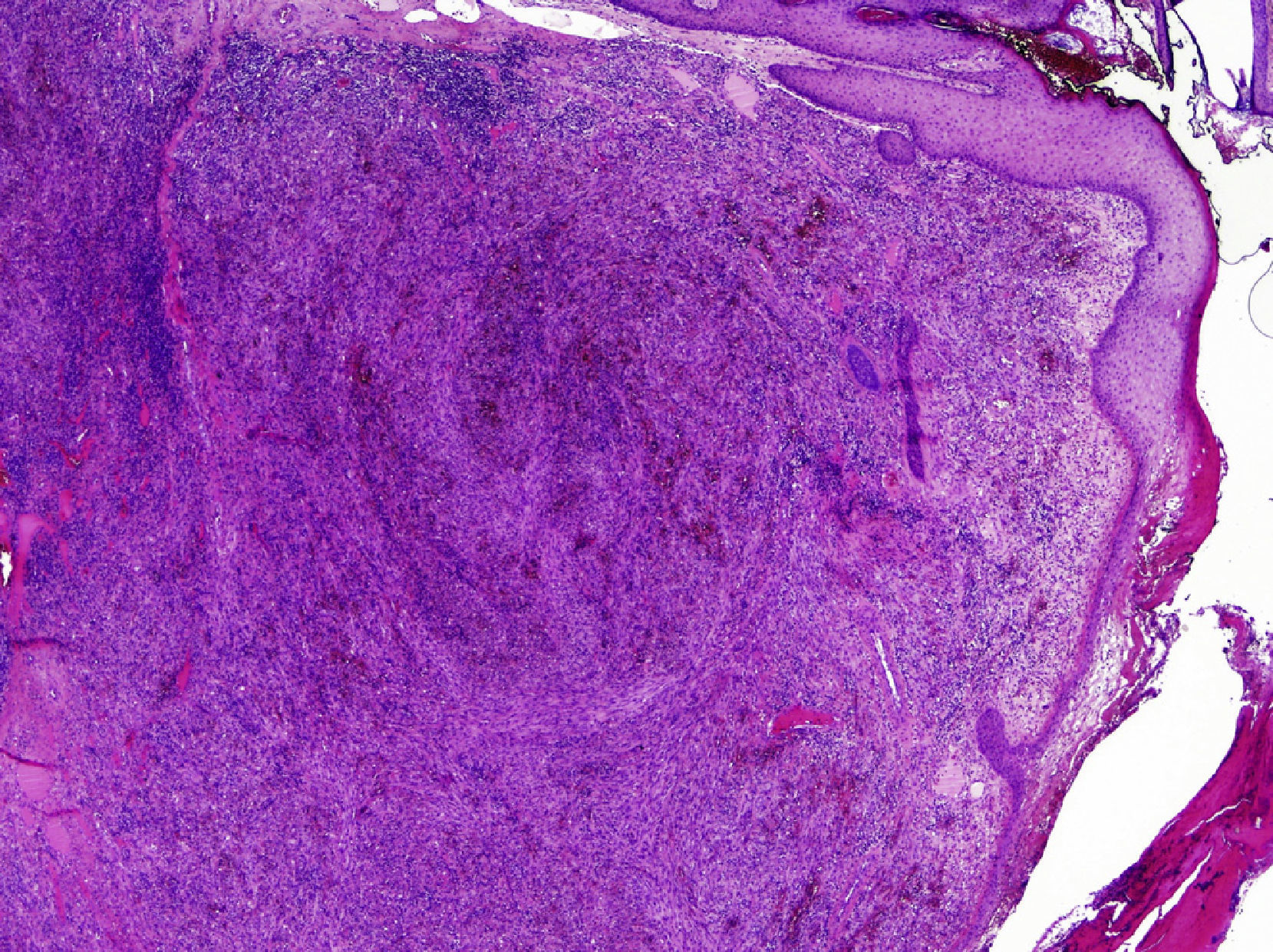
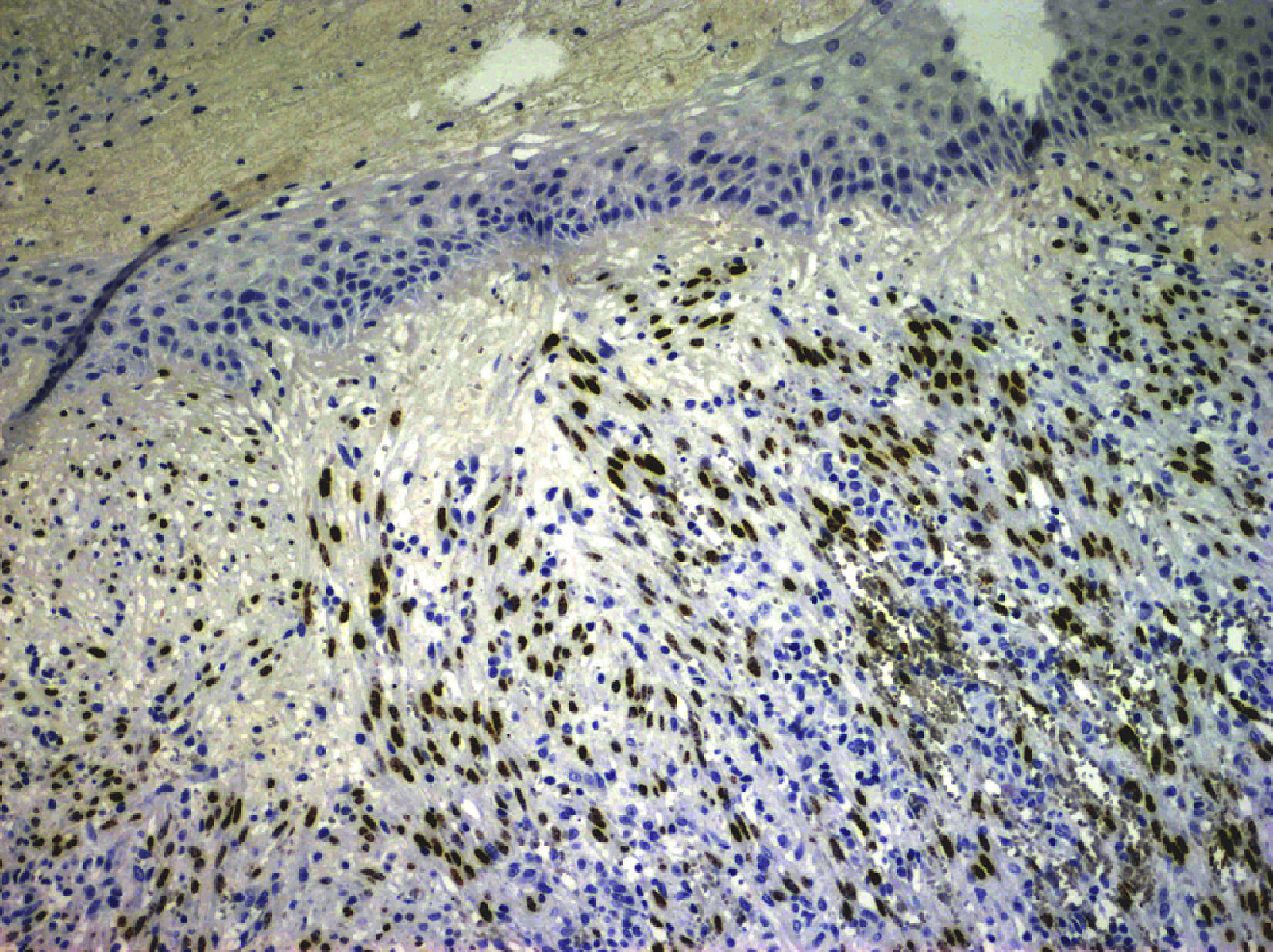
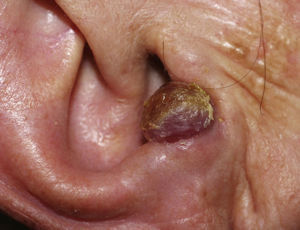
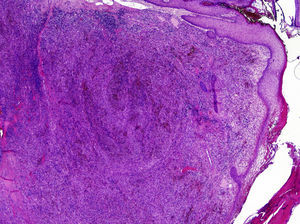
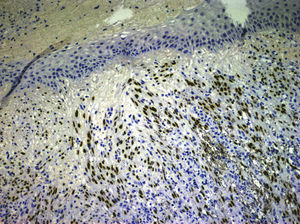
We describe a rare presentation of KS of the external ear in an immunocompetent patient. A 77-year-old woman came to our dermatology department with a firm, slow-growing, red-bluish nodule measuring 1.4cm in diameter on the anterior helix of the right pinna (Fig. 1). She was otherwise well and had no relevant past history of skin disorders, other medical conditions, or associated immunosuppression. The tumor was painless, and there was no bleeding or lymphadenopathy. It had a vascular appearance, and the tentative diagnosis was pyogenic granuloma, although other diagnoses considered were amelanotic melanoma, epidermoid carcinoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, and atypical fibroxanthoma. The lesion was excised completely, and histologic examination revealed a proliferation of fine, irregular vascular channels, with erythrocyte extravasation and minimal pleomorphism and mitotic activity (Fig. 2). Positive staining of spindle cells with CD31, CD34, and HHV-8 was consistent with a diagnosis of KS (Fig. 3). Laboratory tests only revealed hyperglycemia. Serology and polymerase chain reaction results were both positive for HHV-8. Serology for HIV, cytomegalovirus, herpes zoster virus, Epstein–Barr virus, HHV-6, and HHV-7 was negative. To rule out gastrointestinal disease, we performed a fecal occult blood test and an endoscopy, but observed no pathological findings. A whole-body computed tomography scan showed no other visceral disease. Screening laboratory tests to evaluate cellular immunity (total lymphocyte count, T-cell, B-cell, and natural killer-cell enumeration using flow cytometry) and functional assessment of helper T (TH) cells based on TH1 and TH2 cytokine production were normal, but early response to stimulation measured by detection of intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis in T cells (Immuknow, Viracor IBT Laboratories Inc.) was low. This suggested defective T-cell activation because the production of intracellular ATP is one of the first steps in cellular activation. During 2 years of follow-up, no recurrences, new lesions, or new immunosuppressive diseases have been detected.
