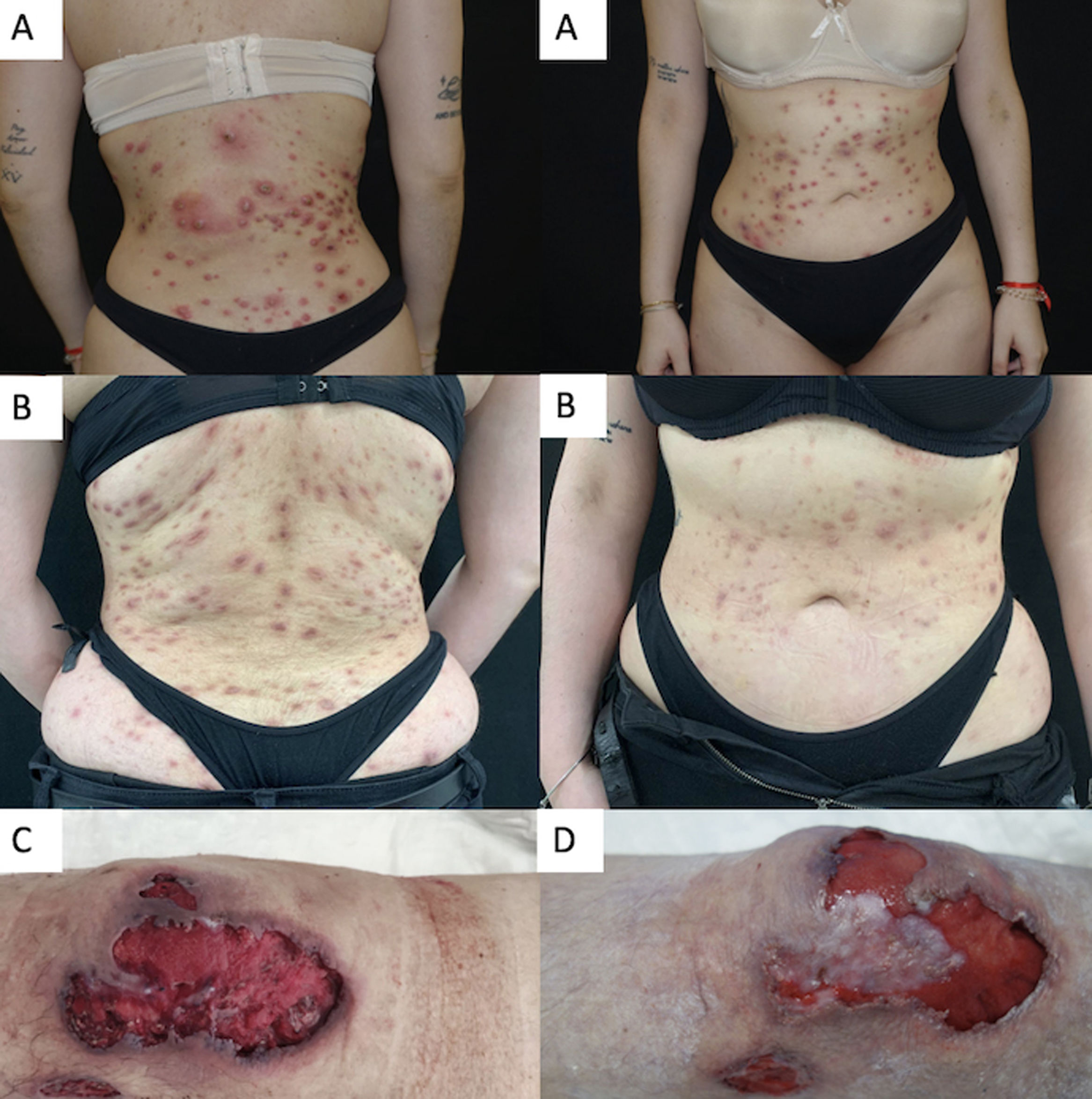
Pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) is an uncommon inflammatory skin disorder characterized by chronic and recurrent blistered or necrotic ulcers, and a predominantly neutrophilic infiltrate on histopathology.1 Several subtypes of PG exist such as ulcerative, bullous, pustular, peristomal and superficial granulomatous, yet the ulcerative variant represents about 85% of cases.1,2 The etiology of this debilitating disease is not fully understood. PG can be idiopathic, or be associated with drug consumption (cocaine/levamisole),3 inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), hematologic disorders, or be part of an inherited inflammatory syndrome.2 The pathogenesis of PG has not yet been completely defined and currently no drugs have been approved for the management of this disease. In most cases, management is based on off-label classical immunosuppressors and biological agents.4 Recent studies have demonstrate that the Janus kinase (JAK) pathway may be involved in the progression of PG.4,5 Off-label treatment with JAK inhibitors has been proposed by some authors6–10 as an optimal therapeutic strategy for the management of refractory PG in patients in whom other systemic therapies have failed. Experience with tofacitinib5–9 has been the most widely reported to this date; however, the use of more-selective JAK inhibitors such as upadacitinib could be also effective with a better safety profile and, indeed, a few cases have already been published.10
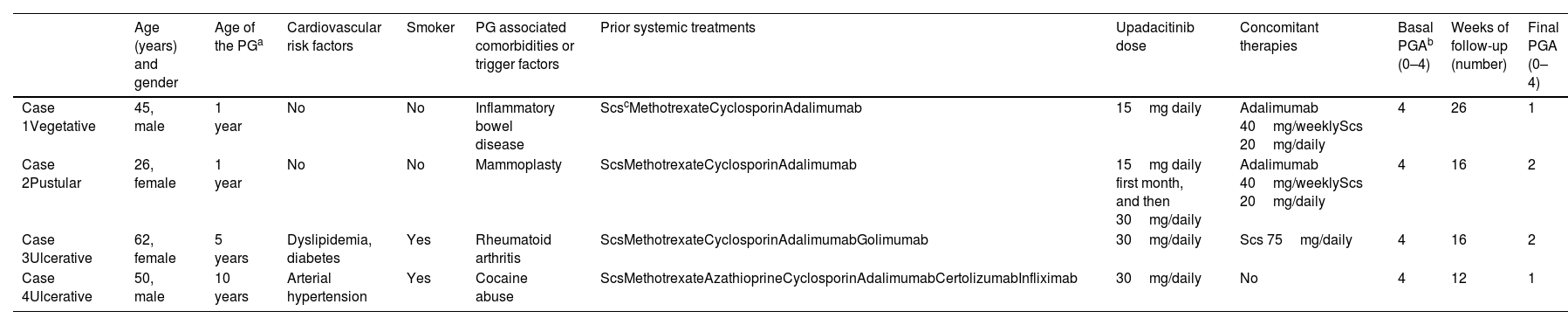
We conducted a retrospective bi-centric case-series evaluating short-term safety and efficacy profile of upadacitinib 15mg/daily or 30mg/daily for the management of refractory PG. Clinical response was assessed by Physician Global Assessment (PGA) during the evaluated period. An optimal response was considered when reaching a PGA ≤2. Four cases of recalcitrant PG were included. Two patients were women and two were men, ranging from 26 up to 62 years. The mean baseline PGA was 4 (ranging from 0 to 4). The mean course of PG prior to upadacitinib treatment was 4.3 years (range, 1–10). A well-known trigger or comorbidity were identified in all patients. One patient had poorly-controlled inflammatory bowel disease and a different participant, well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis. In the last two patients the PG onset was associated with the use of levamisole-adulterated-cocaine in one case and breast surgery in the other one. Two patients had ulcerative PG limited to the lower legs, one patient had generalized pustular PG and the other one, the generalized vegetative subtype. Prior to upadacitinib treatment, a mean 5 (range, 4–6) systemic therapies had failed in all patients. Three patients were on concomitant systemic treatments during upadacitinib initiation; however, they had been on these additional drugs for a significant amount of time without improvement, prior to starting upadacitinib. Systemic corticosteroids could be down titrated or completely removed after upadacitinib introduction in the entire cohort. All patients reached a PGA ≤2 after a mean follow-up of 17.5 weeks (range, 12–26), controlling pain and without developing drug-related severe adverse events or miss-controlling PG-related comorbidities. Baseline characteristics, comorbidities, prior and concomitant therapies are illustrated in Table 1. Clinical response to upadacitinib in patients #2 and #3 can be seen in Fig. 1.
