Scabies is an ectoparasitic dermatosis caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis mite, which lives and reproduces in humans. Its incidence in Spain has increased in recent years. The aim of this study was to complement existing evidence on the increasing number of scabies cases in our country by analyzing changes in ectoparasiticide prescriptions and Internet searches for scabies infestations measured by Google Trends. We also examined correlations between these two variables. Our results show that public interest in scabies has increased in recent years and is positively and significantly correlated with an increasing use of ectoparasiticides. We believe that Google Trends should be considered as a complementary tool for monitoring real-time trends in scabies infestations in Spain.
La escabiosis es una dermatosis ectoparasitaria causada por Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis y cuyo reservorio son los humanos. En los últimos años se ha visto un incremento de los casos de escabiosis en nuestro país. El objetivo de este trabajo es complementar la evidencia existente sobre el aumento de la escabiosis en España mediante el estudio de la evolución del consumo de medicamentos ectoparasiticidas y el análisis temporal en Google Trends de las búsquedas en internet relacionadas con la infestación, así como explorar la relación entre ambos fenómenos. Nuestro estudio demuestra un incremento del interés público en la escabiosis y del consumo de ectoparasiticidas en los últimos años en España, existiendo una correlación positiva y significativa entre ambos fenómenos. Proponemos Google Trends como una herramienta complementaria a tener en cuenta a la hora de monitorizar en tiempo real el comportamiento de esta infestación en nuestro país.
Scabies, which is classified as a neglected tropical disease by the World Health Organization, is an ectoparasitic dermatosis caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis mite, which lives and reproduces in humans.1 Although in the past, scabies was typically associated with situations of poverty, poor hygiene, and overcrowding due to wars, forced displacement, and economic crises, it is currently endemic in many developing countries, and epidemiologically, it can now be considered a broadly global disease.2
It is difficult to estimate the global prevalence and impact of scabies, in part because of the associated stigma and because it is not a notifiable disease in most countries.3 Nonetheless, the number of scabies cases diagnosed in Spain has been on the rise since 2014, with some studies suggesting a recent explosion4,5 and similar reports from other European countries.6–8 Because, however, there are no epidemiological surveillance programs for scabies in Spain, the true magnitude of the epidemic in our country is unknown.
One way of tracking changes to the incidence of diseases not covered by traditional epidemiologic surveillance systems in the public health field is to analyze drug sales data. Another potentially useful method for indirectly estimating certain epidemiologic characteristics of many health conditions, including skin infestations, is to analyze public interest via internet search trends in a given country or region over time.9–11 Google Trends is a free tool that can be used to analyze changes in the popularity of Google search terms applied to specific time periods and places.12 The tool uses a measure called relative search volume (RSV), which has a scale of 0 to 100, where 100 indicates the highest percentage of searches for a term in a given place and time. An RSV of 0 does not necessarily mean that no searches were conducted; it simply indicates low interest relative to terms with a peak RSV (RSVmax).
Google Trends offers several advantages, including a free, simple, and fast tool for analyzing real-time changes in a large database and comparing searches across topics, periods, and geographic areas. It also has its limitations. Notably, people older than 65 years use the internet less, the data provided are relative, and it is not possible to stratify by age, sex, or other variables of interest.
The aim of this study was to complement existing evidence on the increasing number of scabies cases in our country by analyzing changes in ectoparasiticide prescriptions and internet searches for scabies infestations measured by Google Trends. We also examined correlations between these 2 variables.
Material and MethodsWe conducted a targeted search of ectoparasiticide sales (code P03A) on the Spanish Ministry of Health website13 and collected annual data for the years 2009 to 2021 and monthly data from January 2020 to February 2022.
We also examined Google search volumes for terms relating to scabies in Spain for the period January 2004 to June 2022. The terms used were sarna and escabiosis (Spanish terms for scabies), and escabiosi (the Catalan term). Terms such as itch, pruritus, and treatment resistance were excluded as they were considered nonspecific. The Google Trends search was conducted on June 27, 2022.
Statistical analyses were conducted in the software program StatPlus. For the descriptive analysis, mean and standard error of the mean (SEM) were used as measures of central tendency and dispersion, respectively. Correlations between variables were studied using linear correlation analysis.
ResultsChanges in Ectoparasiticide Sales in SpainThe data obtained from the Spanish Ministry of Health showed an uninterrupted growth in the sale of ectoparasiticides with a medical prescription since 2014, with a minimum interannual increase of 15.22% (2014-2015) and a maximum interannual increase of 61.92% (2020-2021).
