Functional impairment is the main consideration when it comes to choosing therapy for infantile hemangiomas (IH). However, since most hemangiomas are treated for cosmetic reasons, it is important to know the cosmetic outcome assessed by the parents.
ObjectiveTo evaluate the aesthetic outcomes of IH, considering the characteristics of the lesions and the treatments used.
Patients and methodsThe Spanish Infantile Hemangioma Nationwide Prospective Cohort (2016–2022) recruited all consecutive patients diagnosed with IH in 12 Spanish hospitals. The children included had two photos of the IH lesion (at both baseline and at the end of the study). A panel of parents blindly assessed all available photos using a scale from 0 (worst cosmetic outcomes) to 10 (best cosmetic outcomes). The different scores – both before and after treatment – as well as the outcomes percent considered excellent (>9) were described and compared. We analyzed the effect of receiving different therapies and performed causal model analyses estimating the mean treatment effect of parents’ assessments.
ResultsThe median follow-up was 3.1 years. A total of 824 photos were evaluated. Baseline aesthetic impact was higher in the propranolol group vs the topical timolol and observation treatment groups (1.85 vs 3.14 vs 3.66 respectively; p<0.001). After treatment, the aesthetic impact was similar between both treatment groups (7.59 vs 7.93 vs 7.90; p>0.2). The causal model could only be applied to the comparison between topical timolol and observation, revealing no differences whatsoever.
ConclusionThis is the first prospective cohort to analyze the aesthetic outcome of IH. The final aesthetic results of the three therapies were similar, with nearly 40% of patients achieving excellent aesthetic outcomes.
El compromiso funcional es la principal indicación para iniciar tratamiento en los hemangiomas infantiles (HI). Sin embargo, muchos hemangiomas se tratan por el impacto estético que ocasiona en los niños, por lo que consideramos importante conocer el resultado cosmético evaluado por los padres.
ObjetivoEvaluar el resultado estético de los HI, teniendo en cuenta las características de las lesiones y los tratamientos utilizados.
Pacientes y métodosLa cohorte prospectiva española de HI (2016-2022) reclutó de manera consecutiva a todos los pacientes diagnosticados con HI en 12 hospitales españoles. A los niños incluidos se les realizaron dos fotografías de la lesión (una basal y otra al final del estudio). Un panel de padres realizó una evaluación ciega de todas las fotos utilizando una escala que iba de 0 (peor resultado cosmético) a 10 (mejor). Se describieron y compararon la diferencia de puntuación antes y después del tratamiento y el porcentaje de resultados considerados excelentes (>9). Se analizó el efecto de recibir diferentes terapias y se realizaron análisis de modelos causales estimando el efecto medio del tratamiento sobre las valoraciones de los padres.
ResultadosLa mediana de seguimiento fue de 3,1 años. Se evaluaron 824 fotografías. El impacto estético basal fue mayor en los grupos de tratamiento con propranolol que en los de timolol tópico y observación (1,85 vs 3,14 vs 3,66, respectivamente; p<0,001). Después del tratamiento, el impacto estético fue similar entre los grupos de tratamiento (7,59 vs 7,93 vs 7,90; p>0,2). El modelo causal solo pudo aplicarse a la comparación entre timolol tópico y observación, sin mostrar diferencias.
ConclusionesPresentamos la primera cohorte prospectiva que analiza el resultado estético de los HI. Los resultados estéticos finales de los tres tratamientos fueron similares, y alrededor del 40% de los pacientes describieron unos resultados estéticos excelentes.
Infantile hemangiomas (IH) are the most common benign vascular tumor in childhood with a prevalence of 2.6% up to 4.5% in newborns.1 Many IH regress spontaneously without leaving severe sequelae. Around 10% may present serious complications such as ulceration, disfigurement, and functional or structural compromise, and treatments are mainly aimed at avoiding them.2 However, most information we have on the long-term progression of hemangiomas is either retrospective studies of patients (with possible selection and follow-up bias),3–5 or prospective cohorts of consecutive patients, whose maximum follow-up time is not usually past 3 years.2,6–8
Hemangiomas are a big concern for parents of affected children, as they are usually located in exposed anatomical regions. This concern is justified by the possible functional sequelae, the potential growth of the tumor within the first few months of life and its possible cosmetic outcomes, which may have a psychological impact on the child.9,10
Several clinical practice guidelines offer recommendations for the management of IH based on the propensity for the development of complications.11,12 However, in the routine clinical practice, aesthetic impairment is the most common indication for therapy.13 Although information on the aesthetic outcome of IH including the results of therapy in common clinical practice would be useful for clinicians and parents to make decisions and have realistic expectations, such information is currently scarce.14 The lack of data on the “parent or child's opinion on improvement; the number of parents or children who consider there is still a problem; and cosmetic appearance” has been highlighted in a recent Cochrane review.14 The Spanish infantile hemangioma prospective cohort had these measures as its main objectives.13 Given the patients's age, parents were involved in the study and their opinions were used as a proxy measurement for aesthetic results.
