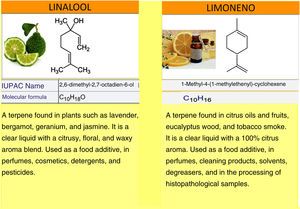
Hydroperoxides of limonene and linalool are found in common fragrances in half of all cosmetic products and household items out there. Also, they can be found in some foods in certain studies.1,2 Their most frequent use is as a food additive, in perfumes, and in cosmetics, and their oxidation products, especially furanoids, pyranoids, and hydroxyperoxides, increase their sensitizing capacity.3 (Fig. 1).
The frequency of positive patch tests to both hydroperoxides in some series of patients with contact dermatitis is high,2,4–6 but their relevance has been poorly studied.
Therefore, we patch-tested 247 consecutive patients with suspected contact dermatitis at Hospital de la Princesa, Madrid, Spain from 2019 through 2021, using the standard series from the Spanish Contact Dermatitis and Allergy Research Working Group (GEIDAC), to which we additionally added 0.5% and 1% limonene hydroperoxide, and 0.1% and 0.3% linalool hydroperoxide (Chemotechnique Diagnostics, Vellinge, Sweden). These allergens were prepared at the time to avoid oxidation. Readings obtained on days D2 and D4 in full compliance with the ESCD guidelines.7
Clinical information was collected before performing the patch tests. The application of a product containing terpene in the area affected by the eczema and its resolution upon discontinuing this drug was established as relevant in patients with positive patch tests.
A total of 21 out of the 247 patients tested (8.1%) showed positivity to, at least, 1 of the 2 hydroperoxides in some of the concentrations tested, 7 (2.8%) to limonene hydroxyperoxide, 14 (5.6%) to linalool hydroxyperoxide, and 3 (1.2%) to both.
Demographic and clinical data, as well as the results from the patch tests (negative or positive, regardless of intensity), are shown in Table 1.
Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of tested patients.
| Sex/age | Hatopy | Loc | Epic limonene | Rel. limonene | Epic linalool | Rel. linalool | Rem. epic | Rel. other | Final diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/75 | No | Folds | POS | NR | NEG | Hydrocortisone/Budesonide | CPR | ACD to corticoids | |
| M/44 | No | T/Folds | POS | CPR | POS | CPR | Fragance m I/II | CPR | ACD to perfume |
| W/77 | No | T/A | NEG | − | POS | IR | None | − | Psoriasis |
| M/74 | No | A | NEG | − | POS | IR | Epoxy resin/benzisothiazolinone | NR/IR | Phytophotodermatitis |
| W/55 | Yes | H | NEG | − | POS | IR | MCI/MI, LL | CPR | ACD/ICD/Atopic d |
| W/81 | No | F | POS | IR | POS | IR | Ni | IR | Hiperpigmentation |
| M/70 | No | Sp | POS | UR | POS | UR | MCI/MI | CPR | ACD to preservatives |
| W/72 | No | H | NEG | − | POS | NR | Ni | PPR | ICD |
| W/67 | Yes | Sp | NEG | − | POS | NR | Phenoxyethanol/Ni/Benzisothiazolinone | CPR/PPR/IR | Atopic d |
| W/33 | Yes | Feet | NEG | − | POS | NR | Formaldehyde 2%/Quaternium imidozolidinylurea/ | PR/PR/PR | Atopic d |
| W/46 | Yes | Folds | NEG | − | POS | NR | Ni | PR | Atopic d |
| M/37 | Yes | H | POS | NR | POS | NR | Black rubber/Cobalt/Textile dye mixture/Thiomersal | IR | Atopic d |
| W/29 | Yes | F | NEG | POS | IR | Ni/LL | IR | Atopic d | |
| W/47 | Yes | S/T | POS | NR | NEG | PPD/Textile dye mixture | CPR | ACD PPD | |
| W/60 | No | S | NEG | − | POS | NR | PPD/Textile dye mixture/NI | CPR/PPR | ACD PPD |
| W/28 | Yes | Sp | NEG | − | POS | UR | MCI/MI; M fragancies I, II | CPR/CPR | ACD to preservatives/fragancies |
| W/49 | Yes | Sp | NEG | − | POS | UR | Ni | PPR | Atopic d |
| M/60 | Yes | H | NEG | − | POS | NR | Fragance m I/Compositae | CPR/UR | ACD and Atopic d |
| W/76 | No | F | NEG | − | POS | UR | Sodium gold thiosulfate | IR | Cuperosis |
| M/81 | Yes | LL | POS | UR | NEG | Ni | PPR | ICD | |
| W/37 | No | Sp | NEG | − | POS | UR | Ni | PPR | Cuperosis |
