A 45-year-old woman presented with a 4-month history of painful erosions on the oral mucosa and lips, and reported a weight loss of 12kg due to difficulties in eating. Over the past 2 months she had noticed painful exudative erosions on the inguinal folds and perineum as well as erythematous conjunctiva and easy tearing. She had been prescribed several systemic and topical medications, but her condition had progressively worsened.
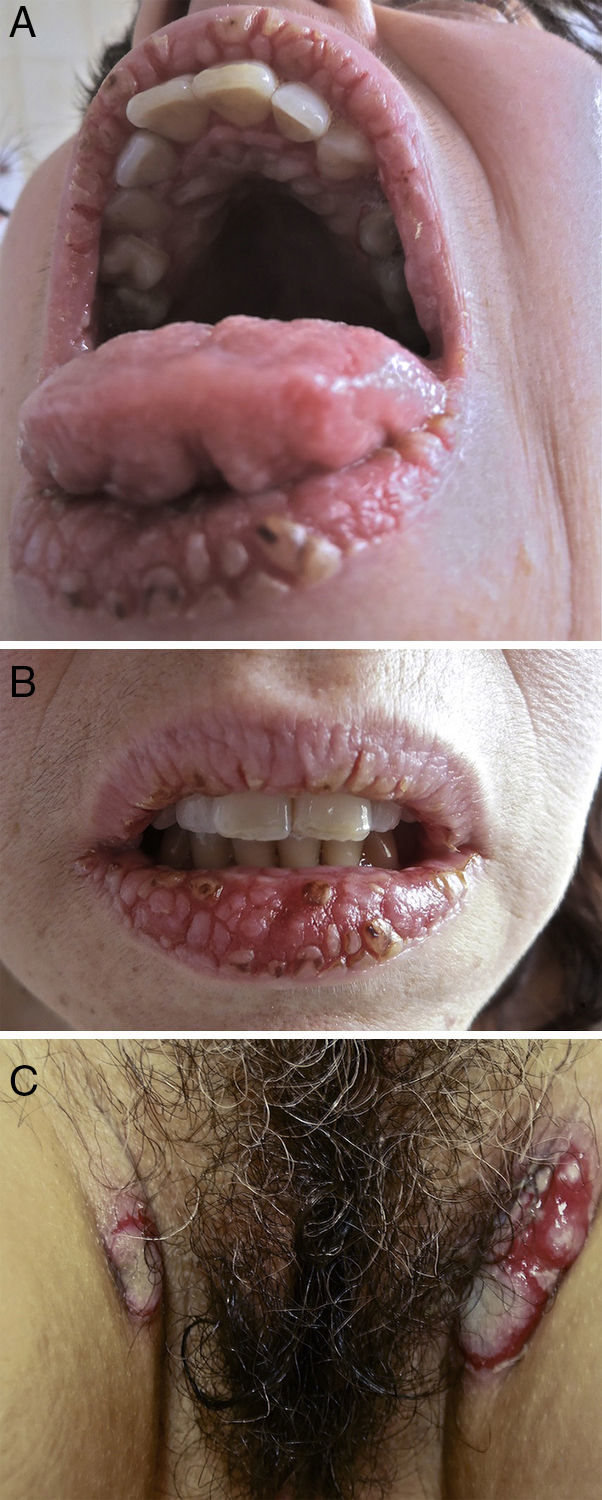
On physical examination, the surfaces of the vermillion border of the lips, the gums, and the hard palate had multiple white verrucous papules, fissures, erosions, and crusts forming a cobblestone pattern. The dorsum of the tongue had sulci and gyri that gave it a cerebriform appearance (Fig. 1A and B). On the perineum, a well-demarcated erosion with a whitish, exudative surface was seen, in addition to painful, oozing, raised erythematous plaques with a verrucous surface on the inguinal folds (Fig. 1C) and right axilla. The complete skin examination also revealed two small flaccid blisters and an erosion on the back and a superficial erosion on the left lower tarsal conjunctiva.
(A, B) Painful white verrucous papules, fissures, erosions, and crusts on the vermillion border of the lips and the hard palate (cobblestone pattern); sulci and gyri on the dorsum of the tongue (cerebriform tongue). © Oozing, raised erythematous plaques with a verrucous surface on the inguinal folds.