There are several treatment options for IH. Depending on a series of factors related to the characteristics of the hemangioma,15 IH is categorized into risk different levels for the development of complications. High-risk hemangioma is an indication for treatment with oral beta-blockers, with propranolol being the standard and only licensed therapy to this date based on the results from several clinical trials.16,17 In intermediate- or low-risk IH the therapeutic decision usually includes topical timolol or observation, with large variability in therapy selection.18
The objective of this study was to evaluate the aesthetic outcome of IH assessed by parents, considering the characteristics of the lesions and the different treatments used.
Patients and methodsThe Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (AEDV) started an IH nationwide prospective cohort in 2016 recruiting all consecutive pediatric patients diagnosed with hemangioma from 12 Spanish hospitals.13 The study ended on July 31st, 2022. The study was approved by Hospital Santa Creu i Sant Pau Research Ethics Committee (Barcelona, 16/079). All patients’ parents or caregivers signed the corresponding prior written informed consent form to participate in the cohort.
Outcomes and assessmentEach child from the study had, at least, two photos, one at baseline and the other at the end of the study (or the last visit, in cases lost to follow-up). All photos were checked to make sure that they showed the location and characteristics of the hemangioma. A panel of 15 parents were contacted by dermatologists participating in the cohort. Parents individually evaluated the photos using an adjectival ranking scale (0–10) on an on-line system that presented them in a random order and were blinded to information about the treatment received and the characteristics of the child.
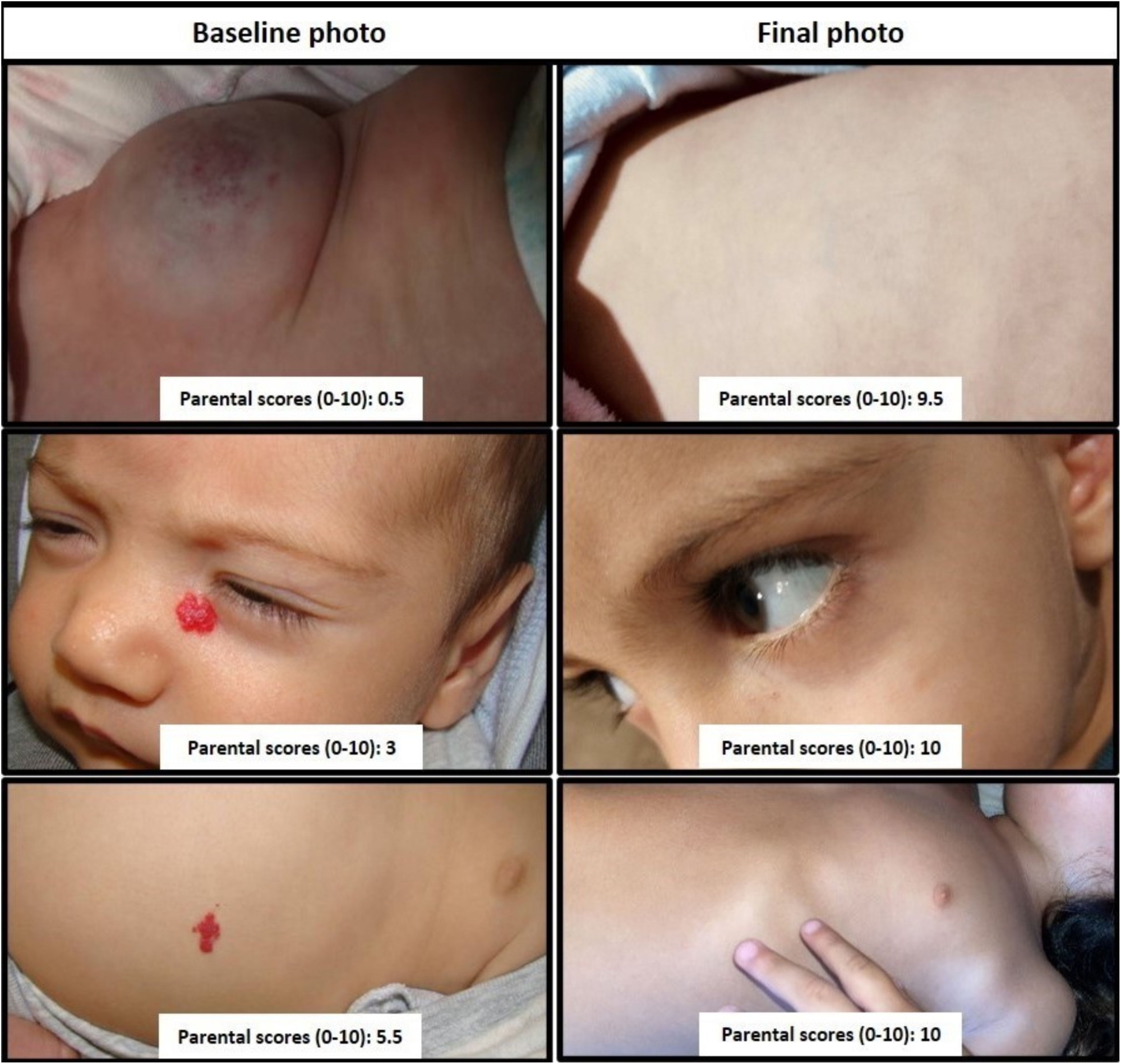
Parents were asked to measure the aesthetic impairment of each picture considering four criteria: the degree of ordinary visibility of the hemangioma, the attractiveness to the gaze of others, the emotional reaction it provoked, and the possibility that it caused disturbances in interpersonal relationships. These criteria were obtained from article 102 of the Spanish Act on Civil Liability and Insurance in the Circulation of Motor Vehicles, as they are accepted by society for accident compensation and lawsuits. A 0 value was defined as the “worst possible aesthetic result (these are usually very visible lesions, which attract a lot of attention, and are capable of generating considerable rejection that can greatly alter the interpersonal relationship)” and 10 indicating the “best possible aesthetic result (no lesions)”. Before the evaluation, parents were shown a set of pictures displaying the full range of aesthetic impairment and ordered using those four criteria (Fig. 1).
