Dermatology and preventive medicine have become inseparable specialties since the introduction of biological drugs with immunomodulatory and immunosuppressive activity. The reality is that, in recent years, multiple new therapies have been introduced for psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, or atopic dermatitis, all of which require prior preparation, such as updating the vaccination schedule.1 In fact, a ministerial recommendation has been issued for the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine, Shingrix®. The primary goal of the herpes zoster vaccine is to prevent its development.2
The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) (herpesviridae family) is responsible for 2 clinical conditions. Although the primary infection is chickenpox, the reactivation of the latent virus—housed in the dorsal or cranial nerve root ganglia—leads to herpes zoster.3 It is estimated that up to 90% of the population has been in contact with VZV at one time or another, 30% of which will end up developing herpes zoster (HZ) in the future, with this figure rising up to 50% in patients older than 85 years.4 According to data published by RENAVE, CNE, and ISCIII, the incidence of HZ from 2014 through 2018 remained stable at around 339/100,000 inhabitants in 2018.5 However, the number of admissions and deaths has increased in the health records from 2017 and 2018 vs previous years.6 These figures rise to a maximum incidence rate of 877.1/100,000 inhabitants in the 80-to-84-year age group due to the association between cellular immunosenescence and the risk of HZ.7 Up to 68.8% of cases diagnosed with HZ occur in patients older than 50 years, being more common among women. HZ virus infection is associated with a low mortality rate; however, complications are truly a public health issue. Risk factors include autoimmune diseases, immunosuppressants, and asthma,8 all of which are closely related to dermatology. Diseases such as psoriasis or atopic dermatitis are increasingly diagnosed in older adults, in whom the administration of immunosuppressive therapies increases the risk of HZ.9
Clinically, HZ starts with pain of varying intensity, itching, or a burning sensation along the damaged dermatome(s). More than 50% of cases will grow between T1 and L2, while in 8% up to 15% of the cases there will be trigeminal nerve involvement.10 Although the vesicular eruption on an erythematous base is easily recognizable, there is also a “zoster sine zoster”,11 where the classic lesions do not appear, and sometimes the patient is misdiagnosed with musculoskeletal disease.
The complication that has the greatest impact on the quality of life of patients who have had HZ is postherpetic neuralgia.12 Pain localized to the damaged dermatome(s) persists > 3 months after the skin lesions—if any—have completely resolved. Occasionally, it may cause functional limitation. Although there is no specific treatment for postherpetic neuralgia, the most widely prescribed therapies include analgesics, topical anesthetics, GABAergic drugs (pregabalin, gabapentin, etc.), an topical capsaicin, among others.13 That is why preventive strategies such as vaccination are essential.
The impact of the ministerial recommendation for HZ vaccination has significantly increased the number of referrals of dermatology patients to preventive medicine units since its availability in public health centers. It not only involves patients treated with the most recent drugs, such as JAK inhibitors, but also classic immunosuppressants like cyclosporine or methotrexate, which are also part of the group of patients who should be vaccinated. Table 1 shows the immunosuppressive drugs and dermatological indications, which increase the risk of HZ.
List of drugs for which complete vaccination with Shingrix® is advised before starting treatment. Most common uses in dermatology (both in technical data sheets and off-label uses).
| Drug | Use in dermatology |
|---|---|
| Rituximab | Blistering diseases (pemphigus, pemphigoid) |
| Brentuximab | Mycosis fungoides |
| Belimumab | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| Type 1 INF receptor antagonist (anifrolumab) | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| Anti-TNF alpha (adalimumab, certolizumab, etanercept, infliximab) | Psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa |
| JAK inhibitors (baricitinib, upadacitinib, abrocitinib, tofacitinib) | Atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, lupus erythematosus, calciphylaxis, dermatomyositis |
| Anti-IL6 (tocilizumab) | Schnitzler syndrome |
| Anti-IL17 (secukinumab, ixekizumab, bimekizumab, brodalumab) | Psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa |
| Anti-IL12/23 (ustekinumab) | Psoriasis |
| Anti-IL23 (tildrakizumab, guselkumab, risankizumab) | Psoriasis |
| Anti-IL1 (anakinra, canakinumab) | Autoinflammatory syndromes |
| Dimethyl fumarate | Psoriasis |
| Cyclosporine | Atopic dermatitis, psoriasis |
| Systemic corticosteroids > 20 mg/week > 10 days or > 10 mg/day for > 4 weeks | Autoimmune diseases, vasculitis, atopic dermatitis flare-ups |
| Methotrexate or > 20 mg/week | Psoriasis |
| Azathioprine | Atopic dermatitis, bullous pemphigoid |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | Blistering diseases |
In Spain, until July 2022, there were 2 vaccine options available to prevent HZ: Zostavax® and Shingrix®. However, the commercialization of Zostavax® was stopped largely due to its contraindication in patients with primary or acquired immunodeficiency, as it contains live attenuated viruses. As an alternative, Shingrix® became the only available vaccine in Spain to address HZ prevention and postherpetic neuralgia becoming a safe option, especially for patients with compromised immune systems.14 Shingrix® is an inactivated vaccine that contains glycoprotein E as an antigen and the AS01B adjuvant.15 The design of the Shingrix vaccine induces antigen-specific humoral and cellular immune responses in individuals with pre-existing immunity to VZV by combining the VZV-specific antigen (gE) with the AS01B adjuvant system. Preclinical studies show that the AS01B system causes local and temporary activation of the innate immune system through specific molecular pathways, which promotes the attraction and activation of antigen-presenting cells that carry gE-derived antigens to the corresponding lymph node, leading to the generation of gE-specific CD4+T cells and antibodies. The adjuvant effect of AS01B arises from interactions between MPL and QS-21, both formulated in liposomes. This immunogenic mechanism of Shingrix® provides, at least, a decade of protection against HZ after initial vaccination.16
