Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)–like cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) is a rare and potentially fatal manifestation of CLE.1 Diagnosis is difficult, and no consensus has been reached on diagnostic criteria. The differential diagnoses include severe adverse drug reactions, infections, autoimmune bullous disease (AIBD), and other vesiculobullous diseases associated with lupus erythematosus, such as Rowell syndrome and bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).2 Indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) can prove extremely useful for the diagnosis of AIBD,3 although it has not been used in TEN-like lupus erythematosus. We present the case of a patient with acute cutaneous TEN-like CLE in which IIF played a key role in diagnosis.
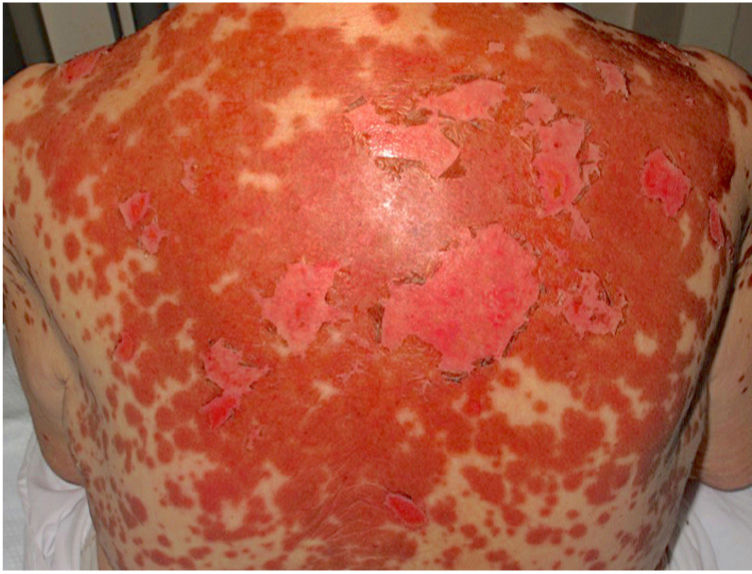
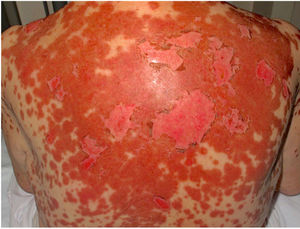
An otherwise healthy 81-year-old woman with a history of allergy to penicillin and procaine consulted for asthenia and painful skin lesions on the thorax and back that had first appeared 3 days previously and had spread to her arms and legs. She did not complain of fever, cough, or joint pain. Fifteen days before the consultation, she had received treatment with doxylamine and the influenza vaccine. She was not taking any other medications. The physical examination revealed poorly defined coalescent erythematous erosions and macules, as well as scaling of the skin on the thorax, back (Fig. 1), and extremities. The Nikolsky sign was positive. Minimal erosions were observed on the tongue and hard palate, with no other mucous membranes affected. Histopathology revealed epidermal necrosis, a normal stratum corneum, and a mild perivascular and periadnexal infiltrate (Fig. 2A). Immunofluorescence was negative. IIF was performed using monkey esophagus and rat bladder to rule out paraneoplastic pemphigus. Testing based on rat bladder yielded negative results; in the monkey esophagus sample, neither the basement membrane nor the intercellular spaces were stained, although, surprisingly, IgG antinuclear antibody (ANA) were detected (Fig. 2B). These results were subsequently confirmed using Hep2 cells, which yielded positive results for ANA, with a titer of 1:320. A complete lupus panel revealed positive results for anti-Ro antibodies, with negative results for the remaining antigens (dsDNA, Sm, La, RNP). The complete blood count, biochemistry, and serology test results for Mycoplasma pneumoniae were normal or negative. Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and laboratory findings, as well as on IIF, the patient was diagnosed with TEN-like acute CLE. The patient did not fulfill the American College of Rheumatology criteria for SLE. She was admitted to hospital, where she started treatment with topical triamcinolone cream 0.1%, which led to a complete clinical response within the following week. Patch testing with doxylamine (10% and 30% [pet]) performed after 6 months yielded negative results. The patient remained free of skin lesions during the 3-year follow-up period.