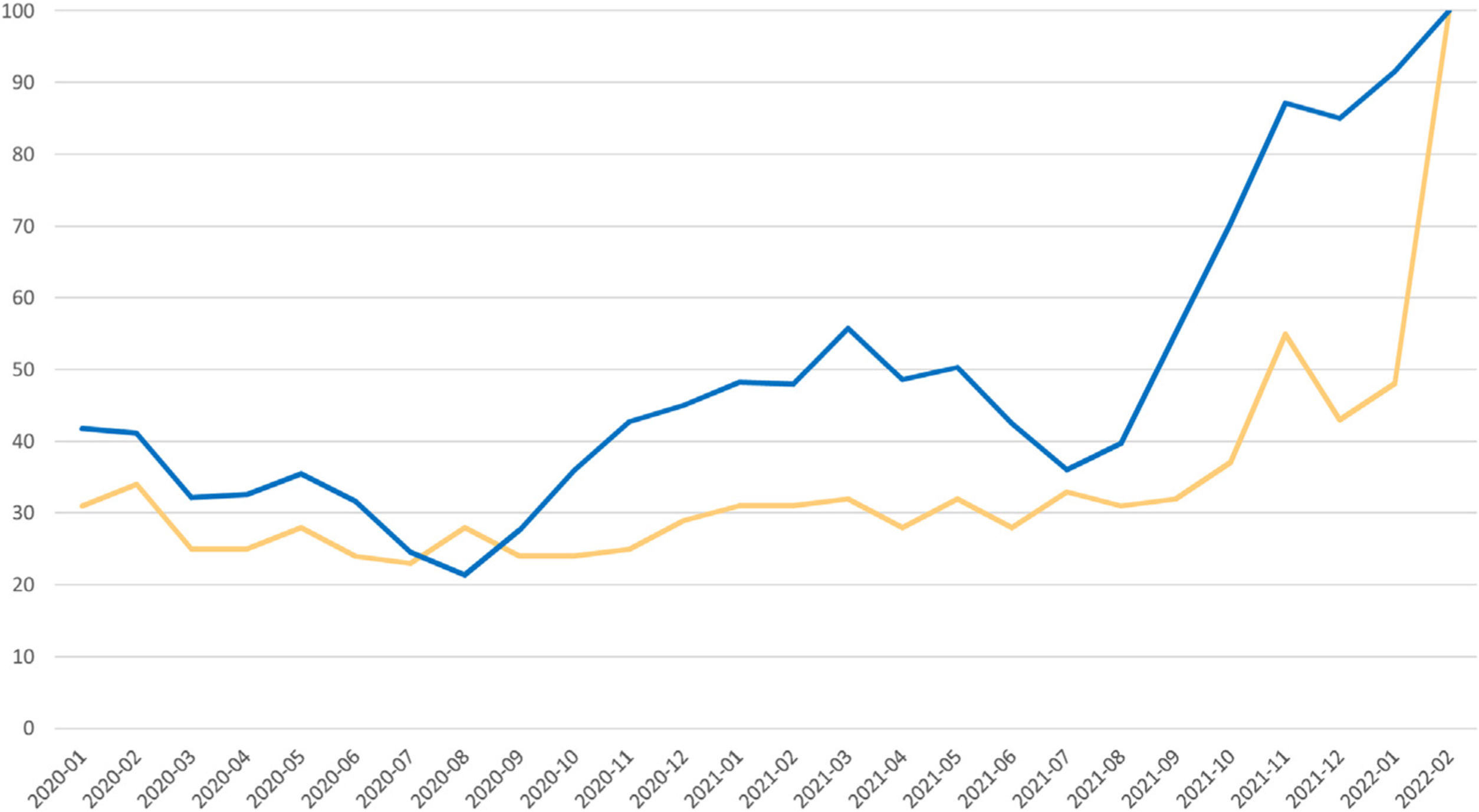
The monthly data (January 2020 to February 2022) also show a growing trend, with higher sales in winter months (December to March, mean [SEM], 29 580 [3820]) than summer months (June to September, mean [SEM] 17 510 [1960]).
The record observed for pharmacy sales of ectoparasiticides was in February 2022, with a total of 50 250 packages sold.
