Solar urticaria (SU) is a rare photodermatosis characterized by sudden onset of urticarial skin lesions, intense itching or burning on photo-exposed areas, occurring a few minutes after sun exposure with great impact on patients’ quality of life. It is considered a type I hypersensitivity reaction, and therefore, it is an immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated condition that may be accompanied by other systemic symptoms and signs, such as dizziness, headache and angioedema. The action of spectrum for SU includes ultraviolet A (UVA), ultraviolet B (UVB), visible light (VL) and some patients may be sensitive to multiple action spectra. Although the diagnosis is made by the characteristic clinical presentation, it can be confirmed by phototesting.1
The treatment of choice consists in broad-spectrum sunscreens and high-dose H1-antihistamines; however, SU is often unresponsive to them. Other treatment options are leukotriene receptor antagonists, UV-hardening, cyclosporine A, antimalarial drugs, plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). Efficacy of these treatments is usually partial or transient and may induce several unwanted effects, i.e. anaphylaxis, immunosuppression and malignancy.
Omalizumab is a humanized monoclonal IgG1-kappa antibody against IgE recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency for antihistamine refractory patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who are at least 12 years of age.2 Omalizumab binds to free IgE with a greater affinity than IgE itself binds to the high-affinity Fc¿RI receptors present on basophils. Thus, it reduces the availability of free IgE for binding and promotes down-regulation of Fc¿RI on the surface of mast cells and basophils preventing IgE-mediated histamine release.3
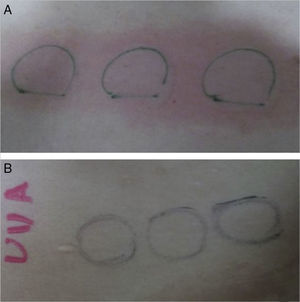
We report a case of a previously healthy 21 year-old Caucasian female with a 4-year history of erythema, intense itch, swelling and hives after minimal sun exposure even through window glass. No history of asthma or food allergy was reported. Phototest performed on the patient's back (Waldman® UV 181 UVA and Waldman® UV 800 broad band UVB) was positive for UVA, minimal urticarial dose 7J/cm2, and showed no reaction to UVB (Fig. 1). Visible light was not tested. IgE serum levels were elevated (294kU/L) and other blood test determinations fell within normal limits; cell count, porphirins, antinuclear antibodies, liver and renal function panel, and serum triptase. She was diagnosed with Solar Urticaria (SU) induced by UVA, and partially achieved to control symptoms with antihistamines (Fexofenadine hydrochloride 180mg/day) and broad-spectrum sunscreens.
Three years after diagnosis, her SU became unresponsive to first-line treatment with antihistamines, even updosing up to 4-fold. Her quality of life, as assessed by the Dermatology Quality of Life Index (DLQI 21) was seriously affected by SU. Thus, after careful consideration we decided to try experimental therapy with omalizumab. Following approval from our institution ethics committee for exceptional medical treatments, an initial dose of 300mg of omalizumab was administered in April 2015, and antihistamines were gradually discontinued. Subsequent doses of 300mg were administered monthly.
The patient reported a complete relief of symptoms within one day of the administration of the first dose (DLQI 0). She remained asymptomatic during the Spanish summer and no side effects were noted. However, a delay of omalizumab administration of one week brought back mild urticaria on one occasion. We repeated the phototest six months later to check treatment response and no reaction occurred to either UVA or UVB spectrum (Fig. 1). One year later, she is still on omalizumab and the effect is sustained.
Treatment of SU with omalizumab is still off-label; however, management of SU with omalizumab has been proved effective on several occasions3–9 and promising clinical results have recently been published.10
On a recently published phase-II multicentric study,10 the response rate of SU to omalizumab appeared close to the mean proportion of patients with CSU achieving a urticarial activity score over 7 days of 6 or less with the same dose of omalizumab, and; similar to what is observed in CSU, the improvement in solar urticaria was rapidly lost when omalizumab was stopped.
Omalizumab seems to be a new well-tolerated effective agent in the treatment of severe SU and might be soon included in SU treatment guidelines as a third-line therapy in the same way it is done with CSU.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.