Capecitabine is an orally administered prodrug of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), which is converted into its active metabolite through the enzyme thymidine phosphorylase. The primary indications for the use of capecitabine include the treatment of breast and colorectal cancer.1 This drug has been associated with various mucocutaneous adverse reactions, including radiation recall phenomenon, photosensitivity, inflammation of actinic keratosis, palmoplantar keratosis, and hand-foot syndrome (HFS).2 Pigmentation disorders, particularly hyperpigmentation, have been described in relation to the use of capecitabine, especially in patients with darker skin types.3 This hyperpigmentation can be diffuse, sometimes with an acral predominance, accentuation in skin folds, and occasional mucosal involvement. However, although capecitabine-related focal pigmentation or acral lentiginosis has been reported, it is likely underreported in the medical literature currently available.
This is the case of a 65-year-old woman with phototype IV treated with third-line chemotherapy with capecitabine due to metastatic breast carcinoma. She presented with pigmented skin lesions on her palms and soles 2 months after starting treatment.
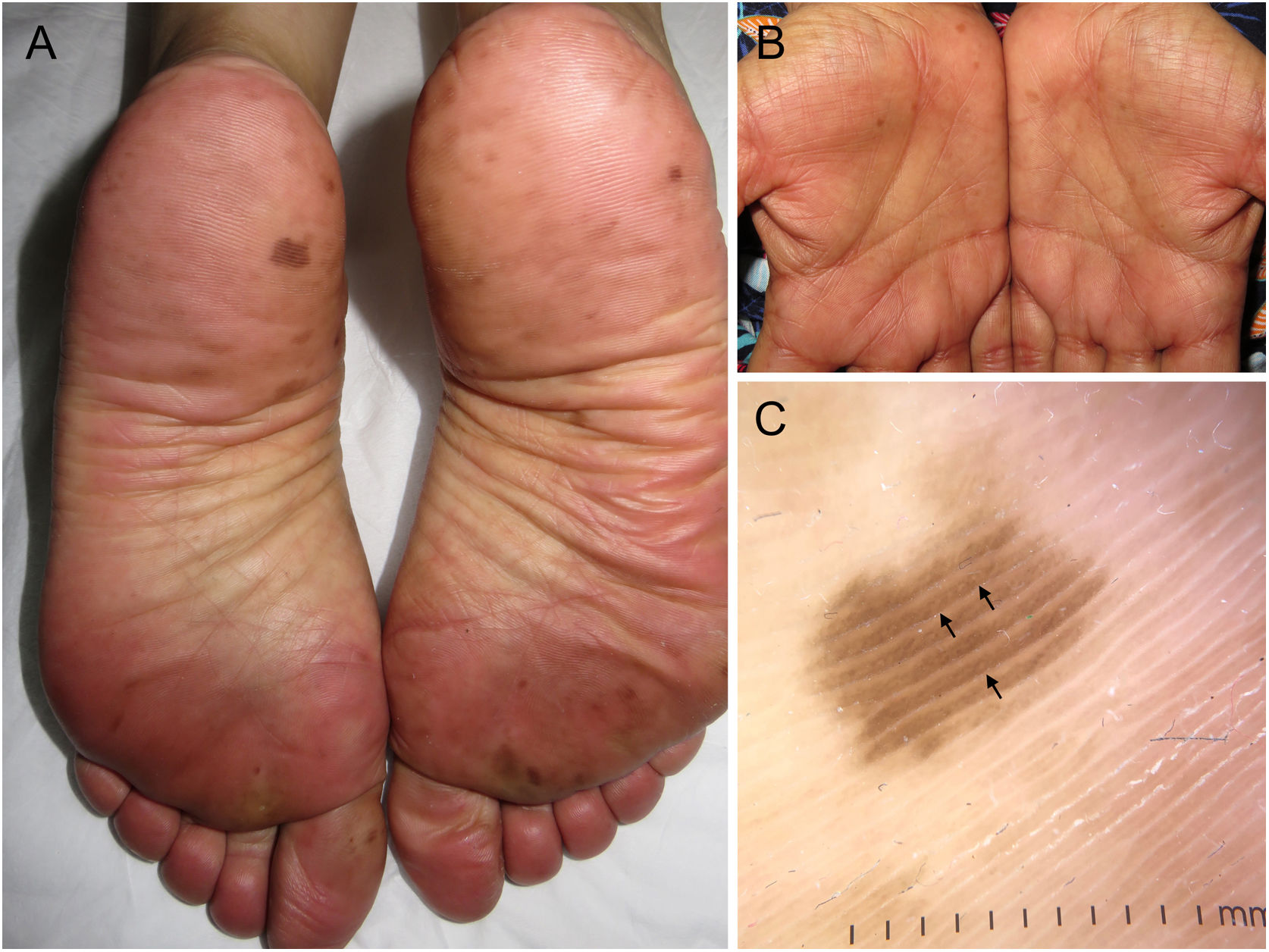
The physical examination revealed the presence of brown, focal, well-demarcated pigmented macules—3 mm to 10 mm in diameter—mainly on the soles and less so on the palms (figure 1A and figure B). Dermatoscopy with polarized light revealed the presence of a parallel ridge