A 22-year-old primipara in her 36th week of gestation (body mass index, 22) came to the clinic because of a change in the appearance of the skin below the umbilicus. The skin first began to change 2 weeks previously and was associated with pain and itching. The patient was afebrile and did not recall previous injury in the area.
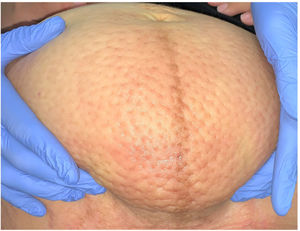
Physical ExaminationPhysical examination revealed a clearly delimited nonerythematous indurated plaque with well-defined borders in the infraumbilical area (15cm×10cm). It was remarkable for its orange-peel appearance, with symmetrical depressed dimples (Fig. 1). Palpation revealed edema with pitting. No edema was observed on the lower limbs or vulva, and there were no palpable enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
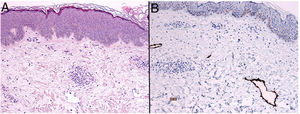
HistopathologyHistopathology analysis revealed marked dermal edema, with mild superficial and deep chronic perivascular inflammation, as well as fibrosis in the dermis (Fig. 2A). Staining for podoplanin (D2-40) highlighted irregular superficial lymphangiectasia (Fig. 2B).
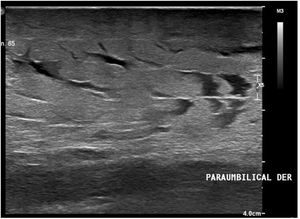
Additional TestsSoft tissue ultrasound (Fig. 3) revealed diffuse thickening of the dermis and subcutaneous cellular tissue, with marked local accumulation of fluid (visible as linear anechoic tracts). Doppler mode revealed no increase in vascularization.
What is Your Diagnosis?
DiagnosisThe patient was diagnosed with lymphedema of the lower abdominal wall secondary to pregnancy.
Clinical Course and TreatmentAfter delivery, the plaque involuted gradually, leaving no scar tissue.
CommentaryPrimary lymphedema is a congenital disease caused by abnormal development of the lymphatic system. Secondary, or acquired, lymphedema is more common and may have multiple underlying causes leading to obstruction of lymph drainage. The main cause of abdominal lymphedema is involvement of the regional lymph nodes that collect the drainage from the abdominal wall owing to resection, ablation, or radiation of the nodes.1 It may also result from invasion of the lymph node by a tumor or infection by filariae. Similarly, lymphedema of the abdominal wall may appear suddenly after high-impact injury.
In morbidly obese patients, lymphedema may appear in the infraumbilical area and is known as panniculus morbidus.2 This can grow very large, taking on the appearance of a pedunculated tumor. It is also thought to be caused mainly by obstruction of lymphatic drainage (owing to the mass effect of abdominal obesity) from the infraumbilical abdominal wall, which is collected in the superficial inguinal lymph nodes and in the common iliac lymph nodes.1 The lymphatic vessels of the supraumbilical abdominal wall, in contrast, drain to the parasternal or axillary lymph nodes, thus explaining why lymphedema usually appears in the infraumbilical area.
Abdominal lymphedema is rarely reported in pregnant women. The differential diagnosis should include malignant entities such as lymphangitis carcinomatosa, liposarcoma, and angiosarcoma.3 The patient should also be screened for infections such as cellulitis and erysipelas. Other differential diagnoses include scleredema of Buschke4 and eosinophilic fasciitis.5 The pathogenic mechanism in pregnant women is similar to that of morbidly obese individuals owing to obstruction of lymph drainage from the abdominal wall.6
The most definitive histological characteristic is marked dermal edema, together with lymphangiectasia and the variable presence of dermal fibrosis.6
This disease does not require treatment in the case of pregnant women, since the edema usually resolves after delivery. The recommendation in the case of morbidly obese patients is weight loss combined with other conservative options, such as lymphatic drainage via massage or abdominal compression bandages. If these measures fail, surgical resection of the redundant tissue is an option.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.