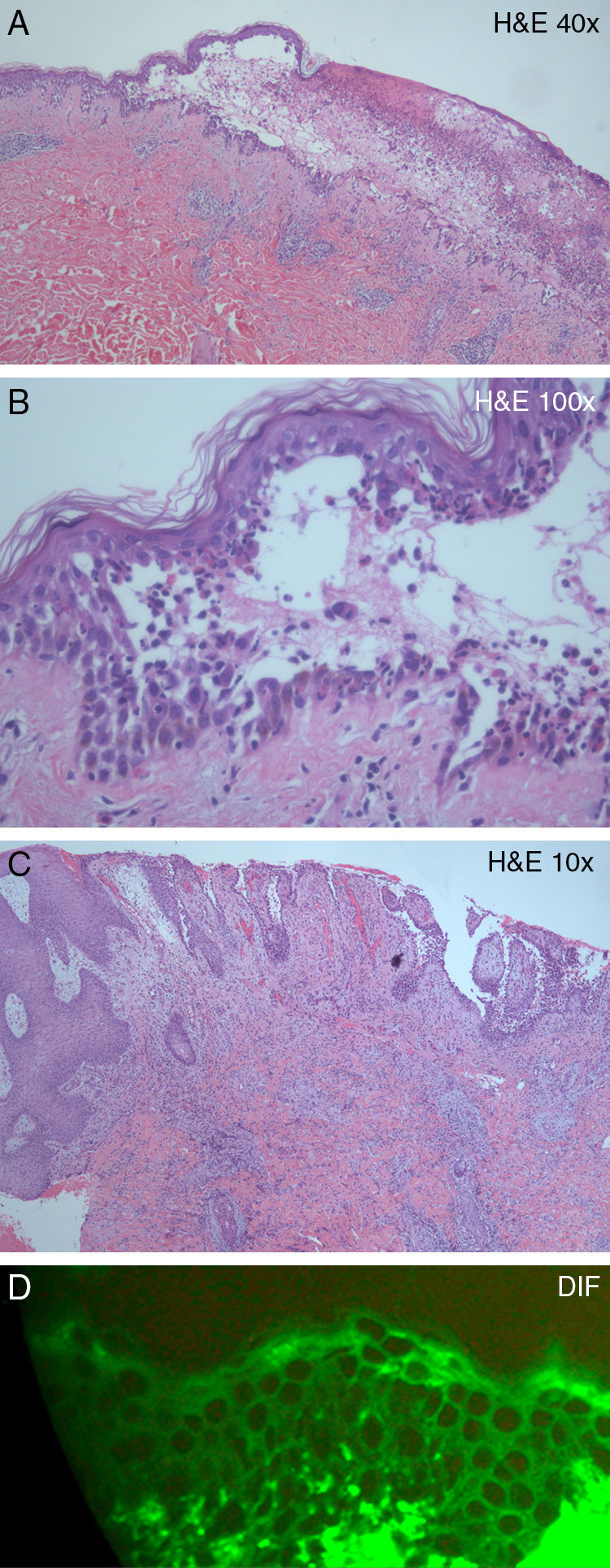
Histological examination of one of the flaccid blisters on the back revealed an intraepidermal blister and suprabasal acantholysis (Fig. 2A), as well as a dense epidermal and dermal inflammatory infiltrate, rich in neutrophils and eosinophils (Fig. 2B). Histological examination of the left inguinal vegetating plaque showed identical findings, in addition to pseudoepitheliomatous epidermal hyperplasia (Fig. 2C). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin showed intercellular staining of the epidermis by immunoglobulin (Ig) G deposits (Fig. 2D).
(A) Intraepidermal blister and a dense epidermal and dermal inflammatory infiltrate (hematoxylin–eosin, original magnification, ×10). (B) Suprabasal acantholysis and inflammatory infiltrate, rich in neutrophils and eosinophils (hematoxylin–eosin, original magnification, ×40). (C) Pseudoepitheliomatous epidermal hyperplasia and dense inflammatory dermal infiltrate (hematoxylin–eosin, original magnification, ×10). (D) Direct immunofluorescence showing immunoglobulin G intercellular epidermal deposits.
A diagnosis of pemphigus vegetans was established. The patient was treated with systemic prednisolone 60mg/d (1 mg/kg/day) with a slow taper, azathioprine 150mg/d, and topical tacrolimus 1mg/g ointment on the lips. The cutaneous and mucosal lesions regressed completely in two months and the patient was kept on azathioprine 150mg/d.
Pemphigus vegetans is a rare variant of pemphigus vulgaris, and is thought to represent a reactive response of the skin to the autoimmune insult of pemphigus vulgaris.1 It is characterized by flaccid blisters that erupt into erosions and eventually form papillomatous vegetations, especially in intertriginous areas and on the scalp or face.1,2 Involvement of the vermilion border of the lips is a clinical hallmark of oral involvement.3 The tongue may show cerebriform-like changes.1 The exuberant cobblestone pattern of the lips and oral mucosa associated with marked weight loss in the current case highlights the importance of oral manifestations of pemphigus vegetans.
Suprabasal acantholysis is an early histopathological finding in pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus vegetans. With time, the lesions acquire a verrucous and hyperkeratotic appearance and biopsy samples from pemphigus vegetans may exhibit epidermal hyperplasia, papillomatosis, and intraepidermal eosinophilic abscesses.2,4 Presence of an eosinophilic response, formation of microabscesses, and extent of vesiculation have been proposed as possible histopathological features for distinguishing pemphigus vegetans from pemphigus vulgaris.4
Direct immunofluorescence usually shows deposits of IgG and possibly C3 on the surface of keratinocytes. Circulating intercellular antibodies against desmogleins, generally of the IgG class, are detected in most patients by indirect immunofluorescence.5 The patient described in this report had elevated titers of both anti-desmoglein 3 (>200RU/mL) and anti-desmoglein 1 antibodies (142RU/mL).
The clinical differential diagnosis should include Hayley–Hayley disease, IgA pemphigus, and paraneoplastic pemphigus,5 while the histological differential diagnosis should include pemphigus vulgaris, Hayley–Hayley disease, Darier disease, and Grover disease. Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans can clinically and histopathologically resemble pemphigus vegetans and only indirect and direct immunofluorescence studies can accurately distinguish between these two entities.6
Please cite this article as: Mendes-Bastos P, Amaro C, Fernandes C. Una boca en empedrado: una presentación oral exuberante de pénfigo vegetante. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106:72–73.