To the Editor:
Mefenamic acid is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory inhibitor of cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 that is marketed in Spain under the name of Coslan (Pfizer). According to the summary of product characteristics, it is indicated for the treatment of pain, inflammation, and fever of any etiology, dysmenorrhoea, menorrhagia due to dysfunctional causes, rheumatoid arthritis, and acute or chronic gout. It can cause cardiovascular, genitourinary, gastrointestinal, hepatic, hematologic, respiratory, and cutaneous adverse effects. Fixed drug eruption (FDE), and multifocal FDE in particular, is an infrequent cutaneous adverse effect of mefenamic acid.1
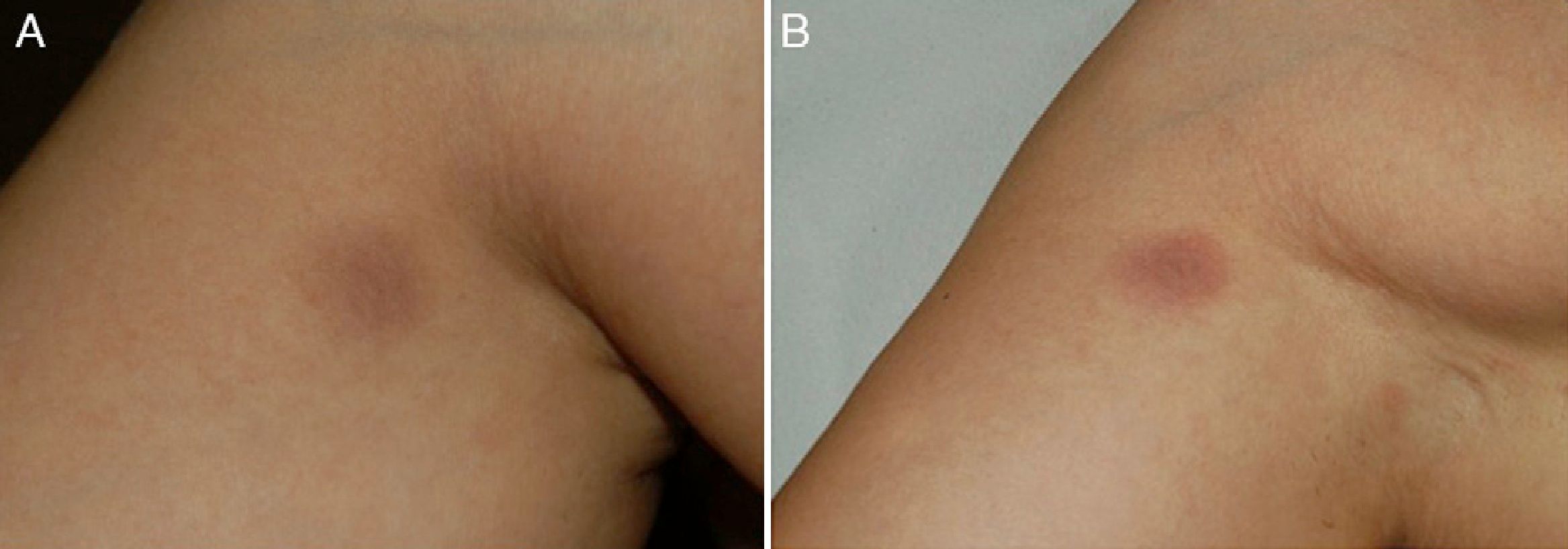
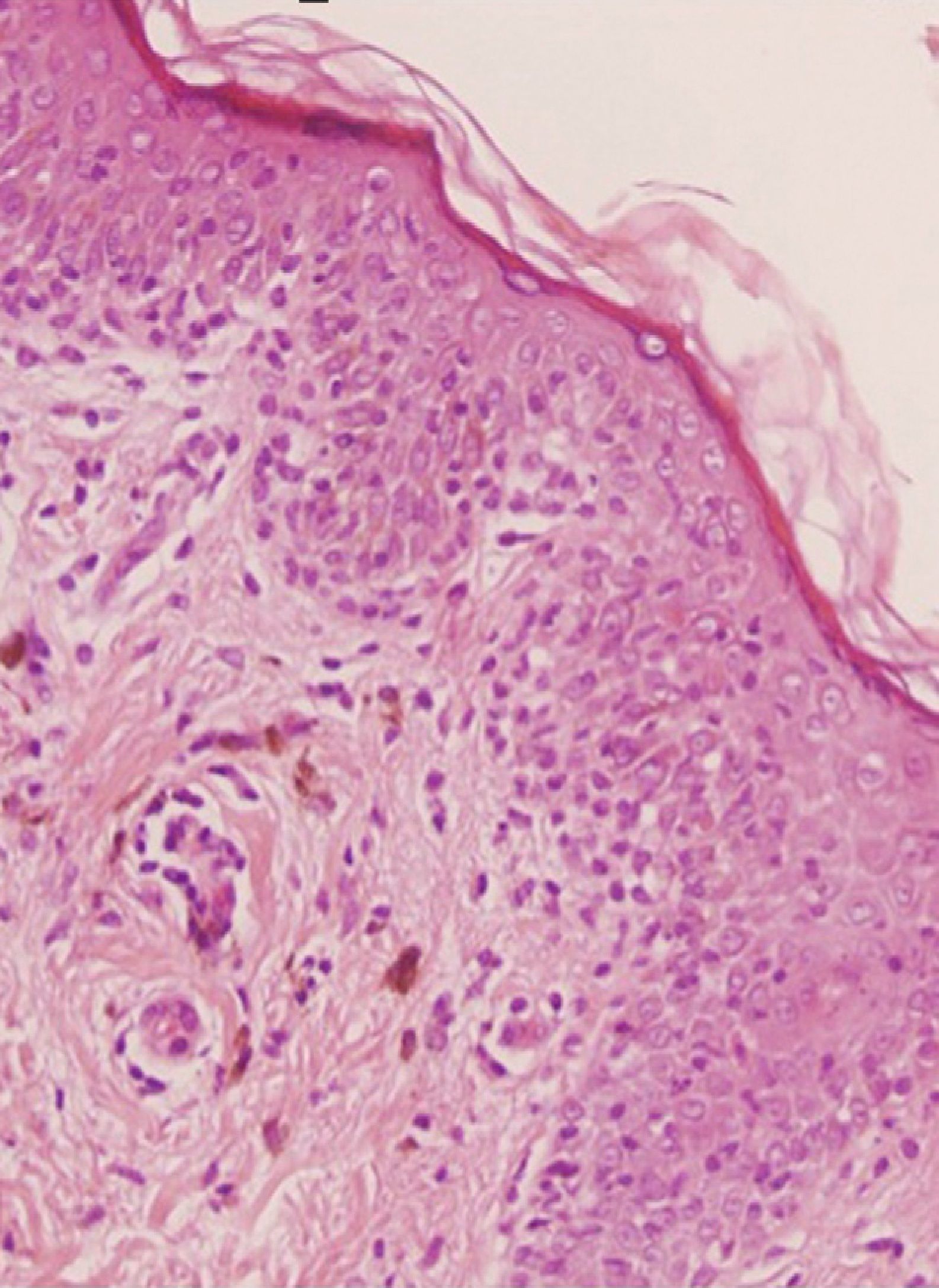
A 36-year-old woman with no relevant medical history apart from occasional treatment with mefenamic acid for dysmenorrhea (Coslan capsules, 250mg/8h) consulted for 4 skin lesions that had appeared some months earlier. She reported that the lesions occasionally caused a burning sensation but that there were no other associated symptoms. Skin examination revealed 4 round, well-demarcated, brownish-grayish macular lesions on her right shoulder, arm, and thigh, and on her left hip; the lesions measured between 1.5 and 2cm in diameter (Fig. 1A). On suspecting FDE due to mefenamic acid, we asked the patient if she noticed any changes in the lesions when she took this drug, and she stated that while she had noticed that the lesions got worse during her period, she had not related this to the drug. We reexamined the patient after an oral challenge with the drug and confirmed worsening of the lesions (Fig. 1B). Skin biopsy showed vacuolar interface dermatitis with necrotic keratinocytes and a predominantly lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate with neutrophils and eosinophils (Fig. 2). Extravasation of red blood cells was also observed in the papillary dermis. Based on the clinical and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of multifocal FDE due to mefenamic acid was made. Patch tests performed with the series recommended by the Spanish Contact Dermatitis and Skin Allergy Research Group (GEIDAC) and Coslan 30% in petrolatum applied directly to healthy and lesional skin were negative. The patient was advised to stop taking mefenamic acid. The lesions cleared gradually and only slight residual hyperpigmentation remained 6 months after the initial visit.