The mean scores were used for outcome calculations. Main outcomes were the initial and final score, change in score (score at the end of follow-up minus baseline score), and the percentage of children with an excellent resolution outcome (end of follow-up mean score ≥9).
Study groups and cohort dataThree comparison groups were defined based on the treatment used: propranolol vs timolol, propranolol vs observation, and timolol vs observation. Analyzed data included children characteristics, information regarding birth, and clinical characteristics of IH (such as location, morphologic and clinical subtypes, size or height).
Statistical analysisWe conducted a descriptive and comparative analysis describing parental scores and total change based on the treatment received. Additionally, a descriptive and comparative analysis of the characteristics of children and hemangiomas per se (both baseline and final) was performed. Continuous symmetrical variables were expressed as mean and standard deviation (SD), and median (25th–75th percentiles) were used for asymmetrical variables. For qualitative variables, absolute and relative frequencies were estimated. Differences between continuous variables were assessed using the Student's t-test or the Mann–Whitney U test. Differences between qualitative variables were assessed using the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test, when necessary.
Selection bias is an issue when treatment allocation is not randomized or controlled, as in our case, which is why we analyzed the effect of receiving one therapy rather or the other using causal models with data from observational studies. We estimated the average treatment effect (ATE) by augmented inverse-probability-weighting (AIPW) while using lasso-based variable selection methods to select from potential control variables to be included in the model. Although AIPW is a common solution to handle selection bias (in the same way as propensity score), AIPW estimators have the double-robust property, as they combine aspects of regression-adjustment and inverse-probability-weighted methods.19
Various sensitivity analyses were performed, changing the definitions of the outcomes (defining excellent outcomes as photo scores of ≥8, or photo scores of 10, using differences between baseline and final outcomes and measuring linear change) and the groups to be compared (those on both topical and oral beta-blocker therapy at the follow-up were excluded from the primary analysis and considered as all topical or all beta-blocker in sensitivity analyses). All analyses were performed using STATA v.17.0 (Stata Corp. 2021. Stata Statistical Software: Release 17). p-Values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