pattern in the lesions, with spared acrosyringium (figure 1C). We should mention that the patient concurrently developed signs of grade II HFS, along with dysesthesia, erythema, and discomfort while walking, all of which began after the patient's third cycle of treatment.
A) Brown pigmented macules with a lentiginous appearance distributed along the plantar surface of both feet added to the presence of erythema and mild edema, predominantly in both forefeet. B) Similar lesions, smaller in size and fewer in number, on both palms of the hands. C) Dermatoscopic image of a plantar lesion showing a parallel ridge pattern with spared acrosyringium (arrows).
Despite the observation of a parallel ridge pattern on the dermatoscopic examination, these lesions were not considered suspicious due to their multifocal nature and recent appearance. Therefore, no histopathological examination or other complementary tests were performed on the patient. Symptomatic management control measures for the HFS were advised, but the patient passed away a few weeks later due to the progression of her neoplastic disease.
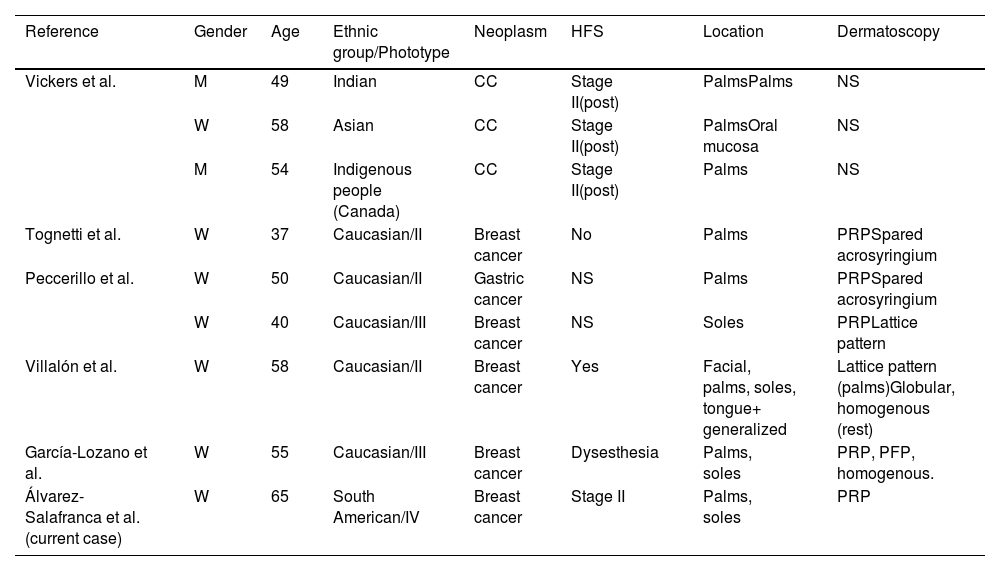
The occurrence of capecitabine-related focal palmoplantar pigmentation is poorly documented. After a detailed review of the medical literature available, only 8 cases were found in 5 different articles published from 2008 through 2019 (table 1). However, we should mention that the terminology used to describe this condition in each case varies, making it even more challenging to conduct a bibliographic search.
