A 70-year-old woman, with no relevant past medical history, consulted due to a 3-month history of yellowish multiple asymptomatic papules on her scalp, without recalling any triggering factor. She denied any other associated systemic symptoms. No other family members exhibited similar lesions either. The patient had no prior history of neoplasms, alopecia, or inflammatory diseases affecting the scalp.
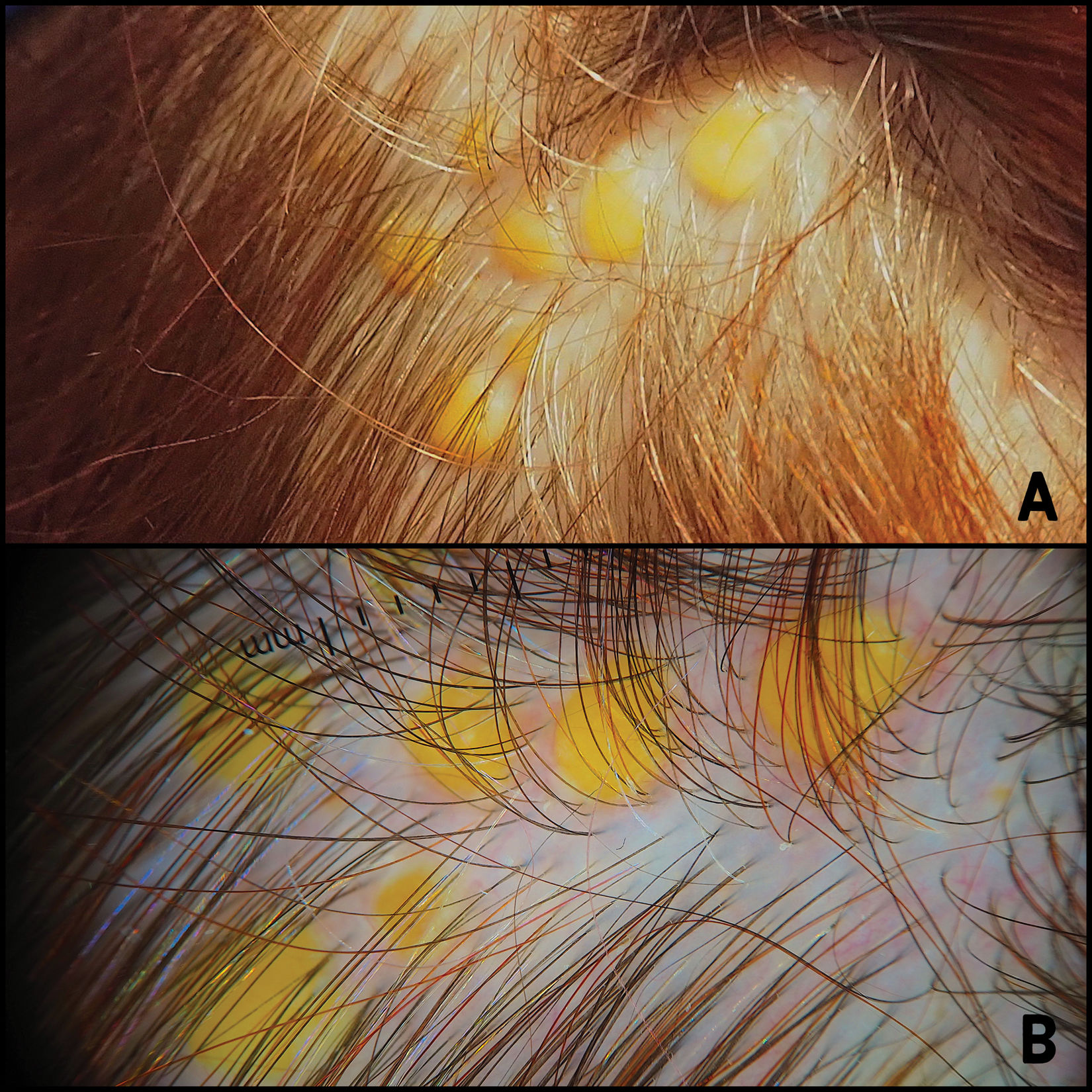
Physical examinationPhysical examination revealed 8 well-demarcated, oval-shaped, yellowish papules of a smooth surface, firm consistency, and variable diameters (3–5mm), located in the occipital region of the scalp (Fig. 1A). Dermoscopy revealed the presence of structureless yellowish areas with some small branched vessels on the surface and periphery of some lesions (Fig. 1B).