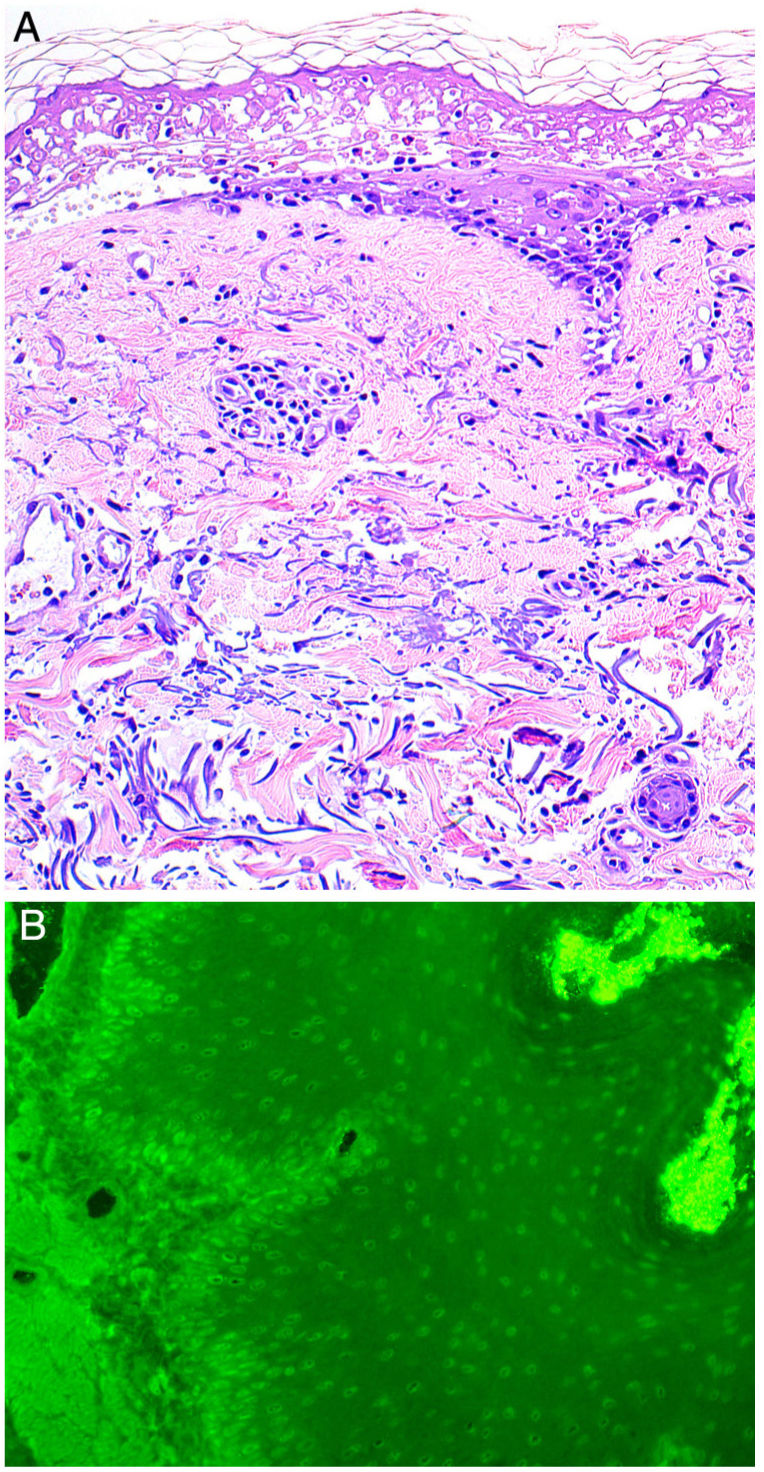
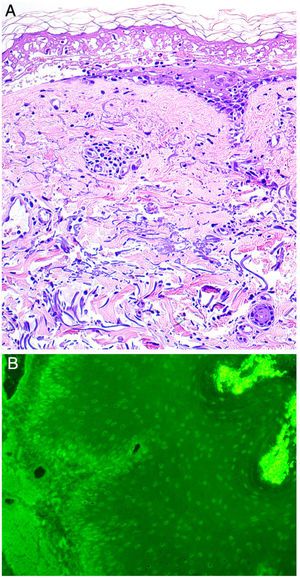
A, Histology indicating epidermal necrosis, normal stratum corneum, and mild perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate (hematoxylin-eosin, ×200). B, Indirect immunofluorescence. Immunofluorescence of the patient's blood in monkey esophagus revealed the presence of circulating immunoglobulin G antibodies bound to the nuclei of epithelial keratinocytes (dilution, 1:20; original magnification, ×200).
Differentiating between TEN-like CLE and AIBD is difficult. The incidence of TEN increases in patients affected by lupus erythematosus,4 with lupus erythematosus or CLE being the first clinical manifestation in 35% of individuals with TEN-like CLE.2 TEN-like CLE is often diagnosed retrospectively, given the complexity of integrating clinical, histologic, and laboratory findings.2 The presence of photodistributed lesions, minimal involvement of mucous membranes, and the better prognosis,4,5 together with the presence of mucin and perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate, the variable presence of melanophages and vacuolar interface dermatitis, may suggest a diagnosis of TEN-like acute CLE2,4 (Table 1), although these findings are not observed in all cases.2
Characteristics of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis-Like Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus.a
| Clinical characteristics | Photodistributed lesions |
| Minimal mucosal involvement | |
| Absence of fever | |
| Better prognosis than toxic epidermal necrolysis | |
| Histological characteristics | Perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate |
| Presence of mucin | |
| Variable presence of melanophages | |
| Vacuolar interface dermatitis | |
| Direct immunofluorescence | IgM, IgG, and/or IgA and complement (C3) deposits at the dermoepidermal junction |
| Indirect immunofluorescence | IgG antinuclear antibodies |
Abbreviation: Ig, immunoglobulin.
Immunofluorescence is the reference criterion for the diagnosis of AIBD. IIF is a complex 2-step process that detects circulating antibodies in the patient's blood. It uses normal human skin, salt-split skin, monkey esophagus, and other substrates (rat bladder for paraneoplastic pemphigus), depending on the suspected clinical diagnosis.3 In the case we report, IIF ruled out paraneoplastic pemphigus, revealing the presence of ANA and enabling us to make a very difficult differential diagnosis. We were unable to find other reports on the use of IIF in TEN-like CLE.
Diagnosis of TEN-like CLE is difficult. IIF can prove useful for ruling out AIBD and revealing circulating ANA.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.