ResultsA total of 765 children were recruited in the cohort, with 456 (60%) having valid photos both at baseline and at the end of follow-up. When comparing the baseline characteristics between those with and without valid photos there were very limited differences (supplementary data, Table S1). Eleven out of the 15 invited parents agreed to participate in the panel (2 fathers and 9 mothers). A total of 912 photos of these 456 children were evaluated as follows: 304 photos were evaluated by two parents, another 304 photos were evaluated by four other parents plus a third group of 304 photos evaluated by five different parents. Finally, data from 412 children with 824 photographs were included for main analysis, as 44 (10%) children received both topical and oral beta-blocker therapy at the follow-up and were excluded from the main analysis. They were, however, used for sensitivity analyses.
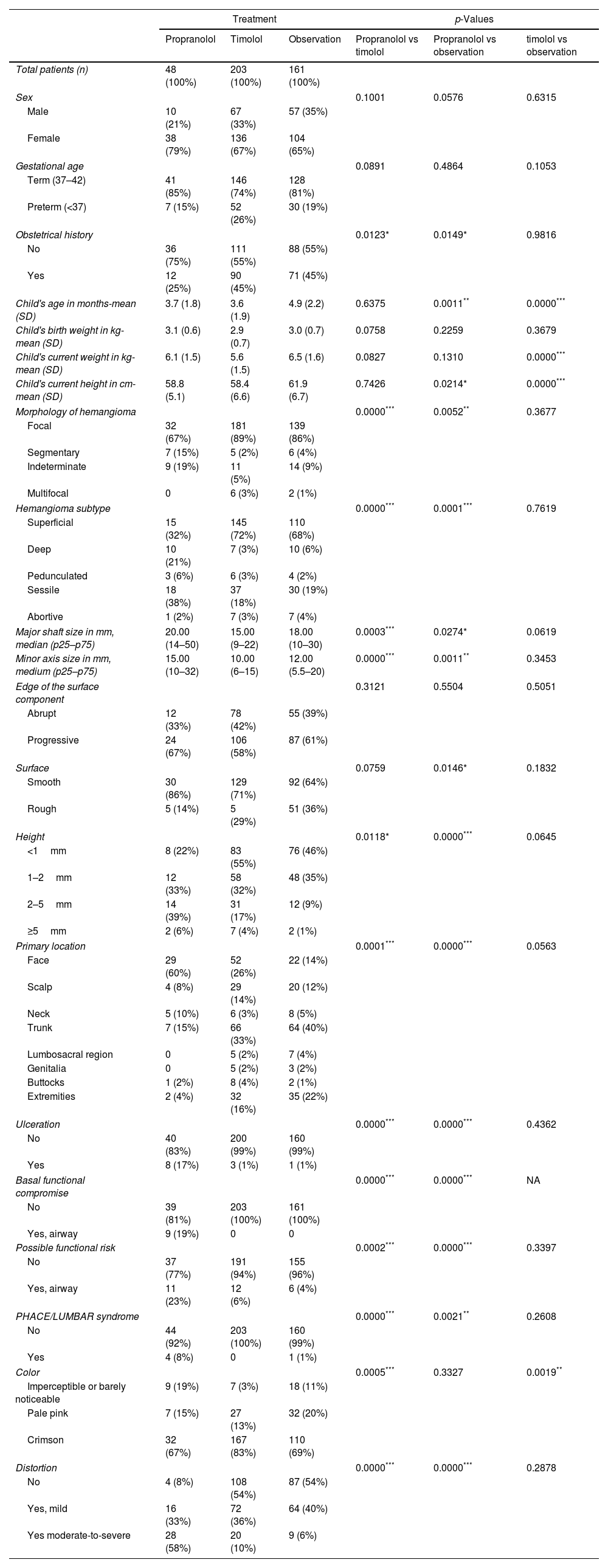
Baseline characteristicsChildren had a mean age of 4.1 months at baseline (standard deviation [SD] of 2.1) with a predominance of female sex (67%). The most frequent treatment group was topical timolol (n=203 [49%]), followed by clinical observation (n=161 [39%]) and the oral propranolol group (n=48 [12%]). The characteristics of both children and IH by therapeutic group are listed in Table 1. Children on propranolol were generally younger and had a less common history of obstetric complications, while their hemangiomas were more commonly segmentary, deep, darker, larger, higher, and ulcerated. They were also more commonly located in the face and associated to functional impairment or risk. Children on topical timolol were very similar to those who received no therapy: the only statistically significant differences between those groups were that children on timolol were younger, and their hemangiomas much darker.
Characteristics of patients on propranolol, timolol and observation (baseline visit).
| Treatment | p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propranolol | Timolol | Observation | Propranolol vs timolol | Propranolol vs observation | timolol vs observation | |
| Total patients (n) | 48 (100%) | 203 (100%) | 161 (100%) | |||
| Sex | 0.1001 | 0.0576 | 0.6315 | |||
| Male | 10 (21%) | 67 (33%) | 57 (35%) | |||
| Female | 38 (79%) | 136 (67%) | 104 (65%) | |||
| Gestational age | 0.0891 | 0.4864 | 0.1053 | |||
| Term (37–42) | 41 (85%) | 146 (74%) | 128 (81%) | |||
| Preterm (<37) | 7 (15%) | 52 (26%) | 30 (19%) | |||
| Obstetrical history | 0.0123* | 0.0149* | 0.9816 | |||
| No | 36 (75%) | 111 (55%) | 88 (55%) | |||
| Yes | 12 (25%) | 90 (45%) | 71 (45%) | |||
| Child's age in months-mean (SD) | 3.7 (1.8) | 3.6 (1.9) | 4.9 (2.2) | 0.6375 | 0.0011** | 0.0000*** |
| Child's birth weight in kg-mean (SD) | 3.1 (0.6) | 2.9 (0.7) | 3.0 (0.7) | 0.0758 | 0.2259 | 0.3679 |
| Child's current weight in kg-mean (SD) | 6.1 (1.5) | 5.6 (1.5) | 6.5 (1.6) | 0.0827 | 0.1310 | 0.0000*** |
| Child's current height in cm-mean (SD) | 58.8 (5.1) | 58.4 (6.6) | 61.9 (6.7) | 0.7426 | 0.0214* | 0.0000*** |
| Morphology of hemangioma | 0.0000*** | 0.0052** | 0.3677 | |||
| Focal | 32 (67%) | 181 (89%) | 139 (86%) | |||
| Segmentary | 7 (15%) | 5 (2%) | 6 (4%) | |||
| Indeterminate | 9 (19%) | 11 (5%) | 14 (9%) | |||
| Multifocal | 0 | 6 (3%) | 2 (1%) | |||
| Hemangioma subtype | 0.0000*** | 0.0001*** | 0.7619 | |||
| Superficial | 15 (32%) | 145 (72%) | 110 (68%) | |||
