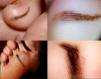
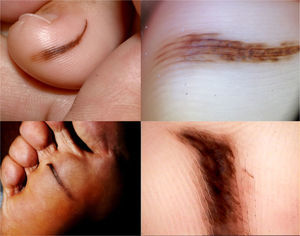
Acquired melanocytic nevi usually exhibit an oval or round shape on all body skin surfaces. Although this morphology is also the most frequent among nevi localized on the sole of the foot, we have observed a group of lesions in this location with a marked disproportion between width and length. This particular appearance has not been previously described, and it could be mistaken for malignancy. We present a series of 9 patients with elongated plantar nevi and discuss their main clinical, dermoscopic and histopathological features. Interestingly, all the lesions presented with a linear appearance, with a length greater than 7mm. Although this measurement has been considered highly suggestive of suspicious malignant lesions in the literature, we have only found one melanoma among our cases. We would like to highlight the importance of this particular presentation of acral melanocytic nevus to avoid an incorrect diagnosis of malignancy.
We describe the clinical and dermoscopic characteristics of nine patients with a clinical diagnosis of melanocytic sole nevi who presented between 2007 and 2013 at the Pigmented Lesion Unit of the Dermatology Department of the General Hospital of Alicante (Fig. 1). The dermoscopic evaluation was performed by DermLite Foto™ (3Gen, LLC, Dana Point, CA, U.S.A.) mounted on a digital camera (Canon G9 and G12™) and with a digital videodermoscope (MoleMax II™). Melanocytic lesions with suspicious clinical or dermoscopic features were excised and histopathologically evaluated and cases without evidence of malignancy underwent videodermoscopic follow-up. Characteristics of the cases are summarized in Table 1.
Characteristics of the cases of the nine elongated nevi on the sole.
| Age (years)/sex | Congenital/Adquired | Location | Dimensions(lengh×width) | Dermoscopy acral pattern | Histology | Time of follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43/woman | Congenital | Forefoot, right sole | 10×4mm | Fibrillar pattern | Intradermal melanocytic nevus | − |
| 47/man | Adquired | Forefoot, right sole | 28×3mm | Parallel furrow pattern+fibrillar pattern | No: follow up | 28 months |
| 24/woman | Adquired | First finger, right foot | 17×3mm | Lattice-like pattern | Combined melanocytic nevi | − |
| 13/woman | Congenital | First finger, right foot | 10×3mm | Parallel furrow pattern | No: follow up | 50 months |
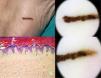
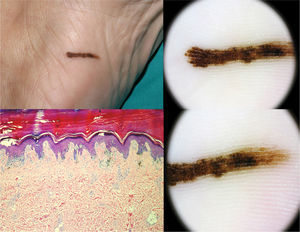
| 49/woman | Adquired | Midfoot | 20×2mm | Parallel ridge pattern | In situ melanoma | − |
| 40/woman | Adquired | Forefoot, right sole | 14×3mm | Fibrillar pattern | No: follow up | 55 months |
| 10/man | Congenital | Midfoot, left sole | 16×2mm | Parallel furrow pattern+lattice-like pattern+broad, bluish-gray structureless | No: follow up | 68 months |
| 11/man | Congenital | Fourth finger, right foot | 18×2mm | Parallel furrow pattern+lattice-like pattern+broad, bluish-gray structureless | Combined melanocytic nevi | – |
| 8/man | Congenital | Third finger, right foot | 14×4mm | Parallel furrow pattern+lattice-like pattern+broad, bluish-gray structureless | Combined melanocytic nevi | − |
The cases included 4 men and 5 women, ranging in age from 10 to 49 years old (median age 21) and all were Caucasian. The median length nevus was 17mm, while the median width was 3.1mm. Dermoscopy showed a combination of various types of acral benign dermoscopic patterns (parallel furrow and typical fibrillar patterns) in 8 out of the 9 nevi (Table 1). These melanocytic nevi without dermoscopic signs of malignancy were all closely monitored (every 6 months) by videodermoscopy without evidence of neoplastic transformation. Melanoma in situ was detected in one out of ten patients, whose lesion had shown an atypical dermoscopic parallel ridge pattern (Fig. 2). An analysis of the recorded images permitted us to observe a particular disproportion between length and width in these plantar skin nevi. Despite their large size (diameter>7mm is considered a dermoscopic criterion of suspicion of malignancy) and asymmetry, we have observed that most nevi with this morphology are benign lesions.
The clinical morphology and histology of melanocytic nevi are conditioned by the anatomical location of the lesions. The pressure supported by plantar skin determines the expression of particular clinical, dermoscopic and histological features, making the diagnosis of plantar melanocytic lesions sometimes difficult in these areas.1 In the difficult clinical dermoscopic evaluation of pigmented lesions on acral skin, the most useful feature to rule out a melanoma is the absence of a parallel ridge pattern.2–4 However, size has been also reported in the literature as a crucially important factor for the correct diagnosis of melanoma with nevoid features on the plantar area. Saida et al. studied 140 melanocytic lesions and only a few benign acquired melanocytic nevi on the sole were more than 7mm in maximum diameter and none exceeded 9mm.5 There is widespread agreement that size of acral lesions is an important clinical criterion when considering malignancy, and nevi with diameters over 7mm are at least suspicious.5,6 It is important to note that five of our cases presented congenital nevi. Congenital lesions usually show a larger diameter and are diverse in size, and they show more heterogeneous color and shape than acquired melanocytic nevi. In addition, acral nevi have characteristic dermoscopic features such as a globulostreak pattern, a homogeneous pattern, and a nontypical pattern.7
In conclusion, we have identified a subgroup of patients who presented with pigmented lesions located on the soles with a marked disproportion between length and width, with a diameter greater than 7mm. We do not know the pathogenesis of the particular morphology of the nevi in our series, but we hypothesize that the distribution of melanocytes following the lines of Blaschko on the acral skin could be responsible for this particular shape. These pigmented nevi showed variable dermoscopic findings, without any particular location on the sole. Although this larger size is regarded as a suspicious finding in itself, we suggest that nevi with this particular morphology are benign lesions in most cases when associated with typical dermoscopic criteria. We recommend the early extirpation of all suspicious nevi presenting a parallel ridge pattern of any size and morphology, and a close follow-up of elongated lesions over 7mm in their maximum diameter with benign parallel furrow dermoscopic pattern (and its variants), until these particular melanocytic lesions have been better characterized.