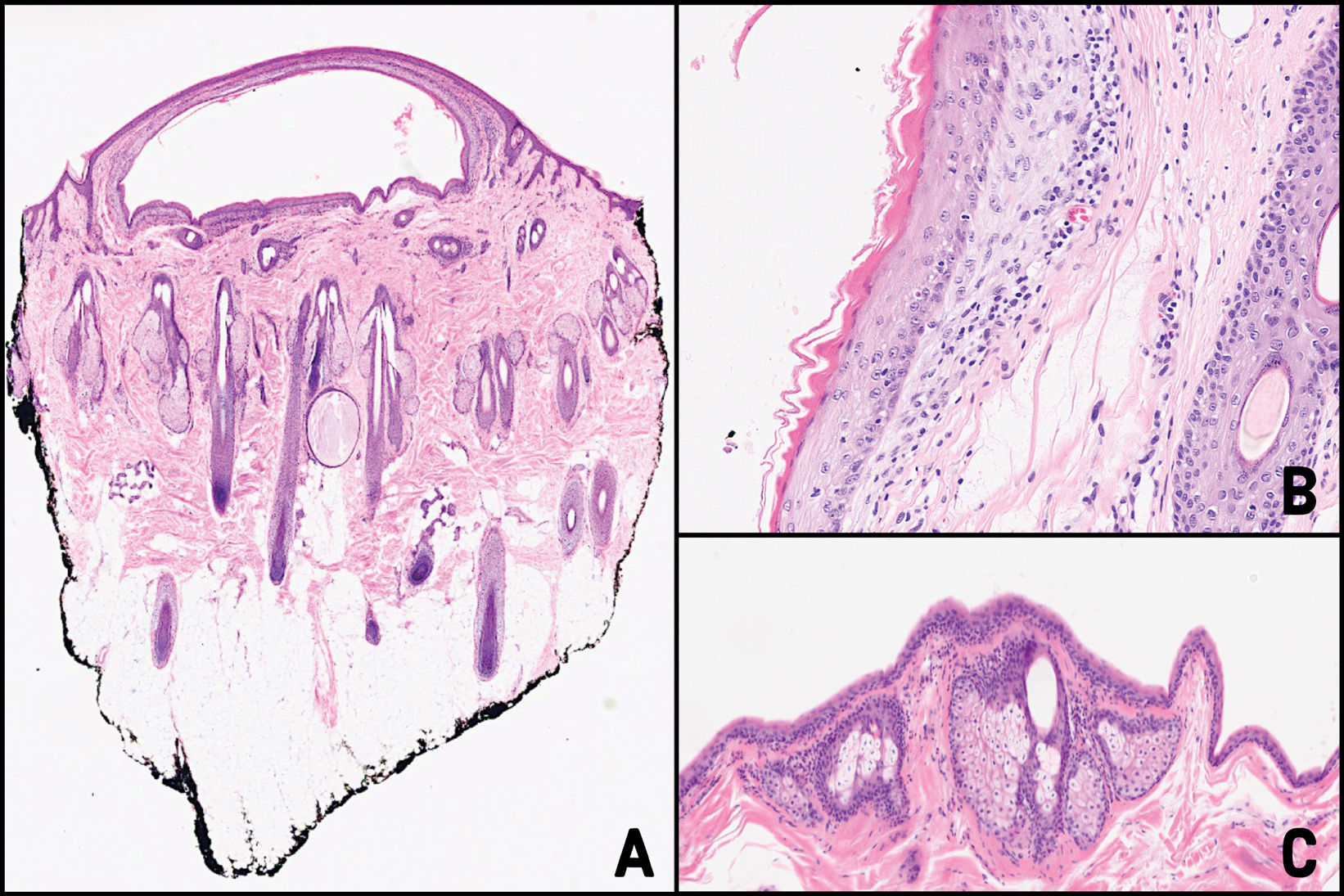
HistopathologyA 4mm punch biopsy was performed on one of the lesions. Histopathological examination revealed the presence of a cystic cavity in the superficial dermis, without internal contents (Fig. 2A). The cyst wall consisted of a stratified squamous epithelium with a few cell layers, without a granular layer, and internally lined by an eosinophilic cuticle with an undulating contour and fine projections extending into the lumen (Fig. 2B). Several sebaceous glands were adjacent to the cystic cavity (Fig. 2C).