| Deep | 10 (21%) | 7 (3%) | 10 (6%) | |||
| Pedunculated | 3 (6%) | 6 (3%) | 4 (2%) | |||
| Sessile | 18 (38%) | 37 (18%) | 30 (19%) | |||
| Abortive | 1 (2%) | 7 (3%) | 7 (4%) | |||
| Major shaft size in mm, median (p25–p75) | 20.00 (14–50) | 15.00 (9–22) | 18.00 (10–30) | 0.0003*** | 0.0274* | 0.0619 |
| Minor axis size in mm, medium (p25–p75) | 15.00 (10–32) | 10.00 (6–15) | 12.00 (5.5–20) | 0.0000*** | 0.0011** | 0.3453 |
| Edge of the surface component | 0.3121 | 0.5504 | 0.5051 | |||
| Abrupt | 12 (33%) | 78 (42%) | 55 (39%) | |||
| Progressive | 24 (67%) | 106 (58%) | 87 (61%) | |||
| Surface | 0.0759 | 0.0146* | 0.1832 | |||
| Smooth | 30 (86%) | 129 (71%) | 92 (64%) | |||
| Rough | 5 (14%) | 5 (29%) | 51 (36%) | |||
| Height | 0.0118* | 0.0000*** | 0.0645 | |||
| <1mm | 8 (22%) | 83 (55%) | 76 (46%) | |||
| 1–2mm | 12 (33%) | 58 (32%) | 48 (35%) | |||
| 2–5mm | 14 (39%) | 31 (17%) | 12 (9%) | |||
| ≥5mm | 2 (6%) | 7 (4%) | 2 (1%) | |||
| Primary location | 0.0001*** | 0.0000*** | 0.0563 | |||
| Face | 29 (60%) | 52 (26%) | 22 (14%) | |||
| Scalp | 4 (8%) | 29 (14%) | 20 (12%) | |||
| Neck | 5 (10%) | 6 (3%) | 8 (5%) | |||
| Trunk | 7 (15%) | 66 (33%) | 64 (40%) | |||
| Lumbosacral region | 0 | 5 (2%) | 7 (4%) | |||
| Genitalia | 0 | 5 (2%) | 3 (2%) | |||
| Buttocks | 1 (2%) | 8 (4%) | 2 (1%) | |||
| Extremities | 2 (4%) | 32 (16%) | 35 (22%) | |||
| Ulceration | 0.0000*** | 0.0000*** | 0.4362 | |||
| No | 40 (83%) | 200 (99%) | 160 (99%) | |||
| Yes | 8 (17%) | 3 (1%) | 1 (1%) | |||
| Basal functional compromise | 0.0000*** | 0.0000*** | NA | |||
| No | 39 (81%) | 203 (100%) | 161 (100%) | |||
| Yes, airway | 9 (19%) | 0 | 0 | |||
| Possible functional risk | 0.0002*** | 0.0000*** | 0.3397 | |||
| No | 37 (77%) | 191 (94%) | 155 (96%) | |||
| Yes, airway | 11 (23%) | 12 (6%) | 6 (4%) | |||
| PHACE/LUMBAR syndrome | 0.0000*** | 0.0021** | 0.2608 | |||
| No | 44 (92%) | 203 (100%) | 160 (99%) | |||
| Yes | 4 (8%) | 0 | 1 (1%) | |||
| Color | 0.0005*** | 0.3327 | 0.0019** | |||
| Imperceptible or barely noticeable | 9 (19%) | 7 (3%) | 18 (11%) | |||
| Pale pink | 7 (15%) | 27 (13%) | 32 (20%) | |||
| Crimson | 32 (67%) | 167 (83%) | 110 (69%) | |||
| Distortion | 0.0000*** | 0.0000*** | 0.2878 | |||
| No | 4 (8%) | 108 (54%) | 87 (54%) | |||
| Yes, mild | 16 (33%) | 72 (36%) | 64 (40%) | |||
| Yes moderate-to-severe | 28 (58%) | 20 (10%) | 9 (6%) | |||
SD, standard deviation.
Children were followed for a total median time of 3.1 years (p25–p75=2.2–3.8 years), which was slightly longer in the propranolol group [3.4 years (p25–p75=2.8–4.0) vs 2.9 (p25–p75=2.0–3.6), in the timolol group, and 3.1 (p25–p75=2.5–3.8) in the observation group]. We did not find any differences in the losses to follow-up between treatment groups, with 17% of cases reported in the propranolol group, 15% in the timolol group and 11% in the observation group. The median duration of treatment was similar in both groups, with a median of 8.0 months (p25–p75=6.6–11.7) for propranolol and 9.2 (p25–p75=6.0–14.9) for timolol (there were no statistically significant differences).