A, arms; ACD, allergic contact dermatitis; Atopic d, atopic dermatitis; CPR, current positive relevance; Epic, epicutaneous; F, face; Fragance m, fragance mix; H, hands; Hatopy, history of atopy; ICD: irritant contact dermatitis; IR, irritative; LL, lower limbs; loc, location of the lesion; M, man; MCI/MI: Methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone; NEG, negative; Ni, nickle; NR, non-relevant; POS, positive; PPD: paraphenylenediamine; PPR, past positive relevance; PR, past relevance; Rel., relevance; Rem. epic, remaining epicutaneous tests (only the positive ones shown); S, scalp; Sp, spread; T, trunk; UR, unknown relevance; W, woman.
The mean age of patients who tested positive to both terpenes was 57 years (range, 29-81 years). A total of 66% of the patients were women, and none had an occupational origin. The most frequently affected eczema ravaged regions were the hands (in 42% of our cases).
Only in 1 patient (4.7%) the hydroperoxides coexisting with concurrent contact sensitization to FM I and FM II were considered relevant. The remaining positive patches to linalool and/or limonene—a total of 6 (28.6%)—were irritative, not relevant, or of unknown relevance.
In 20 out of 21 patients, other positive reactions were found in the patch tests. The most common one, considered relevant, were 8 positive cases for nickel sulfate, with current or past relevance in 6 cases; 4 positive cases for methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone (MCI/MI); 3 for FM I or II, and another 3 for paraphenylenediamine (PPD)/textile dye mixture. The diagnoses of patients with positive patches to hydroperoxides varied and included atopic dermatitis, allergic contact and irritant eczemas, and psoriasis, as seen in Table 1.
In this series of patients who were patch tested with limonene and linalool hydroperoxides with suspected contact dermatitis, most positive patches were irrelevant. In most patients, atopic dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis explained the clinical lesions. In fact, in cases of contact dermatitis, other allergens from the standard series were involved.
The clinical relevance of hydroxyperoxides in the studies conducted varies widely, ranging from 29% to 97% of the cases reported.4-6 In the GEIDAC prospective series, it was considered that 50% of the patients had clinical relevance, with a prevalence of positive reactions in 5.1% of the patients.3 Nonetheless, the criteria used for relevance are classical, and they do not take the clinical course into consideration. In contrast, in our series, only 4.7% of the positive reactions reported were relevant, and these results are consistent with those reported by Natsch et al.8.
However, we agree with the authors of other series with high prevalences like ours, who also mentioned that the allocation of clinical relevance to these positive reactions is poorly documented and that criteria need to be standardized on this regard.9 Also, that patients with atopic dermatitis may show irritative reading patterns which may be different from those of the overall population.10
In our experience, the clinical relevance of both hydroperoxides is very low, meaning that exposure sources need to be thoroughly investigated before considering their inclusion in the standard series in Spain.
Conflicts of interestM. Llamas-Velasco: participation in clinical trials, lectures, research support, and advisory boards of Abbvie, Amgen, Almirall, Boehringer, Brystol-Meyers, Celgene, Leo, Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and UCB.
J. Sánchez Pérez: research support, and participation in clinical trials for Abbvie, Almirall, Galderma, Leo, and Boehringer.
The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest whatsoever.
None of the conflicts of interest reported are associated with the information provided in this article.