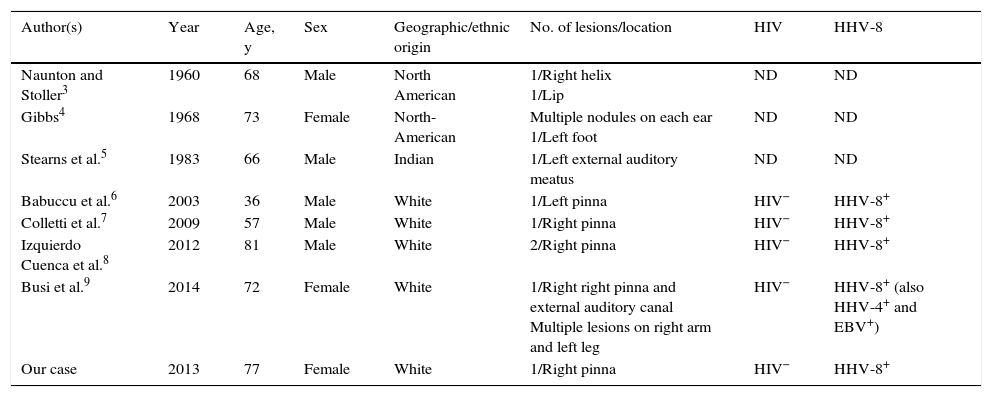
The head is a common site for multiple lesions in HIV patients with KS. However, the presence of a solitary lesion on the ear of an immunocompetent patient is a very rare finding, and very few cases of KS have been reported on the pinna in patients without a history of immunodeficiency (Table 1). Like our patient, most of the patients described in the literature are elderly, with the exception of a healthy 36-year-old white man. We do not know why certain vascular proliferations, such as angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, have a special predilection for the pinna, but we hypothesize that the sum of certain traumatic/infectious factors in an acral area with complex, fine, and insufficient vascularization could make access difficult for immune cells. All these conditions could favor the occurrence of these vascular tumors in certain individuals with immune dysfunction that has not been adequately studied. We highlight the importance of contemplating KS in the differential diagnosis of tumors with a vascular appearance involving the ears in immunologically competent individuals.
Cases of Kaposi sarcoma involving the external ear of patients without AIDS.
| Author(s) | Year | Age, y | Sex | Geographic/ethnic origin | No. of lesions/location | HIV | HHV-8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naunton and Stoller3 | 1960 | 68 | Male | North American | 1/Right helix 1/Lip | ND | ND |
| Gibbs4 | 1968 | 73 | Female | North-American | Multiple nodules on each ear 1/Left foot | ND | ND |
| Stearns et al.5 | 1983 | 66 | Male | Indian | 1/Left external auditory meatus | ND | ND |
| Babuccu et al.6 | 2003 | 36 | Male | White | 1/Left pinna | HIV− | HHV-8+ |
| Colletti et al.7 | 2009 | 57 | Male | White | 1/Right pinna | HIV− | HHV-8+ |
| Izquierdo Cuenca et al.8 | 2012 | 81 | Male | White | 2/Right pinna | HIV− | HHV-8+ |
| Busi et al.9 | 2014 | 72 | Female | White | 1/Right right pinna and external auditory canal Multiple lesions on right arm and left leg | HIV− | HHV-8+ (also HHV-4+ and EBV+) |
| Our case | 2013 | 77 | Female | White | 1/Right pinna | HIV− | HHV-8+ |
EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; HHV, human herpes virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ND, not determinated.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.