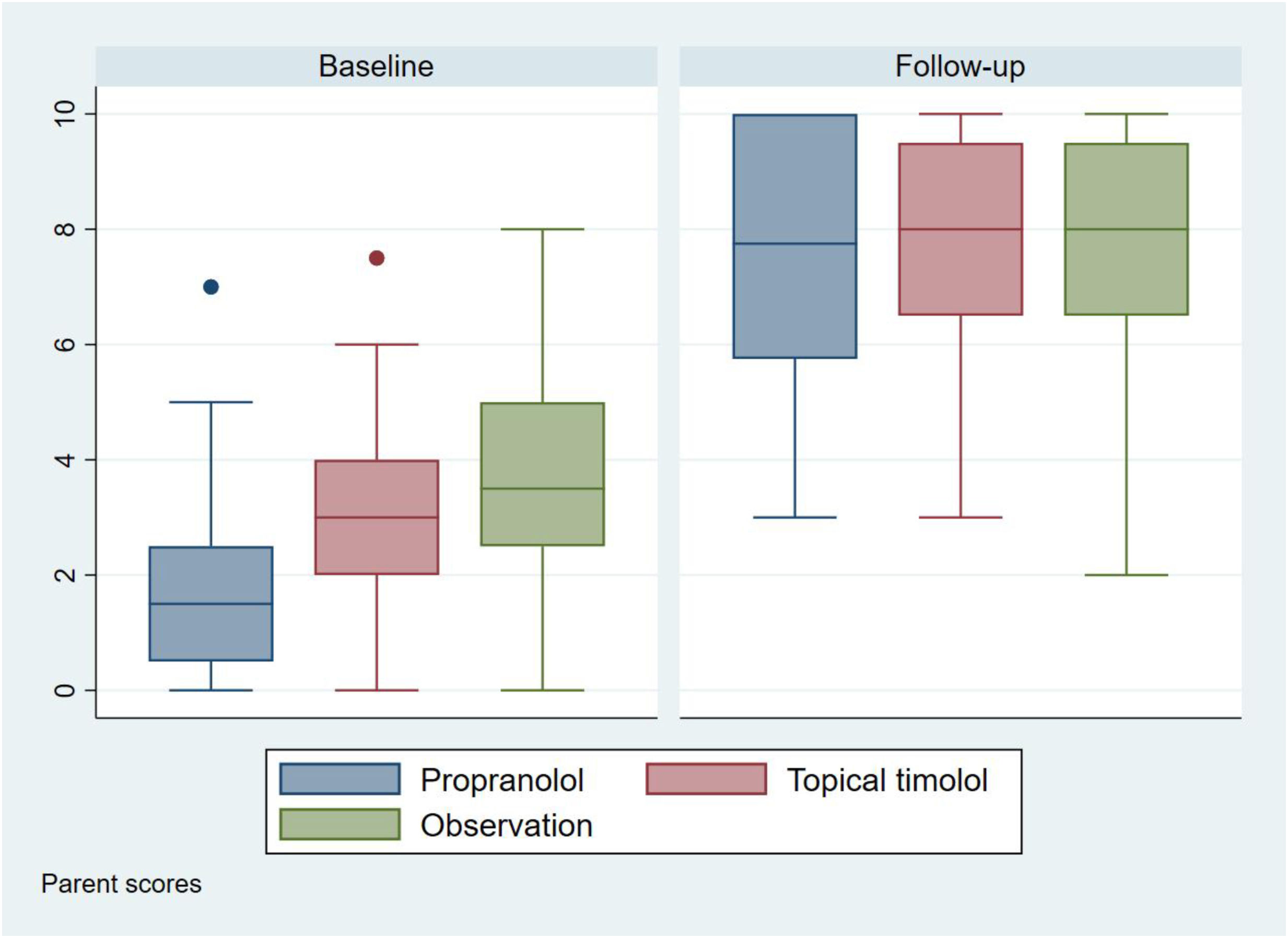
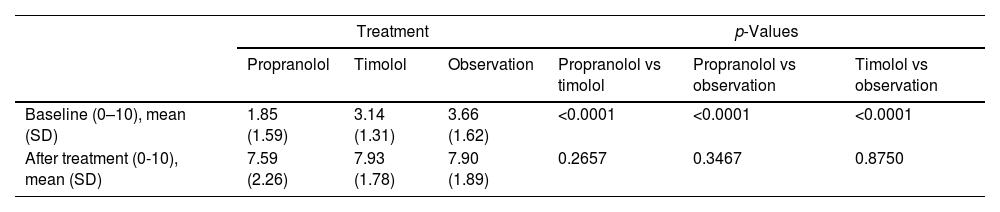
OutcomesThe initial aesthetic assessment by the parents (Fig. 2 and Table 2) was different among the three treatment groups, with lower scores in the propranolol group (1.85 [SD: 1.59]), followed by the timolol group (3.14 [SD: 1.31]), and finally by the observation group (3.66 [SD: 1.62]).
Parents’ aesthetic assessment.
| Treatment | p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propranolol | Timolol | Observation | Propranolol vs timolol | Propranolol vs observation | Timolol vs observation | |
| Baseline (0–10), mean (SD) | 1.85 (1.59) | 3.14 (1.31) | 3.66 (1.62) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| After treatment (0-10), mean (SD) | 7.59 (2.26) | 7.93 (1.78) | 7.90 (1.89) | 0.2657 | 0.3467 | 0.8750 |
Parent scores: 0 represents worst case hemangioma; 10 describes complete involution.
