A 49-year-old male smoker sought care after 3 ulcerated lesions appeared on his tongue. He had a history of erosive lichen that affected mucosal surfaces but was symptom-free at the time. The first lesion had appeared 15 days earlier on the dorsum of the tongue and was followed by a further 2 lesions on the side and base 2 days later. He reported no other relevant history.
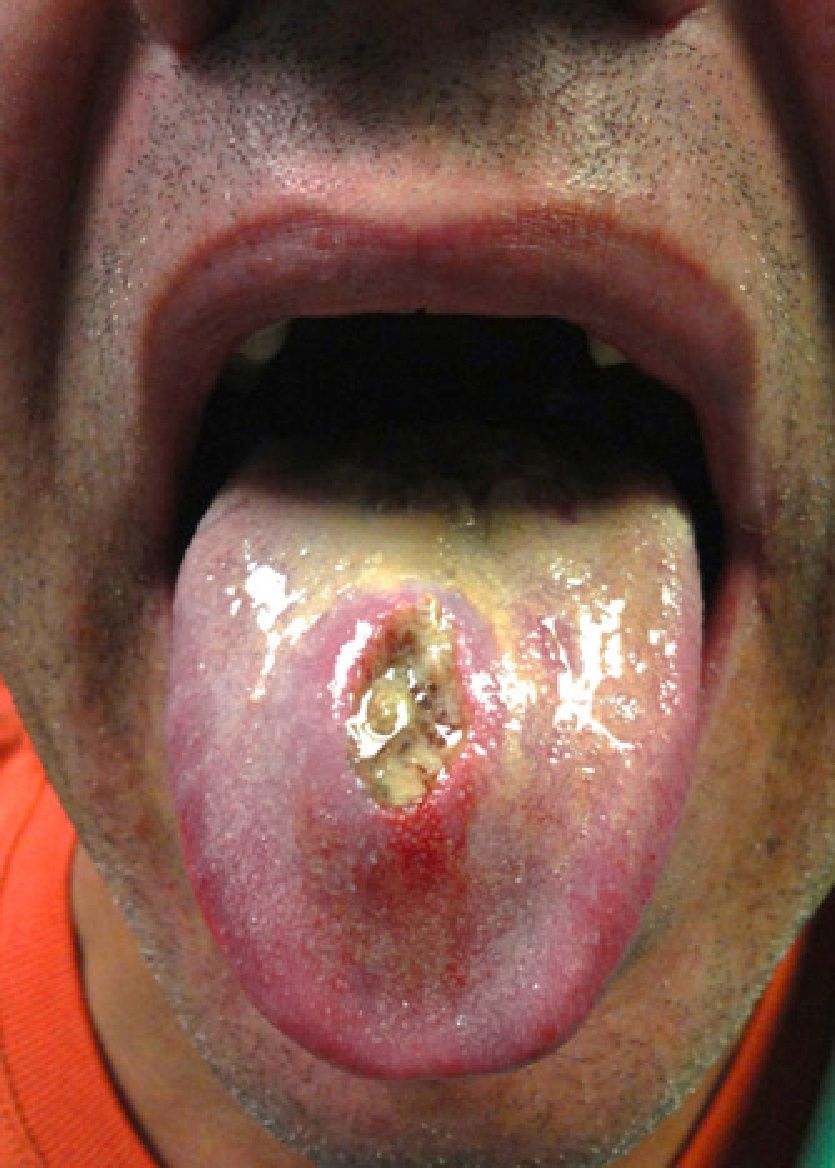
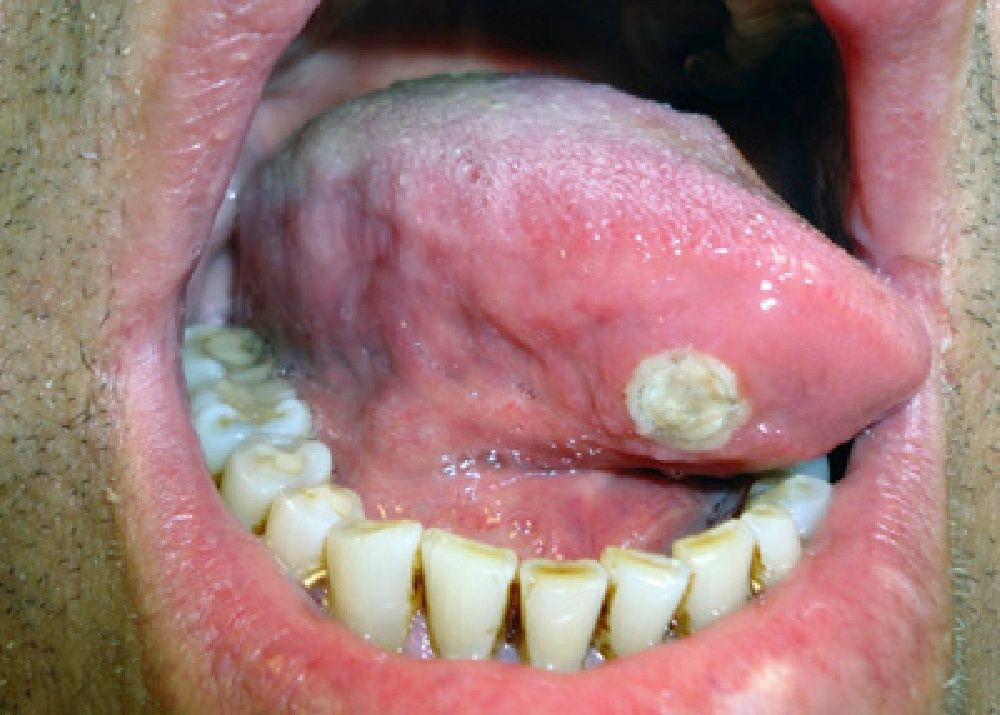
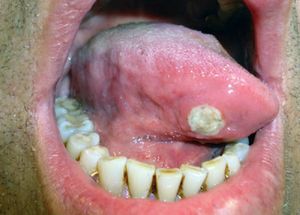
Physical ExaminationExamination revealed 2 foul-smelling ulcerated lesions (dorsum and base of the tongue), measuring around 2×1cm in diameter, with nonindurated excrescent borders and a necrotic base. A smaller ulcer, measuring around 1cm and with well-defined borders and necrotic base, was also present on the right side of the tongue (Figs. 1 and 2).
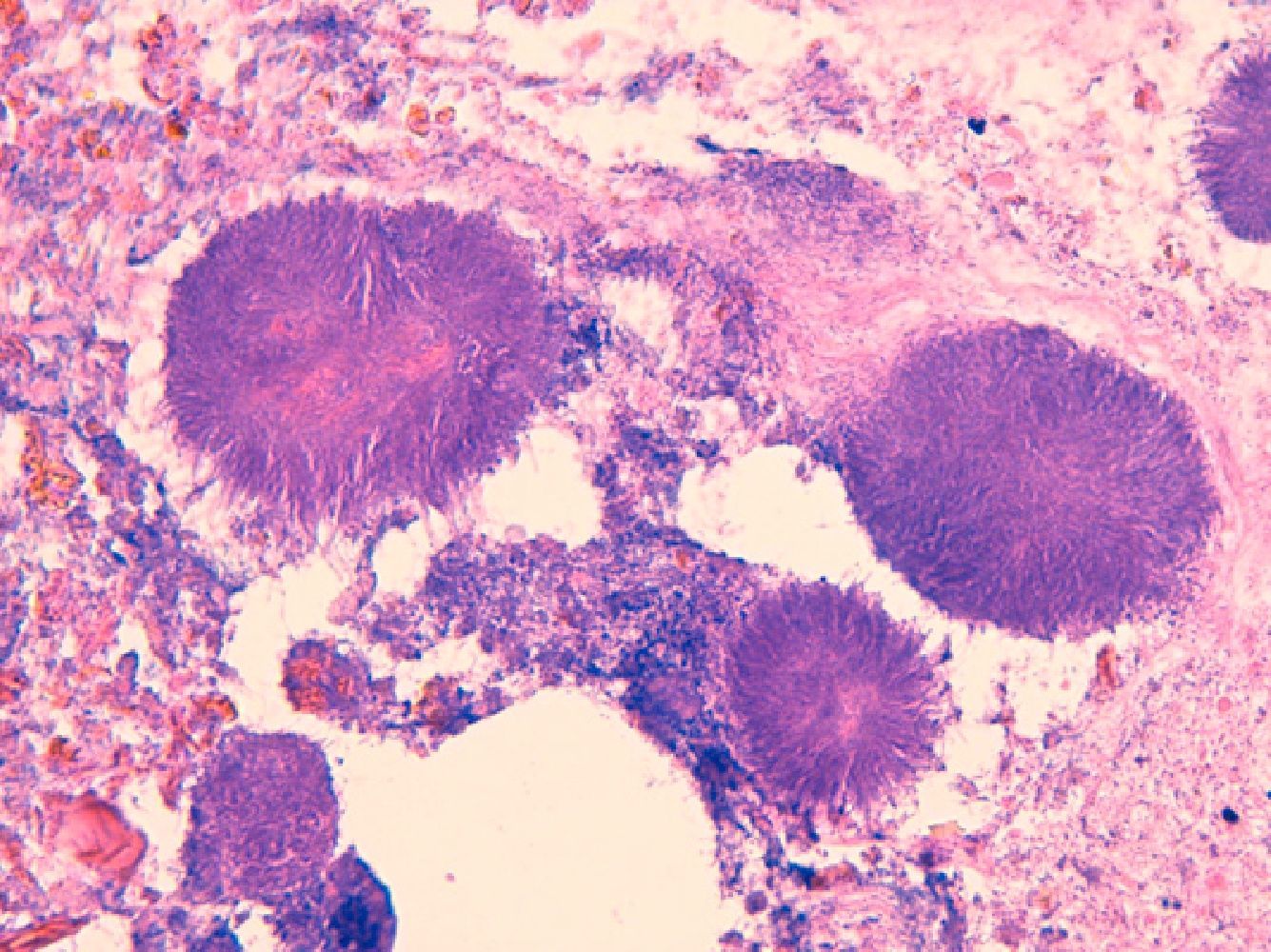
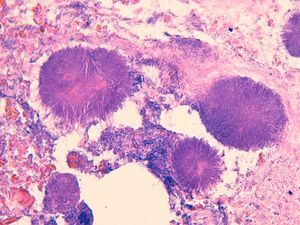
Additional TestsA punch biopsy at 1 edge of the ulcer revealed a moderate inflammatory component and occasional eosinophils alongside accumulations of granule-like, basophilic filamentous structures against a necrotic base (Fig. 3). No neoplastic cells were observed.
A complete blood count and biochemistry were normal, except for C-reactive protein, with a concentration of 34.4mg/L (normal range, < 5mg/L). Serology was negative for syphilis and the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Antinuclear antibody, rheumatoid factor, perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, and cytoplasmic antineutrophil antibody levels were also normal.
