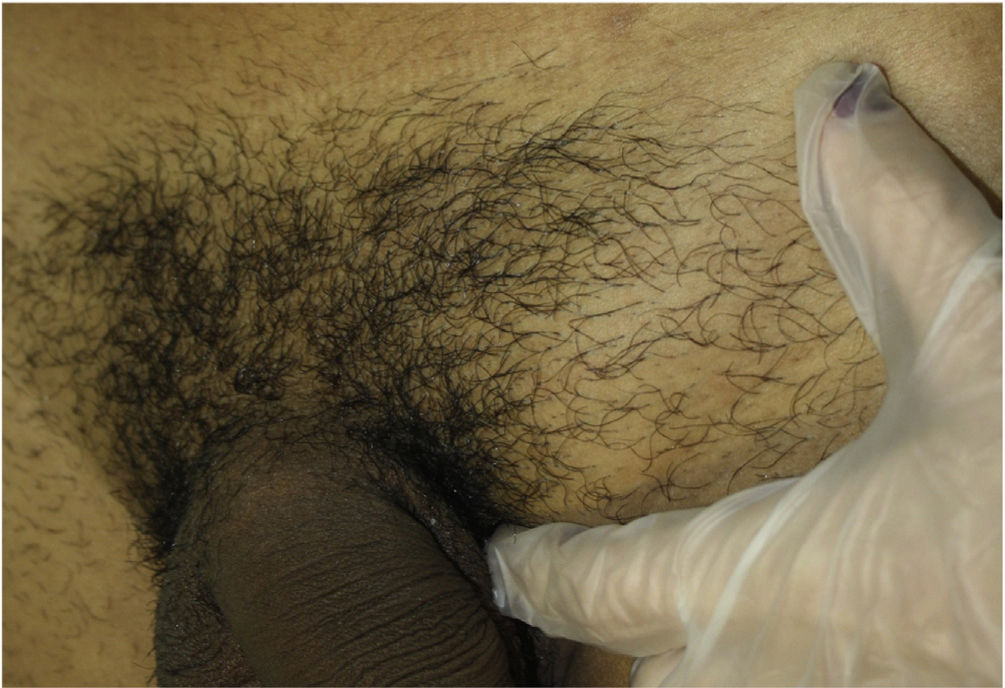
We report the case of a 23-year-old man who visited our department with a painful swelling in the left groin area that had appeared 2 weeks earlier. The patient had no fever, systemic symptoms, or constitutional symptoms. The patient’s personal past history included a gonococcal infection and multiple high-risk homosexual relations. Physical examination revealed a painful, elastic, subcutaneous nodule not adhered to the deep layers, measuring 4 cm, with normal overlying skin (Fig. 1). The patient presented no oral, genital, or anal lesions, or urethral secretion, and presented no enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, axillae, or groin, nor accompanying skin lesions.
A sexually transmitted infection was suspected and serology, cultures, and PCR of an anal and a urethral sample for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae were requested. All serology and microbiological studies were negative.
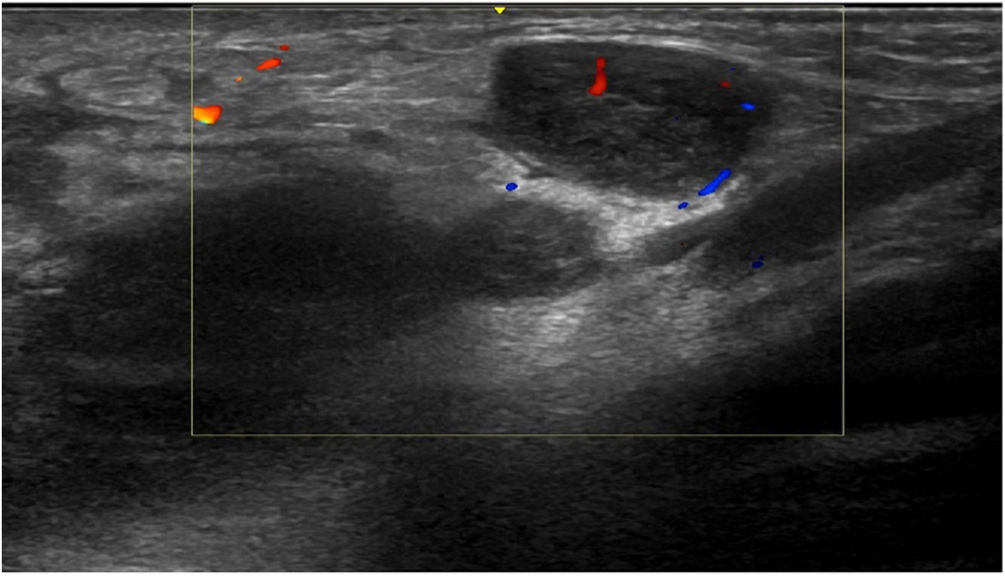
Three weeks later, the patient presented with an increase in size of the nodule in the left groin; the nodule then measured 8 cm, with a discrete fluctuation, and ultrasound was performed, together with fine-needle aspiration of the content of the lesion for a microbiological study. Ultrasound of the left groin showed multiple nodular images with hypervascularization, compatible with enlarged lymph nodes of significant size and appearance (Fig. 2). PCR of the aspirate was positive for serovar L C. trachomatis.
In light of the diagnosis of lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV), the patient was treated with doxycycline at a dosage of 100 mg every 12 hours for 21 days, with complete remission of clinical symptoms.
LGV is a sexually transmitted infection caused by serovars L1, L2, and L3 of Chlamydia trachomatis, which is endemic in tropical countries of Asia and the Americas.1–4 It is transmitted via vaginal, anal, or oral sexual contact. This infection was rare in Europe until 2003, when the incidence of cases of the disease began to increase, mainly affecting men who have sex with HIV-positive men.1,3–6 The growing incidence of this disease in Spain led it to be included as a disease subject to mandatory reporting, individualized since 2015.5
The clinical presentation of LGV varies depending on the geographic location of the cases. Classical presentation of LGV, typical of Asia and the Americas, is divided into 3 phases: the first phase is characterized by a painless sore at the inoculation site, which appears between 3 and 30 days after contact; the second phase involves the appearance of painful enlarged lymph nodes; and the final phase involves lymphedema and elephantiasis due to the irreversible destruction of the lymphatic system if left untreated.1,2
In Europe, this sexually transmitted infection manifests as proctitis with rectal pain, tenesmus, anorectal bleeding, and constipation, which can develop into abscesses, fistulae, and rectal stenosis if not treated in the initial phases of the disease. These clinical signs and symptoms require a differential diagnosis with other causes of proctitis, such as inflammatory bowel disease.1,2,5,6
The diagnosis of LGV consists of detecting the nucleic acids of C. trachomatis in the exudate of the anogenital sore, rectal exudate, or the aspirate from fluctuating enlarged lymph nodes. It is common for the PCR of anal and urethral samples to be negative in the second phase of LGV, with positive results in 20% of rectal samples and 0.8% of urethral samples; a microbiological study of the lymph-node aspirate is therefore useful.7 If infection with C. trachomatis is confirmed, the serovar is then identified.1,3 It is important to note that screening for this infection should be performed in men who have sex with men who have had receptive anal relations in the previous 6 months.5,8
The first line of treatment for LGV is 100 mg of oral doxycycline every 12 hours for 21 days, which produces complete resolution in most cases.1,3,8
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Vallejo-Ruiz MS, Kueder-Pajares T, Hernández-Núñez A, Borbujo J. Adenopatías inguinales dolorosas tras relaciones sexuales sin protección. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113:89–90.