Its use has been authorized in adults aged 50 and older, regardless of underlying health conditions, and in adults aged 18 and older with underlying conditions that increase the risk of HZ according to the information provided in the technical sheet.17
Initially, Shingrix® vaccination was introduced for people with the following risk conditions: aged 18 and older, hematopoietic stem cell transplants, solid organ transplants, HIV, malignant hematologic diseases, solid tumors undergoing chemotherapy, and treatment with Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. The latter have especially been added to the dermatological therapeutic armamentarium for atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, and are under investigation for diseases such as vitiligo, lupus, and other autoimmune diseases. In recent years, this vaccine has garnered interest in dermatology,18 initially due to the addition of JAK inhibitors, yet currently, the list of therapies requiring prior immunization has increased significantly.
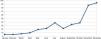
In November 2023, Shingrix® vaccination recommendations were expanded to patients with a history of 2 or more episodes of HZ—affecting up to 5% up to 6% of infected patients.19 The list of drugs for which prior HZ vaccination is recommended was expanded too. This recent situation has increased referrals of patients from various specialties significantly, generating a significant demand for preventive medicine services. The resulting increase in patient flow to preventive medicine may lead to longer waiting times for vaccine consultations, potentially delaying the start of required immunosuppressive treatment, thereby missing the window of opportunity for treating at the optimal time. Figure 1 illustrates the increase in patients at Hospital Clínico Universitario San Cecilio, Granada, Spain vaccinated against HZ as part of a preventive medicine campaign held back in 2023.
The constant increase in the use of immunomodulatory drugs in dermatology underscores the importance of being updated on the therapies and vaccines currently available. Communication between dermatology and preventive medicine services, as well as the creation of referral pathways are crucial to avoid delays in the introduction of the selected treatment. Lack of disease control is associated with more frequent visits to the ER, overuse/abuse of drugs like systemic corticosteroids, and even unscheduled patient visits, all of which come with associated costs. Therefore, vaccination in these patients needs to be prioritized, which can be achieved through a specific circuit between dermatology and preventive medicine. In our hospital, there is a specific vaccination consultation to assess this patient profile with a mean waiting time of 15 days.
In our hospital, the number of referrals from this service to preventive medicine has increased year by year, with a total of 28 patient referrals in 2021, 89 in 2022, and 169 in 2023 (Figure 1). These data show the importance of preventive medicine vaccination consultation for dermatology patients.
These changes observed in 2023 reiterate the need to create specific referral pathways across units to improve the system efficiency and standardize referral criteria, thereby improving clinical practice. There may be differences with other national and international hospitals, which is why we share our perspective in this field. The standardization of protocols benefits both the patient and the health care worker in any area. Ultimately, by seeking cohesion in knowledge and clinical practices, we can strengthen our ability to provide quality and individualized health care.
We, also, need to weigh the prescription of marketed drugs based on the risk-benefit ratio and work in full compliance with evidence-based recommendations to make the best decision regarding patient vaccination, primarily to avoid complications associated with development of HZ in more vulnerable patients. Although Shingrix® is considered a safe vaccine for all age groups, a few vaccination-related complications—mainly virus reactivation—have been reported.20 Despite this, HZ vaccination with Shingrix® is considered a cost-effective strategy,21 which is also useful for preventing HZ-related complications, especially in older adults.22
Coordination between preventive medicine and dermatology services is essential to determine the optimal time to start vaccination, whenever feasible. The HZ vaccine should preferably be administered before starting immunosuppressive treatment. Therefore, if a physician anticipates the start of immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive treatment in the near future, it is advisable to refer the patient early to the specialized vaccination consultation. However, vaccination should not be delayed if treatment is essential.23 If possible, it is recommended to complete both doses of Shingrix® before starting treatment and start treatment 4 weeks after the second dose.
In conclusion, the evident growth in referrals from dermatology to preventive medicine requires the creation of appropriate referral protocols and pathways to improve health care, avoid treatment delays, and reduce the number of complications associated with the use of immunosuppressive drugs, including the development of HZ.
FundingNone declared.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.