What Is Your Diagnosis?
DiagnosisActinomycosis of the tongue.
Clinical Course and TreatmentTreatment was prescribed with clindamycin, 600mg every 8hours, and mouth rinses of chlorhexidine digluconate. At 1 week, the lesions showed marked improvement and at 6 weeks had healed completely, leaving only depressed scars on the tongue.
CommentActinomycosis is a chronic granulomatous disease caused by a gram-positive microaerophilic bacterium belonging to the Actinomyces genus; the culprit is usually Actinomyces israelii.
This microbe forms part of the commensal flora of the oral mucosa and has also been isolated in the upper respiratory and digestive tracts and the female genital mucosa. It is not usually pathogenic and requires a previous solution of continuity (surgery, injury, inflammatory process, etc.) in order to cause infection. In our patient, the erosive oral lichen lesions may have played a key role in the development of actinomycosis, and in our review of the literature we found 2 other cases with this association.1 Conditions that influence immunosuppression (diabetes, HIV infection, etc.) may favor the development of this disease.2,3 The patient's poor oral hygiene and septic mouth would also have facilitated development as exemplified by another case of oral actinomycosis in the literature.4
Actinomycoses are classified according to their location: cervicofacial, thoracic, ileocecal, and pelvic. Cervicofacial actinomycosis, the most common form, can affect several structures: pharynx, larynx, tear ducts, oral mucosa, paranasal sinuses, jaw, and scalp. Tongue involvement, as in this case, is extremely rare; the authors of a 2006 review article found only 15 cases reported.5
Clinically, actinomycosis may present as a progressive infiltration of the organ (mimicking a neoplastic process), leading to abscess and fistula formation, but ulcerative lesions, as in our patient, have also been reported.
Differential diagnosis should include chancres, granulomatous lesions such as gummas or tuberculous defects, pyogenic abscesses, and benign and malignant tumors.
For diagnosis, an anaerobic culture reveals characteristic sulfur granules (formed by aggregates of thin filamentous bacilli shown by Gram or Gomori stain), while biopsy of a lesion displays filamentous aggregates with a degree of tissue response in the form of fibrosis, inflammation, or both. The pathogen was not isolated in the culture in our case, as often occurs (in up to 70% in a review of 181 cases of actinomycosis).6
Treatment consists of surgical debridement and/or antibiotics. Penicillins, cephalosporins, erythromycin, streptomycin, lincomycin, vancomycin, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, and tetracyclines have been used successfully.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Escoda M, et al. Úlceras dolorosas en la lengua. Actas Dermosifiliogr.2013;104:77-8.