Previously published case reports of capecitabine-induced acral focal pigmentation.
| Reference | Gender | Age | Ethnic group/Phototype | Neoplasm | HFS | Location | Dermatoscopy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vickers et al. | M | 49 | Indian | CC | Stage II(post) | PalmsPalms | NS |
| W | 58 | Asian | CC | Stage II(post) | PalmsOral mucosa | NS | |
| M | 54 | Indigenous people (Canada) | CC | Stage II(post) | Palms | NS | |
| Tognetti et al. | W | 37 | Caucasian/II | Breast cancer | No | Palms | PRPSpared acrosyringium |
| Peccerillo et al. | W | 50 | Caucasian/II | Gastric cancer | NS | Palms | PRPSpared acrosyringium |
| W | 40 | Caucasian/III | Breast cancer | NS | Soles | PRPLattice pattern | |
| Villalón et al. | W | 58 | Caucasian/II | Breast cancer | Yes | Facial, palms, soles, tongue+ generalized | Lattice pattern (palms)Globular, homogenous (rest) |
| García-Lozano et al. | W | 55 | Caucasian/III | Breast cancer | Dysesthesia | Palms, soles | PRP, PFP, homogenous. |
| Álvarez-Salafranca et al.(current case) | W | 65 | South American/IV | Breast cancer | Stage II | Palms, soles | PRP |
CC, colorectal cancer; HFS, hand-foot syndrome; NS, not specified; post, posterior; PFP, parallel furrow-pattern; PRP, parallel ridge pattern.
Capecitabine-induced focal acral hyperpigmentation seems to be more common in patients with darker phototypes and certain ethnic groups.4 However, data are limited, and some cases have been reported in the Caucasian population as well.5,6 Additionally, over half of all cases reported have been associated with the development of HFS.4,6 Although the frequency of occurrence of HFS during capecitabine treatment is high, there is not enough evidence to establish a clear relationship between these 2 entities.
The etiopathogenesis of hyperpigmentation associated with 5-FU or its prodrugs is largely unknown. In some cases, it has been associated with a photosensitivity mechanism, but this probably doesn’t explain hyperpigmentation in non-photoexposed areas, including palmoplantar skin.3 In these locations, the skin is characterized by a higher rate of basal cell proliferation and increased expression of thymidine phosphorylase. This could explain a greater sensitivity to these cytotoxic drugs and has been hypothesized as a possible explanation to the development of HFS in patients treated with capecitabine.8
Regarding the histopathology of these lesions, no available data relate specifically to capecitabine perhaps due to the absence of suspicion of malignancy and the patients’ baseline characteristics. However, in 2 similar cases associated with tegafur—another 5-FU prodrug—variable findings included basal layer hyperpigmentation, large and atypical melanocytes in the basal layer, proliferation of single melanocytes without nest formation, or presence of melanophages in the upper dermis.9,10 In this regard, Park et al. suggest that tegafur-related acral lentiginosis could be due to drug-induced stimulation and hyperplasia. Also, they state that it disappears after treatment withdrawal.
Dermatoscopically, these lesions may show a parallel ridge pattern—which is characteristic of acral melanoma but with spared acrosyringium—as seen in our patient.5,6 Less frequently, other dermatoscopic patterns such as parallel furrow, lattice, or globular patterns have been reported.7,11 We should mention that other benign entities such as exogenous pigmentation, pigmented warts, or subcorneal hemorrhages can also show a parallel ridge pattern. As a matter of fact, certain acquired or hereditary syndromes such as the Laugier-Hunziker syndrome and the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome can show pigmented acral macules with this dermatoscopic pattern.12,13 The latter is particularly important regarding differential diagnosis due to these patients’ predisposition to develop GI and breast tumors, which by the way are the main indications for capecitabine.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.