The skin is the largest and most visible organ of the body, so its condition can affect our mental health and vice versa.1,2 It is common to see patients in consultations who suffer from primary psychiatric disorders that lead them to self-inflict cutaneous signs and symptoms.
Recently, an article was published to help dermatologists in the psychopharmacological management of 5 common psychiatric disorders ofte found in dermatology.3 This review includes a list of commonly used psychotropic drugs and details their prescription, dosage, and side effects to initiate early treatment in these patients who often lack awareness of their illness and may refuse a referral to a psychiatrist.
The disorders covered are delusional parasitosis (DP), body dysmorphic disorder (BDD), trichotillomania (TTM), onychophagia, and excoriation disorder (ED). The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM5) categorizes DP as a psychotic disorder, while the others are categorized as obsessive-compulsive disorders, with TTM, onychophagia, and ED being subcategorized as body-focused repetitive behaviors (BFRBs).
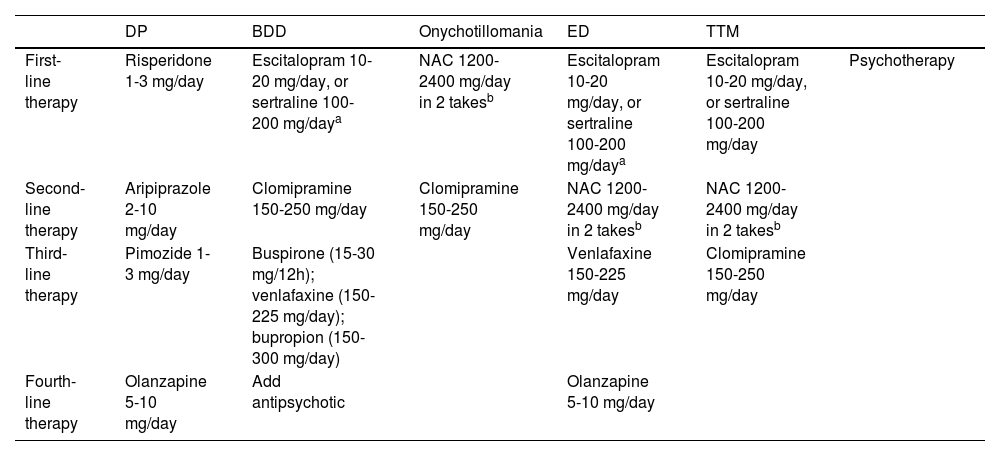
Of note that all these disorders benefit from combined treatment, consisting of pharmacological therapy and psychotherapy (Table 1), with varying techniques depending on the illness.
Pharmacological management of the main psychiatric disorders with cutaneous involvement.
| DP | BDD | Onychotillomania | ED | TTM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-line therapy | Risperidone 1-3 mg/day | Escitalopram 10-20 mg/day, or sertraline 100-200 mg/daya | NAC 1200-2400 mg/day in 2 takesb | Escitalopram 10-20 mg/day, or sertraline 100-200 mg/daya | Escitalopram 10-20 mg/day, or sertraline 100-200 mg/day | Psychotherapy |
| Second-line therapy | Aripiprazole 2-10 mg/day | Clomipramine 150-250 mg/day | Clomipramine 150-250 mg/day | NAC 1200-2400 mg/day in 2 takesb | NAC 1200-2400 mg/day in 2 takesb | |
| Third-line therapy | Pimozide 1-3 mg/day | Buspirone (15-30 mg/12h); venlafaxine (150-225 mg/day); bupropion (150-300 mg/day) | Venlafaxine 150-225 mg/day | Clomipramine 150-250 mg/day | ||
| Fourth-line therapy | Olanzapine 5-10 mg/day | Add antipsychotic | Olanzapine 5-10 mg/day |
DP: delusional parasitosis; NAC: N-acetylcysteine; BDD: body dysmorphic disorder; ED: excoriation disorder; TTM: trichotillomania.
For DP, also known as Ekbom's disease, the recommended pharmacological treatment of choice is risperidone, at a dose of 0.5 milligrams (mg) per day. If the patient tolerates the dose, it can be up titrated every 2 weeks to 0.25-0.5mg until control is achieved or even up to a maximum of 3mg daily. Although pimozide is more familiar in dermatology,4 this drug is considered a third-line option, after aripiprazole.
The first-line drugs for BDD are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), particularly escitalopram and sertraline due to their safety and efficacy profile. If the patient remains unresponsive, it should be replaced for clomipramine. More complex cases may require the addition of antipsychotics.
Pharmacological management in BFRBs is similar. First-line therapy includes the use of N-acetylcysteine (NAC). This drug is safe for both adults and pediatric patients and is free of the side effects associated with SSRIs and antipsychotics. In ED, treatment typically starts with a SSRI, leaving NAC as a second-line therapy. More options include clomipramine and olanzapine.
Finally, dermatologists should become familiar with the regular use of, at least, 1 SSRI and 1 antipsychotic, as these are widely used to treat the most frequent psychodermatological disorders.
Adequate knowledge and understanding of these drugs can facilitate the dermatologist's work and enable a multidisciplinary approach to treating these patients, allowing for the early initiation of pharmacological treatment and continuing management in collaboration with psychiatry.
FundingNone declared.