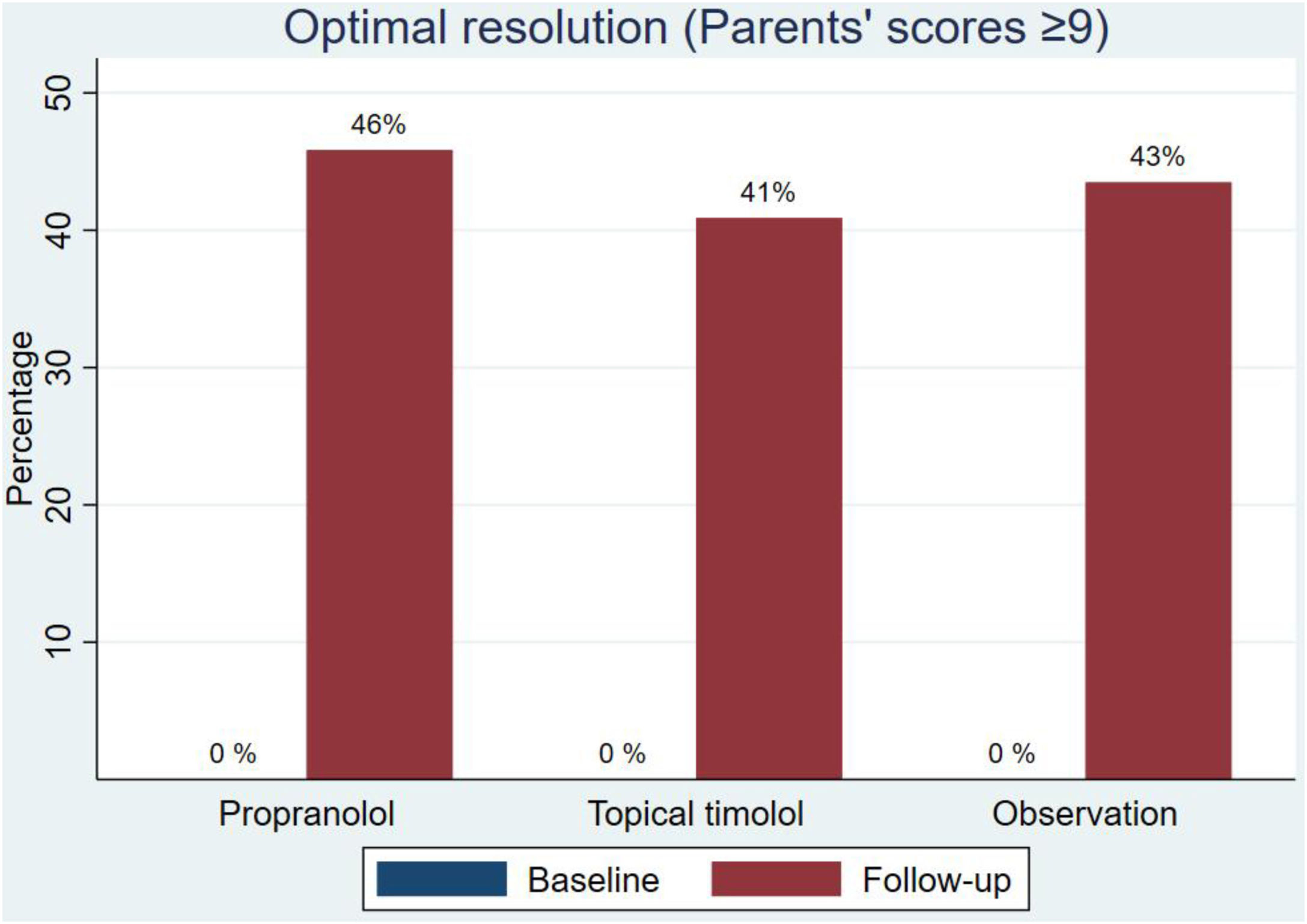
Regarding the final aesthetic assessment (aesthetic outcome), the scores were similar in the three groups: 7.59 (SD, 2.26) in the propranolol group, 7.93 (SD, 1.78) in the timolol group and 7.90 (SD, 1.89) in the observation group (Fig. 2 and Table 2). Differences in scores from baseline to final were not statistically significant (supplementary data, figure). Optimal resolution (score ≥9) was reached in similar percentages in all groups: 46% of those on propranolol, 41% of those on timolol and 43% of those without treatment (Fig. 3).
We also performed an analysis of causal effects using ATE by AIPW to adjust for possible confounding variables and for selection bias to simulate the results of a randomized clinical trial. It was not possible to compare propranolol with the other groups using this method, as the overlap of the two groups was very low. This inadequate overlap indicates that the characteristics of the hemangiomas treated with propranolol are so different that the models used that we cannot estimate the causal effects properly (i.e. the large baseline differences in the groups cannot be controlled for in the existing sample). The overlap between timolol and observation was valid, and the analysis showed no significant effects (difference in change in score=0.04 (95%CI, 1.11; 1.20), p=0.94); OR, ≥9=1.10 (95%CI, 0.80; 1.54, p=0.54)).
Sensitivity analyses described in the methods sections showed the same results with no differences being reported between each of the three pairs of groups compared, regardless of the definition of the outcomes used and the groups compared.
DiscussionHemangiomas on propranolol, topical timolol or observation in real-world practice reached a similar final aesthetic result, despite starting from very different levels of aesthetic impact, and those from the propranolol group having a worse initial situation. Only around 40% of the children had outcomes that were as excellent by the parents (scores of >9 out of 10), the final outcome being similar in all treatment groups.
