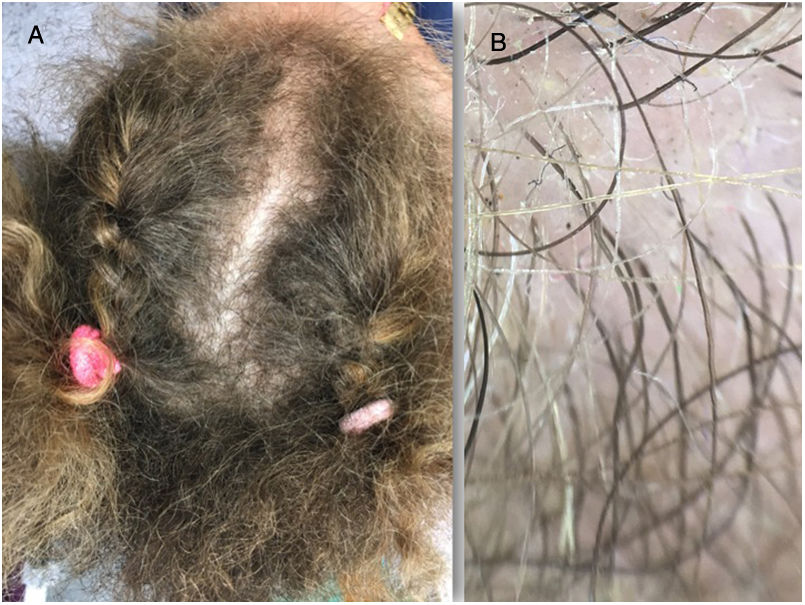
A 5-year-old girl had been born with smooth black hair of normal appearance, but this hair fell out completely after a year and was replaced by new, lighter, very tangled hair of woolly appearance (Fig. 1A), with hair with short waves (Fig. 1B). The present lower central capillary density may be due to traction alopecia. This woolly hair, together with difficulty walking due to progressive loss of strength, and pes plano valgo, constitute a clinical triad that indicates a suspected diagnosis of giant axonal neuropathy, as in our patient. Giant axonal neuropathy is a rare autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder. It is due to a mutation in the GAN gene, which codes for the protein gigaxonin. This leads to the accumulation of neurofilaments in the axons of the central and peripheral nervous system, which interferes with the transmission of nerve impulses. In giant axonal neuropathy, the hair is normal at birth but falls out and regrows with different characteristics, finer, lighter, very curly, clearly different from that of the patient’s parents, and with a woolly appearance. It is not woolly hair, strictly speaking, as this is always congenital, with diffuse, hereditary, localized forms. This would explain why gigaxonin is also involved in the homeostasis of other intermediate filaments such as keratins.
Please cite this article as: Allegue F, González-Vilas D, Zulaica A. Pelo lanoso postnatal: clave diagnóstica en la neuropatía axonal gigante. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020;111:524.