(A) Cystic cavity in the superficial dermis. Hematoxylin–eosin ×10. (B) Higher magnification showing the cyst wall composed of a stratified squamous epithelium, without a granular layer, internally lined by an eosinophilic cuticle with an undulating contour. Hematoxylin–eosin ×50. (C) Sebaceous glands adjacent to the cystic cavity. Hematoxylin–eosin ×40.
Multiple steatocystomas.
TreatmentAfter confirming diagnosis, the patient was informed about the different therapeutic options available for this condition, including surgical excision or drainage, intralesional corticosteroids, CO2 laser therapy, cryotherapy, and even retinoids. Ultimately, given the asymptomatic nature of the lesions and the minimal esthetic impact reported by the patient, a watchful waiting approach was agreed upon.
Follow-upSubsequent follow-up evaluations showed that lesions remained stable, with no increase in number or size, and any new symptoms.
DiscussionMultiple steatocystomas are rare hamartomatous malformations of the pilosebaceous duct, typically developing in childhood or adolescence, either sporadically or in a familial pattern with autosomal dominant inheritance (associated with keratin 7 gene mutations). They present as multiple nodules or cysts of variable size (0.1–3cm) with an elastic consistency, covered by normal-colored skin, and are most widely located on the upper chest, axillae, upper limbs, and scrotum.1,2
Exceptionally, multiple steatocystomas can occur in adulthood, with lesions exclusively affecting the scalp, displaying peculiar characteristics as yellowish “pseudo-xanthomatous” papules, which require clinical differentiation from eruptive xanthomas, xanthogranulomas, or sebaceous differentiation adnexal tumors.3 Scalp-localized cases are usually sporadic and have been observed, as in this case, in middle-aged to elderly women (Table 1).1–4,8–10
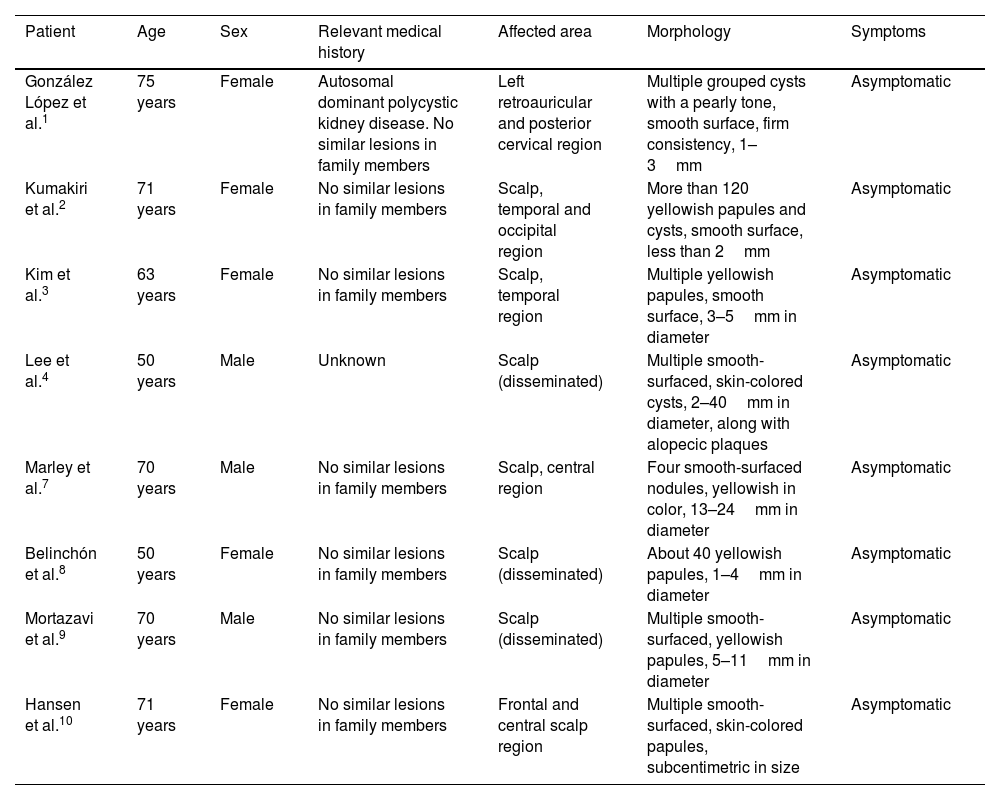
Main characteristics of localized forms of multiple steatocystomas described in literature.
| Patient | Age | Sex | Relevant medical history | Affected area | Morphology | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| González López et al.1 | 75 years | Female | Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. No similar lesions in family members | Left retroauricular and posterior cervical region | Multiple grouped cysts with a pearly tone, smooth surface, firm consistency, 1–3mm | Asymptomatic |