Summary of our cases of PG treated with upadacitinib (including treatment regimens).
| Age (years) and gender | Age of the PGa | Cardiovascular risk factors | Smoker | PG associated comorbidities or trigger factors | Prior systemic treatments | Upadacitinib dose | Concomitant therapies | Basal PGAb (0–4) | Weeks of follow-up (number) | Final PGA (0–4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1Vegetative | 45, male | 1 year | No | No | Inflammatory bowel disease | ScscMethotrexateCyclosporinAdalimumab | 15mg daily | Adalimumab 40mg/weeklyScs 20mg/daily | 4 | 26 | 1 |
| Case 2Pustular | 26, female | 1 year | No | No | Mammoplasty | ScsMethotrexateCyclosporinAdalimumab | 15mg daily first month, and then 30mg/daily | Adalimumab 40mg/weeklyScs 20mg/daily | 4 | 16 | 2 |
| Case 3Ulcerative | 62, female | 5 years | Dyslipidemia, diabetes | Yes | Rheumatoid arthritis | ScsMethotrexateCyclosporinAdalimumabGolimumab | 30mg/daily | Scs 75mg/daily | 4 | 16 | 2 |
| Case 4Ulcerative | 50, male | 10 years | Arterial hypertension | Yes | Cocaine abuse | ScsMethotrexateAzathioprineCyclosporinAdalimumabCertolizumabInfliximab | 30mg/daily | No | 4 | 12 | 1 |
While this is a small case-series with a short follow-up based on our own observations, and according to Kooybaran et al.,10 upadacitinib seems to be a promising therapeutic alternative and possible corticosteroid sparing option for patients with either pustular, vegetative or classic PG with failed multiple systemic therapies (combined or in monotherapy) as previously reported for tofacitinib. Nonetheless, the drug safety profile could be better.10 Currently, no therapies have been approved by the EMA or the FDA for the management of PG; therefore upadacitinib and other JAK-inhibitors5–10 could be considered a reasonable alternative (combined or in monotherapy) especially for patients with inflammatory bowel disease or rheumatoid arthritis. However, future clinical trials and long-term real-world series will be needed to evaluate the efficacy profile of upadacitinib and other JAK inhibitors in the management of refractory PG.
FundingThis research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public or private sector.
Informed consentAll informed consents are available.
Conflicts of interestPedro Mercader-García declared having received speaker fees and compensation for being a member of advisory boards from Sanofi, Leo Pharma, Lilly and Abbvie, outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest whatsoever.
Data availabilityAll data are available on request from the authors.
We wish to thank Almudena Mateu Puchades and Mª del Carmen Hidalgo Boronat for data collection support.