FDE is a skin reaction characterized by skin and/or mucosal lesions that appear at the same site each time the offending drug is taken. It usually manifests as 1 or more round hyperpigmented macular lesions that may exceptionally be accompanied by systemic symptoms, such as fever, anorexia, general malaise, nausea, and diarrhea.2 Some patients may also develop multiple, widespread lesions.1,3,4 A wide range of drugs can trigger FDE, but the most common ones are antibiotics (particularly co-trimoxazole), anticonvulsants, and analgesics.5
Mefenamic acid is an anthranilic acid derivative that inhibits prostaglandin synthesis. It was recently described as an inducer of FDE and has also been implicated in bullous pemphigoid,6 anaphylaxis,7 Stevens-Johnson syndrome,8 and linear immunoglobulin A dermatosis.9
Although mefenamic acid has been widely used in a range of medical fields, only a few cases of mefenamic acid–induced FDE have been reported to date.1,4,10 Furthermore, less common clinical manifestations have been reported in several of these cases, including multifocal dalmatian dog–like lesions,1 reticulated lesions,3 and lesions mimicking erythema multiforme.4
Diagnosis is based on clinical history and characteristic skin findings. An oral challenge test with the relevant drug is the gold standard for confirming clinical suspicion of FDE, as occurred in our case. Patch testing of lesional and healthy skin is a safe, noninvasive alternative, but it has variable sensitivity, with results differing according to the concentration and penetration of the test substance, the vehicle used, and the thickness of skin at the test site. A negative patch test result, therefore, does not rule out FDE.2
Please cite this article as: Pérez-Pérez L, et al. Exantema fijo medicamentoso múltiple probablemente inducido por ácido mefenámico. Actas Dermosifiliogr.2013;104:85-7.