Inherited ichthyoses are a group of genetic Mendelian disorders of cornification that are clinically characterized by hyperkeratosis, scaling, or both, and affect all or most of the integument.1 At the First Ichthyosis Consensus Conference (Sorèze, 2009), autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI) was proposed as an umbrella term for harlequin ichthyosis, lamellar ichthyosis, and congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma.1 ARCI is a rare disorder, with an estimated prevalence of 1 case per 200000 population in Europe and 1 case per 200000–300000 population in the United States.2 According to a recent study, the estimated prevalence in Spain is 7.2 cases per million population (95% CI, 5.7–9.7).3 ARCI is diagnosed on the basis of skin findings at birth and in infancy.4
Neonates with lamellar ichthyosis typically present with a collodion membrane, which dries and peels away and is replaced by a brown, plate-like scale over the entire body. Disease course ranges from very mild to severe, with the latter involving ectropion, eclabium, scarring alopecia affecting the scalp and the eyebrows, and palmar and plantar hyperkeratosis.1,4
With respect to the molecular diagnosis of ARCI, mutations have been identified in 6 genes to date: TGM1 (transglutaminase 1), ABCA12 (ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A, member 12), NIPAL4/ichthyin (NIPA-like domain containing 4), CYP4F22 (cytochrome P450, family 4, subfamily F, polypeptide 22), ALOXE3 (arachidonate lipoxygenase 3) and ALOX12B (arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase, 12R type).5
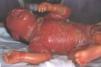
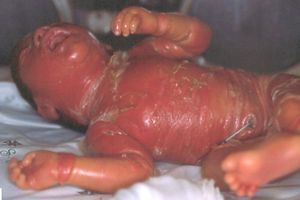
We herein report the case of a preterm girl with lamellar ichthyosis born with collodion membrane, ectropion, and eclabium at 35 weeks of gestation (Fig. 1). There was no family history of ichthyosis and the patient had no siblings. Skin biopsy revealed hyperkeratosis with stratum corneum detachment (corresponding to collodion membrane), acanthosis, and a mild lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the dermis.
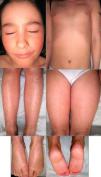
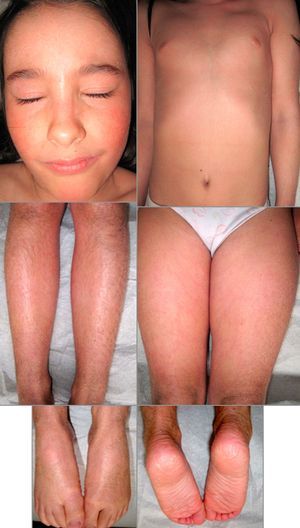
The patient has progressed favorably over a 9-year follow-up at our Pediatric Dermatology Clinic, and now presents with diffuse fine brown scaling and mild palmoplantar keratoderma; there is no ectropion, eclabium, or cicatricial alopecia (Fig. 2). Oral retinoids have been administered intermittently since the age of 5 according to dermatological status and cholesterol levels. She is currently taking oral isotretinoin 5mg (0.2mg/kg/d) every other day. She still has no siblings.
The patient was initially referred to the genetics department, where the following genes were sequentially studied: TGM1, ABCA12, NIPAL4, ALOXE3, and ALOX12B. While the first 4 genes were normal, an apparently homozygous frameshift mutation (c.1272dupC) was identified in exon 9 of ALOX12B, resulting in a truncated ALOX12B protein or diminished ALOX12B messenger RNA (mRNA) due to mRNA decay (GENDIA report). Further studies confirmed that both parents are heterozygous for this mutation.
Molecular diagnosis is crucial in ichthyosis as it provides a firm basis for genetic counseling of affected individuals and families, and also permits DNA-based prenatal diagnosis for families at risk.1In a cohort of 520 independent families with ARCI, mutations were identified by direct sequencing of the 6 ARCI genes identified to date in 78% of patients: 32% harbored mutations in TGM1, 16% in NIPAL4, 12% in ALOX12B, 8% in CYP4F22, 5% in ABCA12, and 5% in ALOXE3.6 At least 22% of the patients did not exhibit mutations in any of the known ARCI genes, indicating the existence of additional loci, such as 2 loci on chromosome 12p11.2-q13.6–8
In another study of 250 independent patients, mutations in TGM1 accounted for 38% of all ARCI cases, while mutations in ALOX12B and ALOXE3 were found in 6.8% of the cases each.9
More recently, a Spanish group identified mutations in 75% of a group of 20 patients with ARCI. TGM1 accounted for 69% of the cases and ALOXE3 mutations were detected in a single patient. No mutations were identified in ALOX12B, NIPAL4, or CYP4F22. Causative mutations could not be found in 4 cases, suggesting the involvement of ABCA12 or other loci3.
A genetic testing protocol has been proposed for individuals with ARCI. Sequence analysis should start with TGM1, except in cases of harlequin ichthyosis, where ABCA12 should be performed first. If negative, further diagnostic testing of ALOX12B, ALOXE3, and NIPAL4 should be performed.4
Generally, there seems to be a limited genotype–phenotype correlation in ARCI.1 However, mutations in ALOX12B have been related in mild to moderate phenotypes, including minor manifestations such as white or light-brown scaling, with moderate or no erythema.5 In fact, a recent study found ALOX12B mutations to be the leading cause of self-healing collodion baby in Scandinavia (8/15 patients)10. The mild ichthyotic phenotype observed in our patient is consistent with these data.
We have reported the case of collodion baby with lamellar ichthyosis and a favorable disease course for whom the search for less common mutations, such as those involving ALOX12B, was essential for correct diagnosis and genetic counseling.