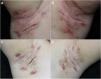
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic and recurrent inflammatory disease of the follicular infundibulum that principally affects the intertriginous regions. The estimated prevalence is 1%. T-helper (Th)-17 lymphocytes and neutrophils are the main source of the proinflammatory cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of HS.1
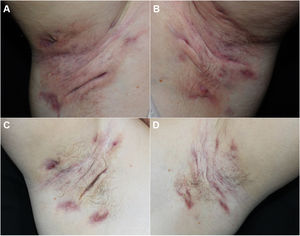
We report our experience with 3 patients with moderate to severe HS treated with 300 mg of subcutaneous secukinumab, as per the induction and maintenance regimen indicated in psoriasis. All patients signed an informed consent of off-label use. The patients were evaluated before and after treatment using the Hurley score, the International Hidradenitis Suppurative Severity Scores System, and the Modified Hidradenitis Suppurativa Score (mHSS). Serum levels of C-reactive protein before and after treatment were evaluated as a parameter of systemic inflammation. We evaluated achievement of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) therapeutic goal. We also performed a quality of life evaluation using the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). We also recorded data on prior and concomitant treatment, response time, and treatment time with secukinumab. All these data are shown in Table 1 and images of 1 of the patients are shown in Fig. 1.
Clinical Characteristics and Evaluation Scores for the 3 Cases.
| Cases | Age, Y and Sex | Previous Treatment | Concomitant Treatment | Response Time | Treatment Time | Hurley Before | Hurley After | DLQIBefore | DLQIAfter | IHS4 Before | IHS4After | mHSSBefore | mHSSAfter | HiSCR | CRP Before | CRPAfter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | 46, F | Oral antibioticsisotretinoin, acitretin, corticosteroids, sulfasalazine,methotrexate, infliximab, anakinra, adalimumab. | Intralesional triamcinolone | 4 wk | 7 mo | 3 | 2 | 28 | 17 | 13 | 3 | 59 | 10 | Yes | 11 | 2 |
| Patient 2 | 21, F | Oral antibiotics, nicotinamide, adalimumab | Dapsone, 100 mg/d | 8 wk | 12 mo | 3 | 2 | 32 | 11 | 15 | 1 | 56 | 12 | Yes | 31 | 8 |
| Patient 3 | 45, M | Oral antibiotics, acitretin, adalimumab, infliximab | Abdominal-fold surgery | 12 wk | 4 mo | 3 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 12 | 2 | 48 | 9 | Yes | 21 | 3 |
Abbreviations: DLQI indicates Dermatology Life Quality Index; F, female; HiSCR, Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response; IHS4, International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Scores System; M, male; mHSS, Modified Hidradenitis Suppurativa Score; CRP, C-reactive protein.
All 3 patients presented stage 3 on the Hurley scale, a score of 10, 28, and 32 on the DLQI, a score of 12, 13, and 15 on the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Scores System, and a score of 48, 56, and 59 on the mHSS prior to start of treatment. The response time was 4, 8, and 12 weeks. All the patients achieved a reduction of 53% on the DLQI, 85% on the IHS, 94.7% on the mHSS, and all patients showed improvement on the Hurley scale (Table 1). Levels of C-reactive protein fell by more than 70% in all cases (74%, 81%, and 85%). All patients achieved the HiSCR therapeutic goal. No adverse effects were observed during treatment.
HS is a systemic inflammatory disease, the pathogenesis of which involves principally Th-17 lymphocytes and neutrophils.2 The IL-23 produced by the dendritic cells favors differentiation into Th-17 lymphocytes. Th-17 lymphocytes promote the recruitment of neutrophils implicated in the inflammatory response of HS.2 Secukinumab is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and the interaction of cytokines with the IL-17 receptors. IL-17 regulates the expression of the antimicrobial peptides and is overexpressed in HS lesions and in the HS perilesional skin, which may explain the efficacy of anti-IL-17 drugs in HS.2
Treatment of HS poses a challenge for dermatologists and includes a medical and surgical approach. Medical treatment is based on scaled regimens of antibiotics, retinoids, and biological drugs.3 Adalimumab is currently the only biological drug approved by both the US Food and Drug Administration and by the European Medicines Agency.1,3 In recent years, however, studies have been published on the efficacy of secukinumab in moderate to severe HS.4–9
To date, secukinumab has demonstrated its efficacy in 5 case reports4–8 and in just 1 open trial with 9 patients,9 for which it was not possible to establish comparable relationships due to the lack of unanimity in the use of severity scores.
We present our experience with 3 patients with moderate to severe HS treated with secukinumab off label. All 3 patients achieved the HiSCR objective and no adverse effects were observed during treatment. Our results, together with the cases published in the literature, support the need for randomized phase-III trials to evaluate the efficacy and safety of secukinumab in HS.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Villegas-Romero I, Collantes-Rodríguez C, Valenzuela-Ubiña S, Jiménez-Gallo D. Hidradenitis supurativa moderada-grave tratada exitosamente con secukinumab. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ad.2019.07.007