Several authors have investigated the quality of life of patients and families with IH20,21 seeking to answer questions related to the psychosocial impact of IH on parents, how IH affects children development, and which characteristics of IH are associated with a worsening of these issues.9 Most authors report that there is a parental reaction of fear and concern surrounding social stigmatization, which decreases the parents’ quality of life, especially during the hemangioma growth phase, being significantly associated with the severity of the hemangioma.22 However, further studies on grown-up children with IH show no differences in their quality of life.23,24 From these studies, we can deduce that the greatest impact of the presence of an IH on parents is seen at the time of diagnosis, because of the uncertainty it causes them. That is why studies such as ours, focused on the evaluation of parents themselves, can be useful in providing them with accurate information, a need that was highlighted in a recent Cochrane review.14 In contrast to the published literature, our study assesses the aesthetic impact of IH on parents, which is the most common reason to initiate therapy, as supported by various clinical practice guidelines.11,12,15
This study has several advantages. Apart from using an outcome especially relevant to patients, it is a prospective cohort of a representative population. The follow-up was longer vs most former studies and the sample size was larger.2,6–8 Our long-term prospective cohort study represents one of the longest to date, which also helps clarify the incidence and percentage of sequelae left by these tumors. As an extended strength and novelty, the evaluation of the aesthetic outcomes was made by a panel of parents, and we present the results associated with different therapies. This allows us to draw conclusions on the expectations for each drug in terms of their final aesthetic outcome. Only a few authors have previously attempted to make this comparison, assessing quality of life at the start of treatment with propranolol and at the 1-month follow-up in a group of patients, observing a nonsignificant improvement in the quality-of-life scale score, justifying their results with the small sample size, or possible parents’ concern with associated syndromes.25,26
The study is limited by its observational nature, so the baseline characteristics related to IH severity among the different treatment groups are bound to be different. We tried to overcome this limitation by using counterfactual methods to simulate the results of a randomized clinical trial. However, as expected,13 patients on propranolol were very different form the rest, including more severe hemangiomas located on the face. We were unable to balance for these differences and the statistical analysis methods were not applicable for this group. However, for children on topical timolol and observation, the methods were applicable, and although the outcome measures were different, they replicate and complement the results of a recent randomized clinical trial, showing no differences in the results between the two groups.27 The scale used could also be considered a limitation, as it has not been formally validated. However, the use of ranking scales is common in the measurement of aesthetic results, and we based ours on legally defined criteria and trained parents in their use before ranking the study Pictures.28 Another possible limitation is that 40% of participants had pictures which lack sufficient quality to allow for good result assessment. However, those excluded for this reason had no relevant differences with the participants included in the final analysis, suggesting that this should not cause a selection bias. Finally, although the follow-up period was longer vs most former studies, it might not be representative of the final outcomes of all IHs. Former studies have shown that in 90% of IH the regression phase is complete after 4 years (perhaps a little longer in deep hemangiomas),29–31 so we can consider the follow-up period long enough to assume that they had acquired their final appearance.
We think that these results will be useful in helping parents adjust their expectations on their children's hemangioma aesthetic outcomes,32 explaining what the tumor will be like, asking about their doubts surrounding the tumor progression and insisting on the importance of treatment.33 We could even use images to show parents what this progression will look like, so they can adjust their expectations based on the type of hemangioma. Another important takeaway is that, although large improvements were described between baseline scores and after treatment, only around 40% of the results were considered excellent (scores of 9 or 10). This percentage is an indication that we should avoid telling parents that the hemangioma is going to disappear completely.34 These results should also stimulate research of new therapies, especially those that improve the aesthetic sequelae after the use of beta-blockers (e.g., laser therapy).35,36
ConclusionsThis is the first large prospective cohort ever conducted to analyze the aesthetic impact of IH by a panel of parents. At baseline and due to the characteristics of IHs, the evaluation was worse in the groups of pharmacological treatment (oral propranolol and topical timolol) vs observation. These differences disappear after completion of follow-up, with around 40% achieving a result considered excellent from an aesthetic point of view. The study did not confirm that patients on timolol have better outcomes vs observation.
We can use these results to show parents the different treatment strategies available and the expected outcomes, and help them copy with the uncertainties.
In a significant number of infantile haemangiomas (IH), the indication for treatment is their aesthetic impact. However, studies assessing parents’ perception of the aesthetic outcome of the most widely used treatments for IH (propranolol, timolol, observation) are lacking.
What does this study add?In this prospective cohort study with a total of 824 photos evaluated by a panel of parents, the group treated with propranolol was found to have the highest impact at the baseline visit. However, after treatment, final aesthetic results of the three strategies (propranolol, timolol, observation) were similar, with about 40% of the patients achieving excellent aesthetic results. We can use these results to explain to parents the different treatment strategies and expected outcomes.
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Spanish Registry of Infantile Haemangiomas and the Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of interest- -
Esther Roé Crespo: advisory board member, consultant, grant and research support recipient, as well as for her participation in clinical trials, and/or speaker fees, with the following pharmaceutical companies: Abbvie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biogen, Cantabria, Celgene, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Pierre-Fabre, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
- -
Asunción Vicente: received funding for attending courses or seminars and participating on clinical trials conducted by Pierre-Fabre.
- -
Mercè Grau-Pérez: received funding for attending courses or seminars from Abbvie, Almirall, Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Pierre-Fabre and Sanofi.
- -
Ignacio García-Doval received funding for attending courses or seminars from Abbvie, MSD, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Spanish Registry of infantile haemangioma (Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venereology).
Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for this study. Data are available from the authors with the permission of Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
We wish to thank Cristina López Sánchez, Marta Feito, Raúl de Lucas, Lucía Quintana, Juan Carlos López Gutiérrez, Julián Boix Vilanova, Oriol Corral, Cristina Salas, Juan Navarro Morón, Minia Campos Domínguez and Marina de Vega for collaborating with the Spanish Hemangioma registry. This paper is part of María Colmenero-Sendra's PhD degree thesis.