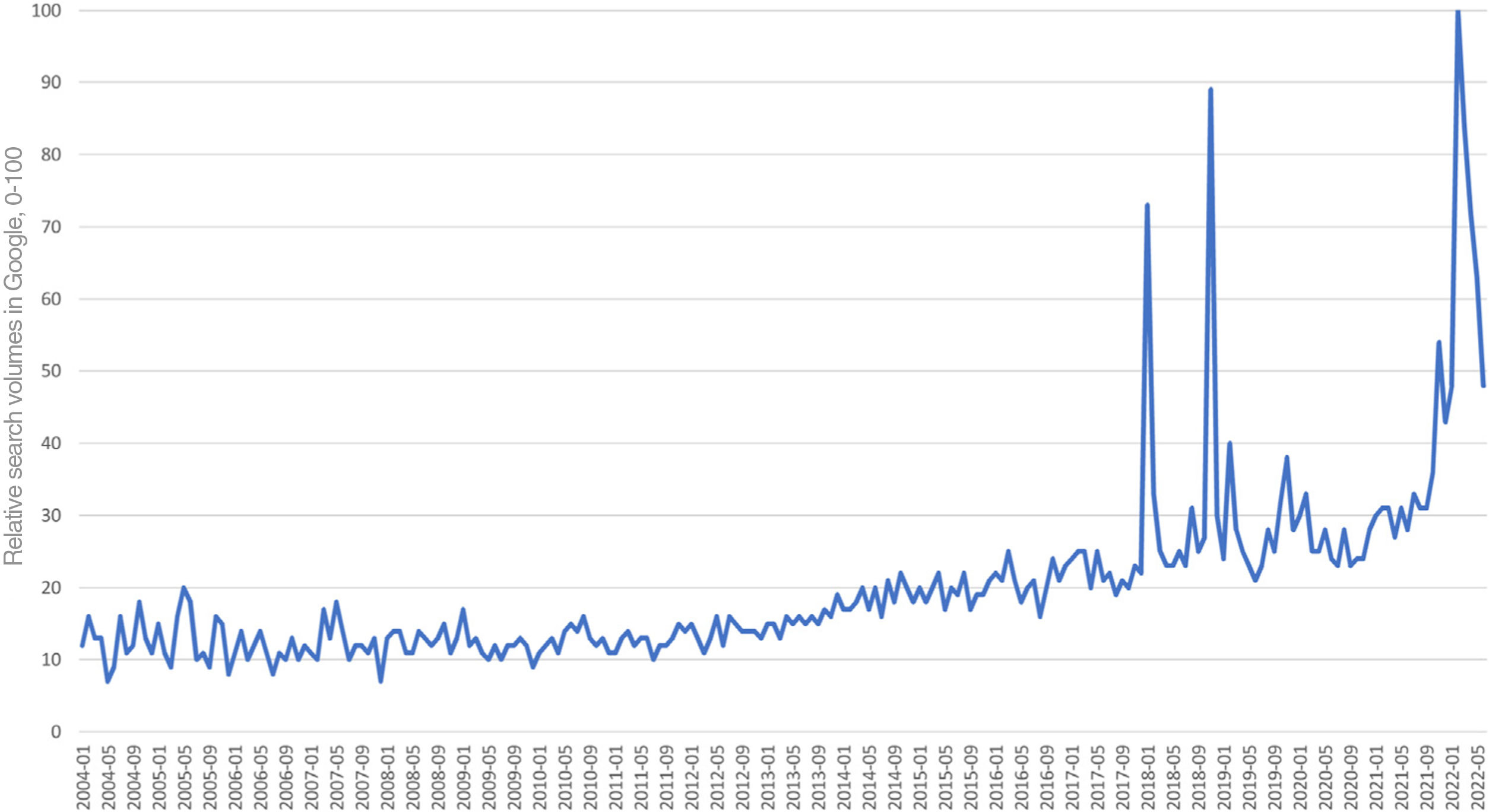
Changes in Public Interest According to Google TrendsThe RSV for scabies in Spain has followed a rising trend since 2004 (Fig. 1), with volumes reaching their minimum (RSVmin=7) in May 2004 and December 2007 and their maximum (RSVmax=100) in February 2022. Mean RSV was higher in winter (December to March) than summer (June to September), with respective rates of 21.04 (1.85) and 17.76 (0.84).
A strong, positive correlation was observed between monthly ectoparasiticide sales data in base 100 with the Google Trends RSV for scabies in Spain (Pearson correlation coefficient, r=0.81; P<.001). Peak popularity in Google search volumes (RSVmax) concurred with the record ectoparasiticide sales noted for February 2022 (Fig. 2). This point was followed by a sharp reduction in searches, which reached an RSV of 35 on June 19, 2022.
DiscussionWe observed an explosion in pharmacy sales of ectoparasiticides in Spain between 2020 and 2021. The number of packages sold does not reflect the number of patients treated, making it impossible to distinguish between increases due to a rise in patients or a rise in prescriptions per patient (e.g., prescriptions for the whole family or repeat treatments). We assume that the changes observed are more indicative of an increase in scabies than in other ectoparasitic infections, as the latter are much less common in Spain. This “large-scale national outbreak” has been attributed to COVID-19 lockdown measures and possible resistance to conventional treatments.14,15
Google searches for terms related to scabies have also shown a rising trend since 2004, with a notable increase observed since the end of 2012. Internet search volumes are a good indicator of public interest in a given topic, but they do not necessarily correlate with epidemiological phenomena. Many factors can drive public interest in a topic, including media coverage, commercial or advertising interests, novelty, and topics with a temporary or periodic nature.
Our data for Spain show that monthly ectoparasiticide sales were strongly and positively correlated with Google searches for scabies during the same period.
Sales and internet search volumes were also higher in winter than summer months, although the difference did not reach statistical significance. Infestations would be expected to be more prevalent in winter, as mites are able to survive for longer outside the host in humid, cold conditions.1,16
We observed a sharp drop in RSV following the peak in February 2022, but were unable to compare this to ectoparasiticide sales for the same period as the data had not been published at the time of writing. Perhaps the drop in search volume will ultimately be reflected in a drop in scabies cases, and with it, a drop in ectoparasiticide sales.
ConclusionsPublic interest in scabies and ectoparasiticide sales in Spain have increased in recent years and show a strong, positive correlation. Despite its limitations, Google Trends could be considered as a complementary tool for monitoring real-time trends in scabies infestations in Spain.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.