| Kumakiri et al.2 | 71 years | Female | No similar lesions in family members | Scalp, temporal and occipital region | More than 120 yellowish papules and cysts, smooth surface, less than 2mm | Asymptomatic |
| Kim et al.3 | 63 years | Female | No similar lesions in family members | Scalp, temporal region | Multiple yellowish papules, smooth surface, 3–5mm in diameter | Asymptomatic |
| Lee et al.4 | 50 years | Male | Unknown | Scalp (disseminated) | Multiple smooth-surfaced, skin-colored cysts, 2–40mm in diameter, along with alopecic plaques | Asymptomatic |
| Marley et al.7 | 70 years | Male | No similar lesions in family members | Scalp, central region | Four smooth-surfaced nodules, yellowish in color, 13–24mm in diameter | Asymptomatic |
| Belinchón et al.8 | 50 years | Female | No similar lesions in family members | Scalp (disseminated) | About 40 yellowish papules, 1–4mm in diameter | Asymptomatic |
| Mortazavi et al.9 | 70 years | Male | No similar lesions in family members | Scalp (disseminated) | Multiple smooth-surfaced, yellowish papules, 5–11mm in diameter | Asymptomatic |
| Hansen et al.10 | 71 years | Female | No similar lesions in family members | Frontal and central scalp region | Multiple smooth-surfaced, skin-colored papules, subcentimetric in size | Asymptomatic |
Although steatocystomas are benign, a definitive diagnosis via histological study is crucial due to their potential association with syndromes or conditions such as LEOPARD syndrome, basal cell nevus syndrome, multiple trichoblastomas, giant intracranial dermoid cyst, hypothyroidism, hypotrichosis, pachyonychia congenita, or hidradenitis suppurativa.5 These associations were ruled out in the patient. Given the benign nature of the condition and the risk of scarring and recurrence, treatment is reserved for symptomatic cases, with both surgical and non-surgical options.6
The clustered (“agminated”) distribution of these lesions, exclusively localized on the scalp, represents a novel and atypical presentation of multiple steatocystomas.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.